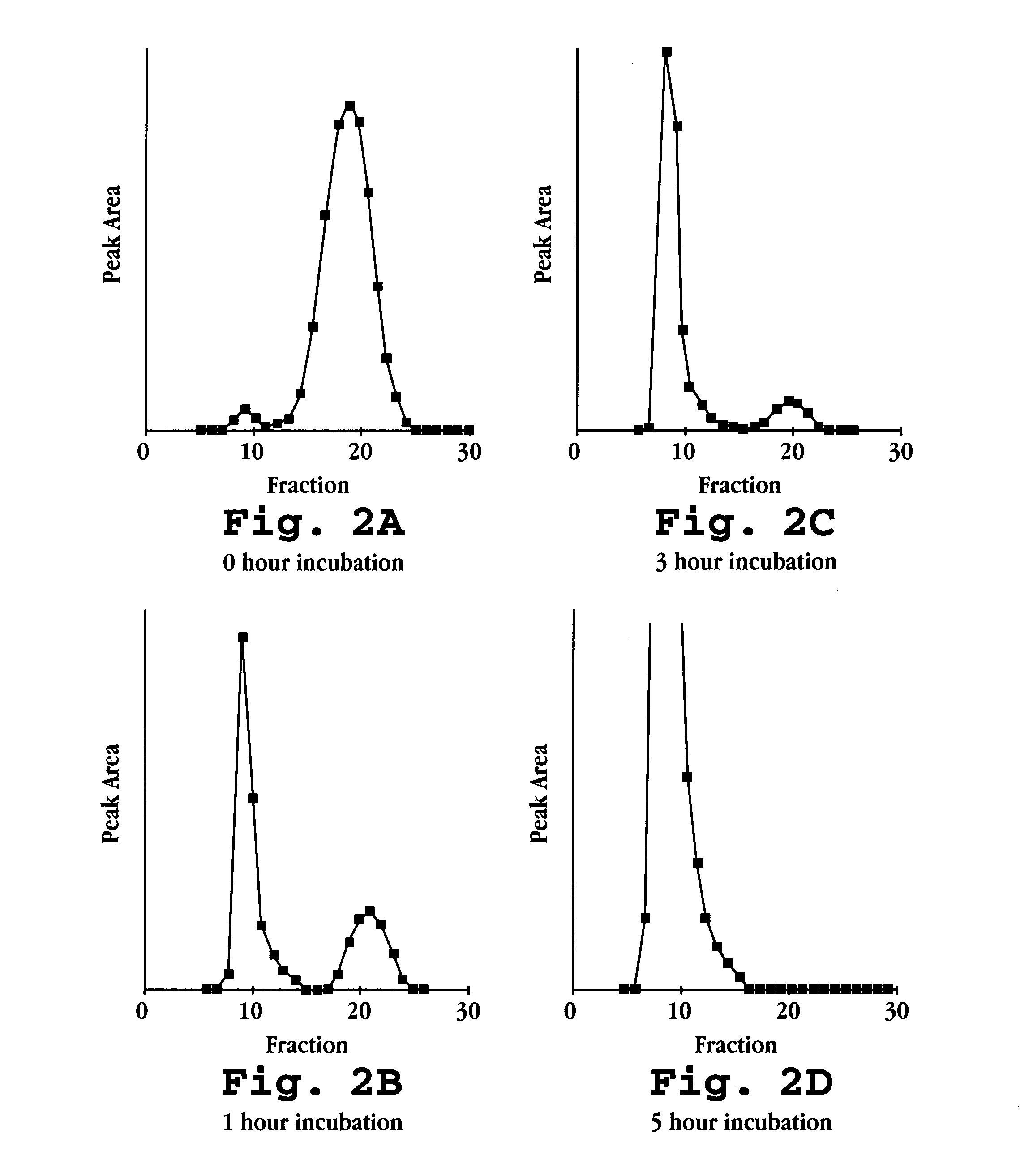
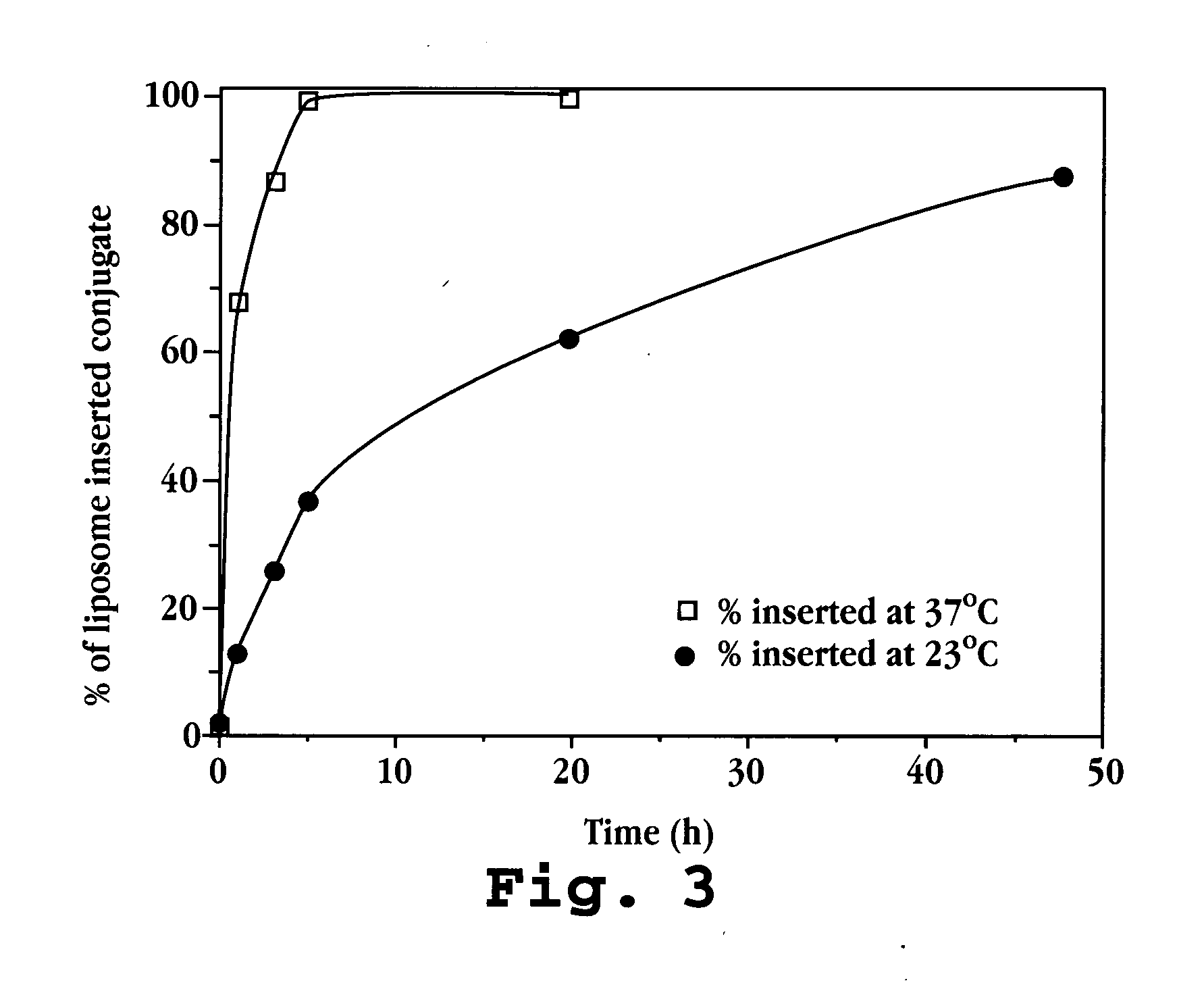
Therapeutic liposome composition and method of preparation
a technology of liposome and composition, which is applied in the direction of biochemistry apparatus and processes, pharmaceutical non-active ingredients, enzymes, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to react all the activated ends with a ligand, lack of flexibility in designing a therapeutic composition, etc., and achieve the effect of tailoring and designing for a particular patien
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Pre-formed Liposomes and Insertion of Targeting Conjugate
[0127] Liposomes were prepared by mixing partially hydrogenated soy-bean phosphatiylcholine (PHPC, iodine value of 35, Lippid (Ludwigshafen, Germany)), cholesterol (Croda (Fullerton, Calif.)) and mPEG-DSPE (prepared as described in Zalipsky, S., et al., Bioconjugate Chemistry, 4:296-299 (1993)) at a molar ratio of 55:40:3 in chloroform and / or methanol in a round bottom flask. The solvents were removed by rotary evaporation, and the dried lipid film produced was hydrated with either sodium phosphate buffer (10 mM, 140 mM NaCl, pH 7) or HEPES buffer (25 mM, 150 mM NaCl, pH 7) to produce large multilamellar vesicles. The resulting vesicles were passed repeatedly