Vapor-liquid separation method for horizontal condenser and condenser
A vapor-liquid separation and condenser technology, used in steam/vapor condensers, heat exchanger shells, lighting and heating equipment, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of ingenious structural design and guaranteeing the ability to prevent steam
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
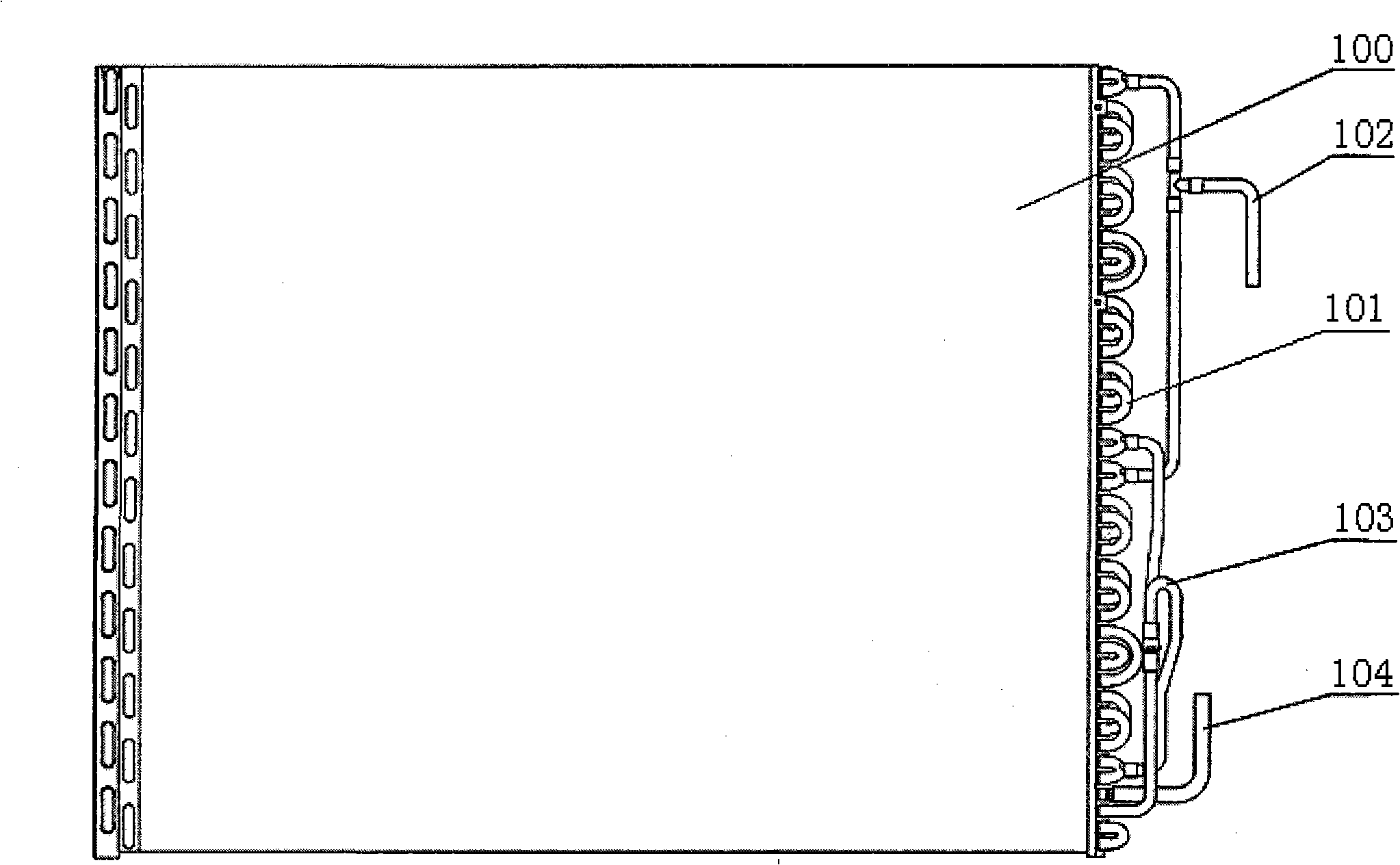
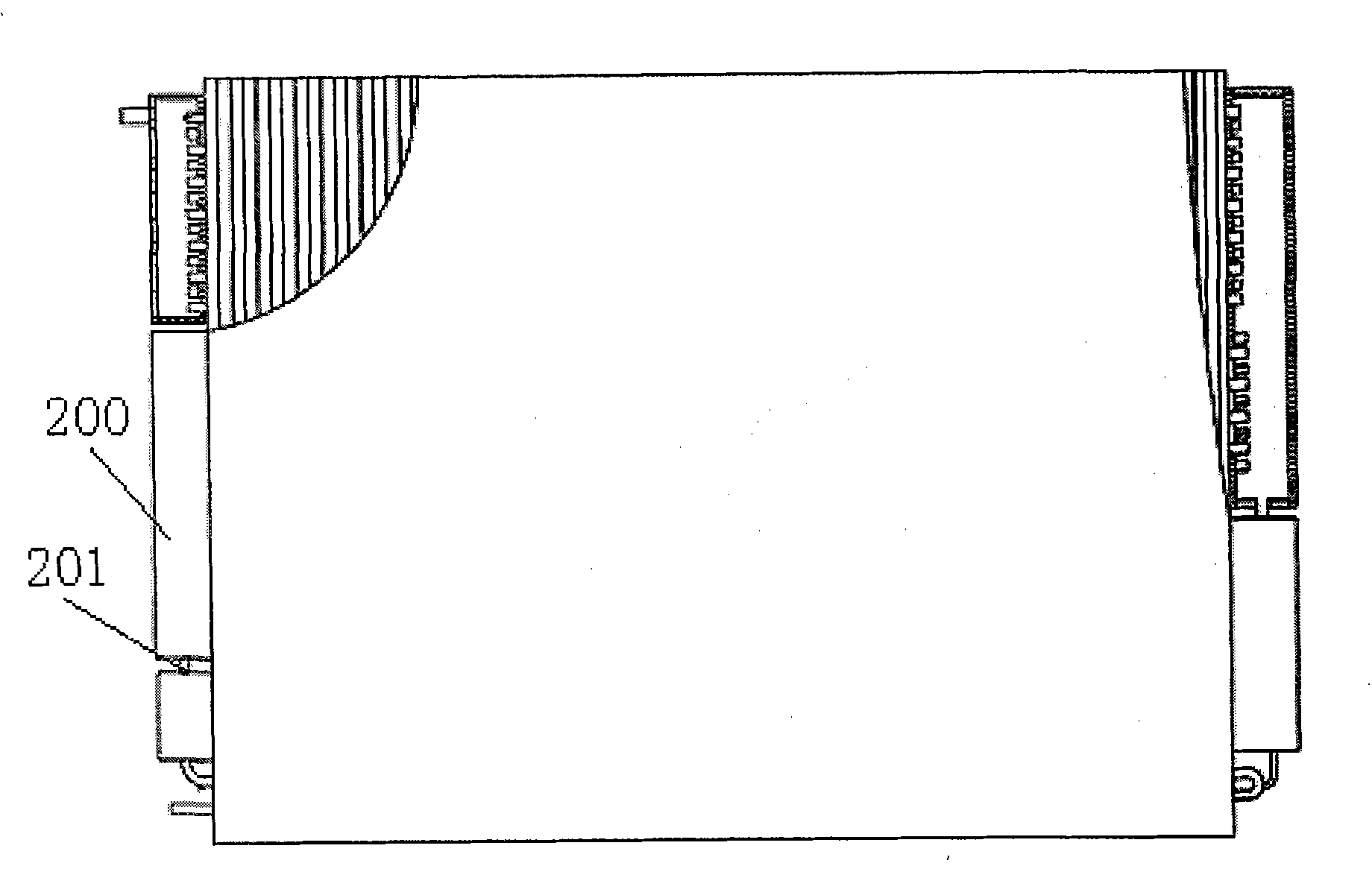
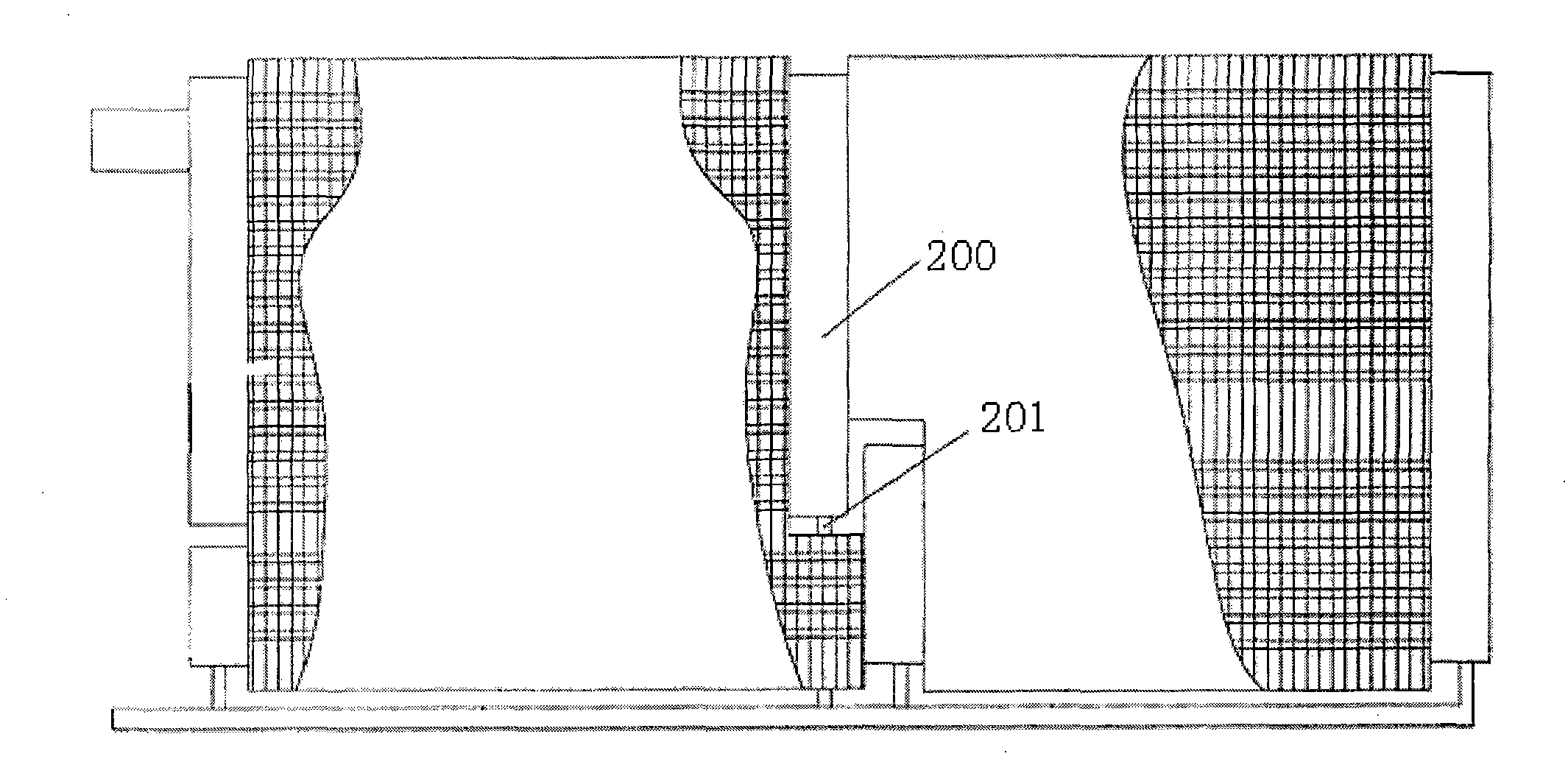
[0049] The liquid leakage and vapor barrier device 3 in this embodiment includes a base plate 31 having the same cross-sectional size as the header 2. The center of the base plate 31 has a main hole 32 with an equivalent diameter of 2 to 5 mm and the same hole diameter. A circle of auxiliary holes 33 with an equivalent diameter less than 2 mm and the same equivalent aperture is arranged. When the condensate produced in the heat exchange tube 1 upstream of the condenser is less, the liquid separated from the header 2 will form a layer of liquid film on the surface of the main hole 32 and the auxiliary hole 33 of the substrate 31, preventing liquid and gas from flowing The main orifice 32 and the auxiliary orifice 33 flow out. When the liquid volume increases slightly, the main hole 32 with a larger aperture will seep first, which is equivalent to the single drain pipe in the prior art. When the amount of separated liquid is large, the pressure of the liquid will destroy the li...
Embodiment 2
[0051] like Figure 8 , Figure 9 As shown, the size ranges of the main hole 32 and the auxiliary hole 33 in this embodiment are similar to that of Embodiment 1, the difference is that the main hole 32 and the auxiliary hole 33 are frustum holes with variable equivalent apertures, and the equivalent apertures can be larger at the top and lower at the bottom. Small; it can also be small at the top and large at the bottom, and it can also be in any form of variable cross-sectional area. This structure enables both the main hole 32 and the auxiliary hole 33 to carry a certain amount of condensate. When the amount of condensate is relatively low, the main hole 32 can also ensure continuous drainage and prevent steam from passing through. The presence of condensate in the pores of the auxiliary holes 33 can improve its steam resistance ability and prevent steam from passing through, and can also improve the steam resistance ability and accelerate liquid discharge according to the ...
Embodiment 3
[0053] like Figure 10 , Figure 11 As shown, the main hole 32 and the auxiliary hole 33 in this embodiment intersect with each other, presenting a "plum blossom" hole structure. The intersecting plum-blossom hole structure can be regarded as an extended structure of the main hole 32. Compared with the single main hole 32 structure, its flow equivalent diameter is increased, which can effectively strengthen the condensate flow capacity of the main hole 32, and at the same time, the auxiliary hole The intersection of 33 and the main hole 32 can adhere a certain amount of condensate through surface tension when the amount of liquid is relatively small, which strengthens the vapor resistance and liquid sealing ability of the device.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com