Rotor for inductive angular displacement sensor
An angular displacement sensor and inductive technology, applied in the direction of converting sensor output, using electric/magnetic devices to transfer sensing components, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as limited cost, not strong, and unsuitable winding rotor resolvers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
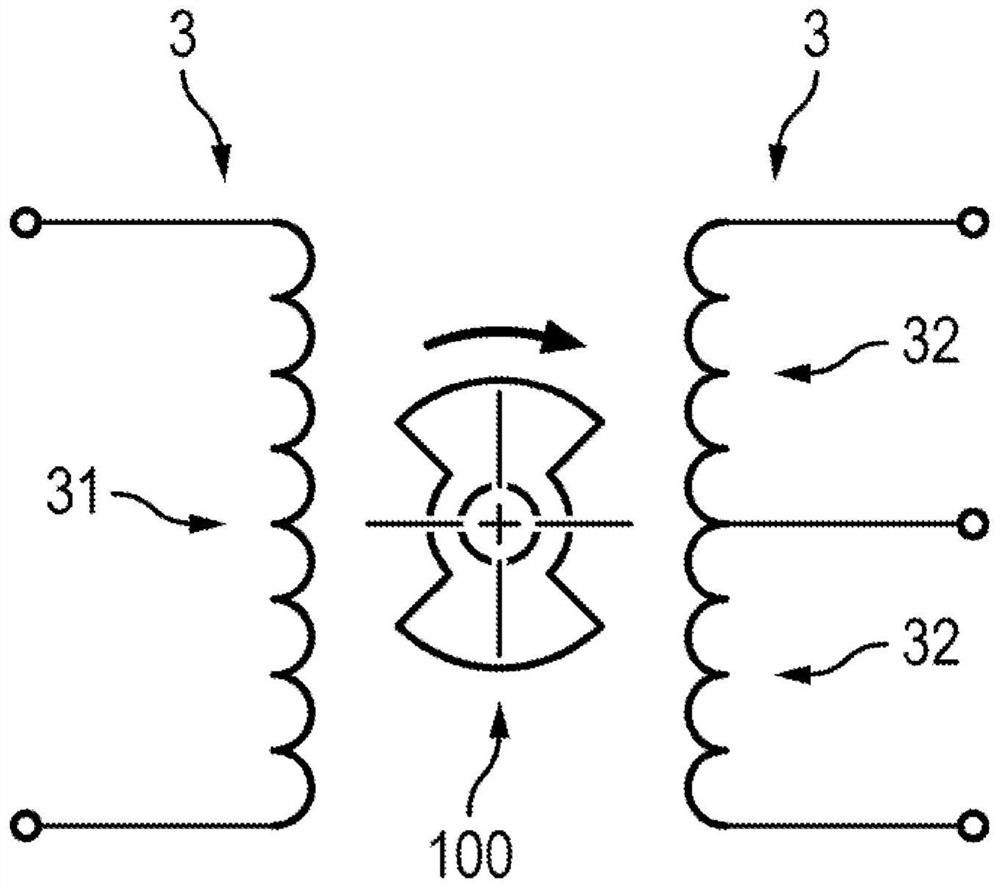
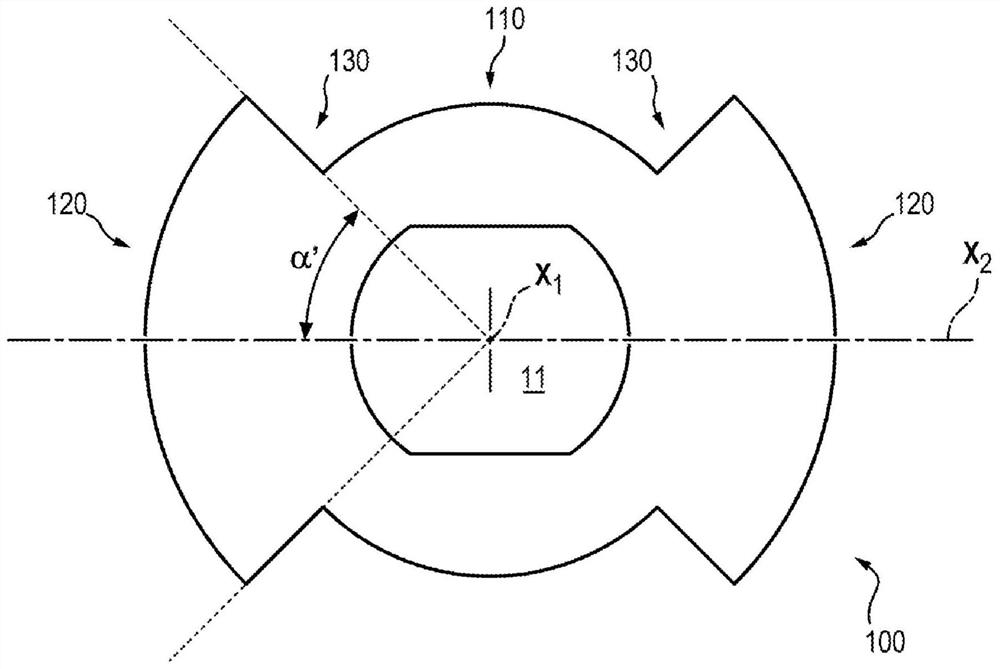
[0042] exist Figure 4 and Figure 5 The rotor 1 for an inductive angular displacement sensor, shown by way of non-limiting example in , is unwound, rotatably movable about a first axis X1 and symmetrical about this first axis X1. Rotor 1 has:
[0043] - central part 10,
[0044] - two movable parts 20 on either side of the central part 10 with respect to the first axis X1, each movable part comprising:
[0045] - an outer surface 21 configured to face the inner surface 33 of the stator 3 of the inductive angular displacement sensor,
[0046] - Two connecting walls 221 , 222 for connecting the outer surface 21 to the central part 10 .
[0047] The rotor 1 also has axial symmetry about a second axis X2 contained in a plane P perpendicular to the first axis X1 and passing through the two movable parts 20 . In the normal plane P, each connecting wall 221 , 222 forms an angle α greater than 45° with the second axis X2. In other words, each connecting wall 221 , 222 forms an ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com