under pressure through 0.2, 0.1 and 0.05 μm pore size polycarbonate membranes, until the average size distribution for the diameter (monitored by dynamic light scattering using a Coulter N4MD (Hialeah, Fla.)) was approximately 100 nm. The mean particle dia...
example 2
Preparation of Anti-E-selectin Fab Conjugate and Insertion into Pre-Formed Liposomes
A. Preparation of the Targeting Conjugate
[0131] An anti-E-selectin Fab fragment was conjugated to PEG-DSPE to form a targeting conjugate as follows. An aqueous solution of 750 mM 2-mercaptoethylamine as a reducing agent was prepared. 10 μl of the mercaptoethylamine was added to 1 ml of 5 mg / ml anti E-selectin Fab fragment in 50 mM sodium acetate and 125 mM NaCl, pH=5.0. The final concentration of reducing agent was 7.5 mM. The solution was incubated at 37° C. for 30 minutes. The excess reducing agent was removed on a 10DG-column (Bio-Rad) equilibrated with 25 mM HEPES / 0.9% saline buffer. The collected fractions were analyzed spectrophotometrically to determine the fractions containing the Fab fragments. These fractions were pooled and diluted 1:50 in phosphate buffered saline to determine the protein concentration.
[0132] The Fab fragments (molecular weight of 3,000 Daltons) were mixed in a 1:1 mo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap