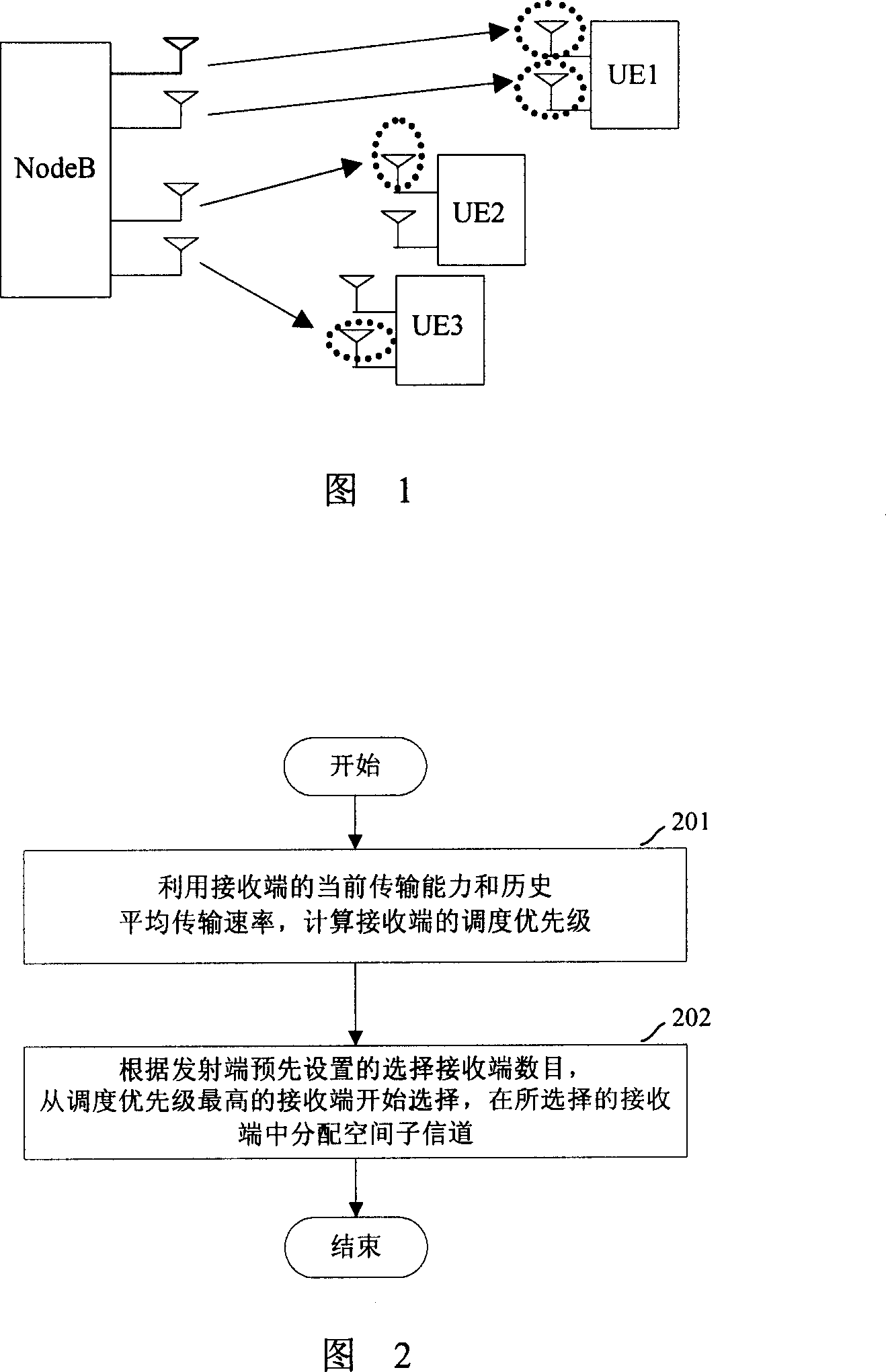
SD/FD dispatching method and device
A technology of scheduling cycle and scheduling priority, applied in multi-frequency code system, preventing/detecting errors through diversity reception, etc. The scheduling method cannot be applied to problems such as cellular communication systems to achieve the effect of ensuring fairness and normal communication
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
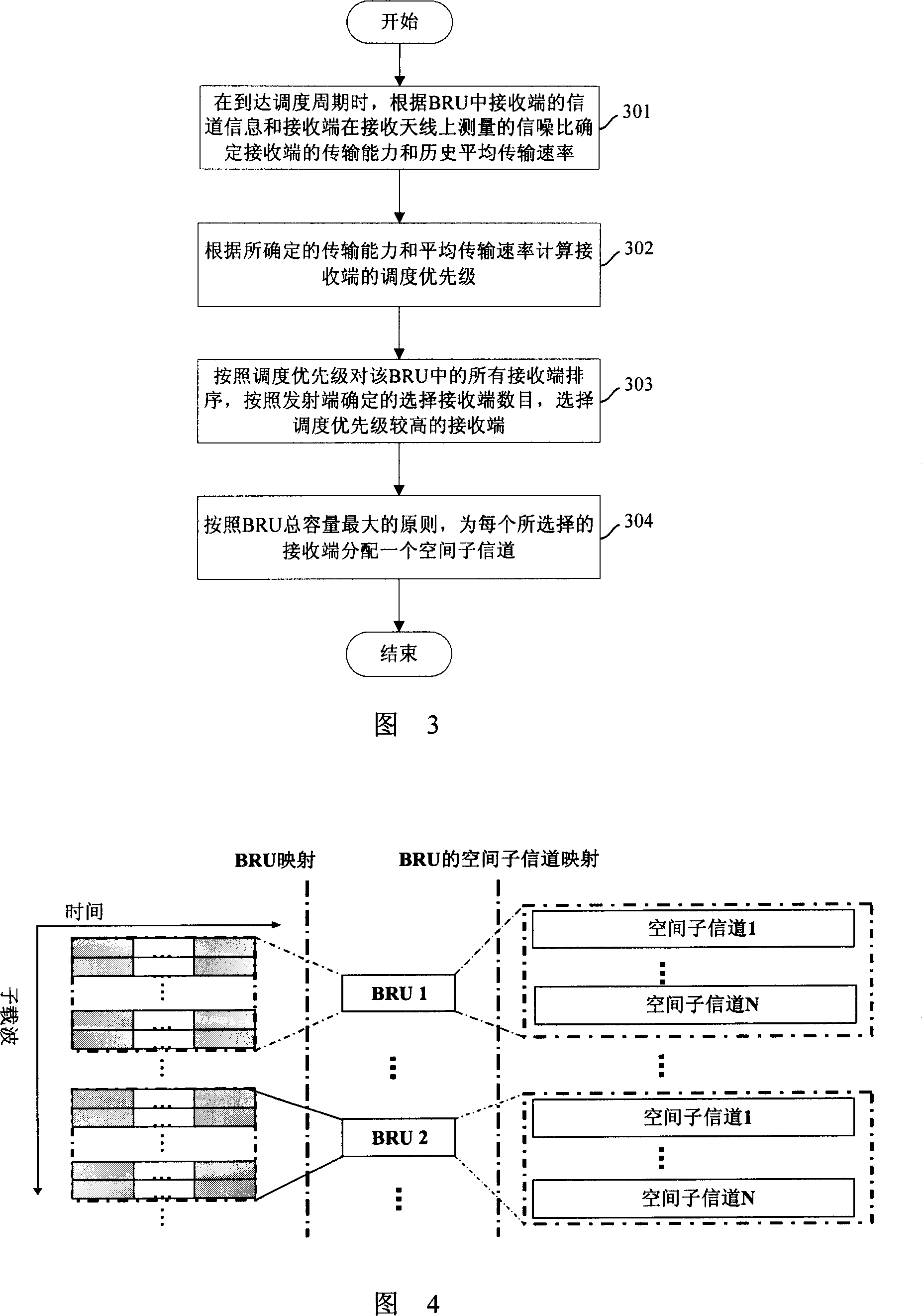
[0078] Figure 3 shows the flow chart of the space-frequency scheduling method in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. In this embodiment, the space-frequency scheduling is performed based on the ZFB method, and the space sub-channels in a basic radio resource unit (BRU) are allocated in an evenly distributed manner. Assign, and pre-set the scheduling cycle. Referring to Figure 3, the method includes:
[0079] In step 301, when the scheduling period is reached, the current transmission capability of the receiving end is determined according to the channel information of the receiving end in the BRU and the signal-to-noise ratio measured by the receiving end on the receiving antenna, and the historical average transmission rate of the receiving end is determined.
[0080] Fig. 4 shows a schematic diagram of the relationship among subcarriers, BRUs and spatial subchannels. As shown in Figure 4, in a MIMO OFDM system, a BRU refers to a group of subcarriers in a preset time slot...
Embodiment 2
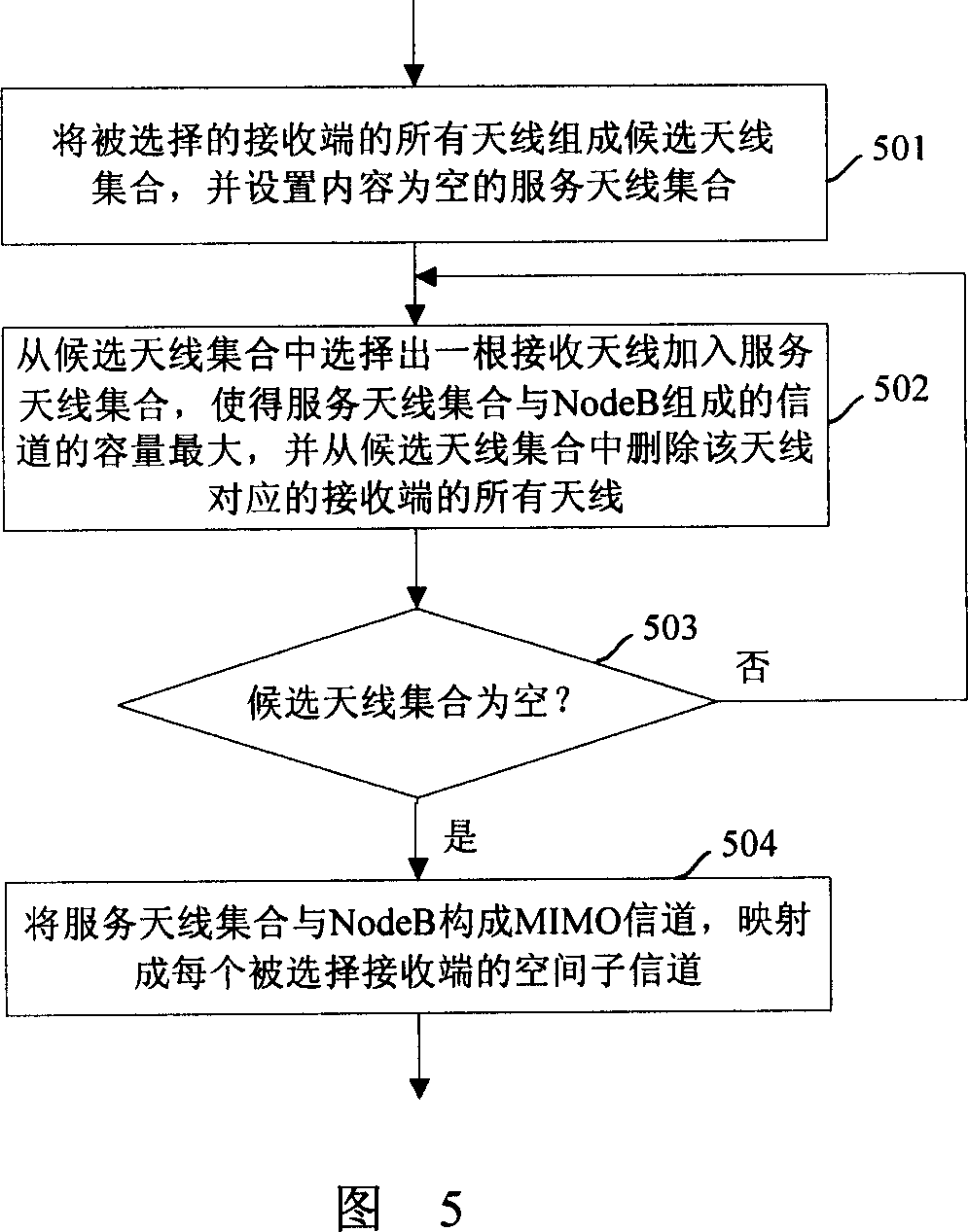
[0112] In this embodiment, the space-frequency scheduling is performed based on the PARC method, and the space sub-channels are allocated in an even allocation manner during the scheduling process. The flow of the space-frequency scheduling method in FIG. 3 is also applicable to this embodiment, but the specific operation of allocating space sub-channels in step 304 is different from that in Embodiment 1.
[0113] In the PARC method of this embodiment, the allocation of the spatial sub-channels is accomplished by allocating the transmitting antennas of the transmitting end.
[0114] In this embodiment, it is assumed that the number of antennas at the transmitting end is less than the number of antennas at the receiving end.
[0115] FIG. 6 shows a flowchart of a method for allocating spatial sub-channels in this embodiment. Referring to Figure 6, the method includes:
[0116] Step 601: According to the channel information H of the receiving end and the signal-to-noise ratio ...
Embodiment 3
[0134] This embodiment is based on the ZFB method and performs allocation of spatial sub-channels in a non-average manner. In order to ensure the normal implementation of the solution in this embodiment, the number of selected receiving ends and the number of spatial sub-channels are predetermined by the transmitting end.
[0135] Figure 7 shows a flow chart of the space-frequency scheduling method in this embodiment, referring to Figure 7, the method includes:
[0136] In step 701, when the scheduling period arrives, the transmission capability of the receiving end is calculated according to the channel information of the receiving end in the BRU and the signal-to-noise ratio measured by the receiving end on each antenna, and the historical average transmission rate is determined.
[0137] In step 702, the scheduling priority of the receiving end is calculated according to the determined transmission capability and the historical average transmission rate.
[0138] In step 7...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap