Base stations and method for synchronously scheduling resources among same
A technology of resource scheduling and resource scheduling instructions, applied in the field of wireless communication, which can solve problems such as increased interference, joint data transmission failure, waste of resources, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0091] Embodiment 1: A method for synchronously performing downlink resource scheduling between eNBs
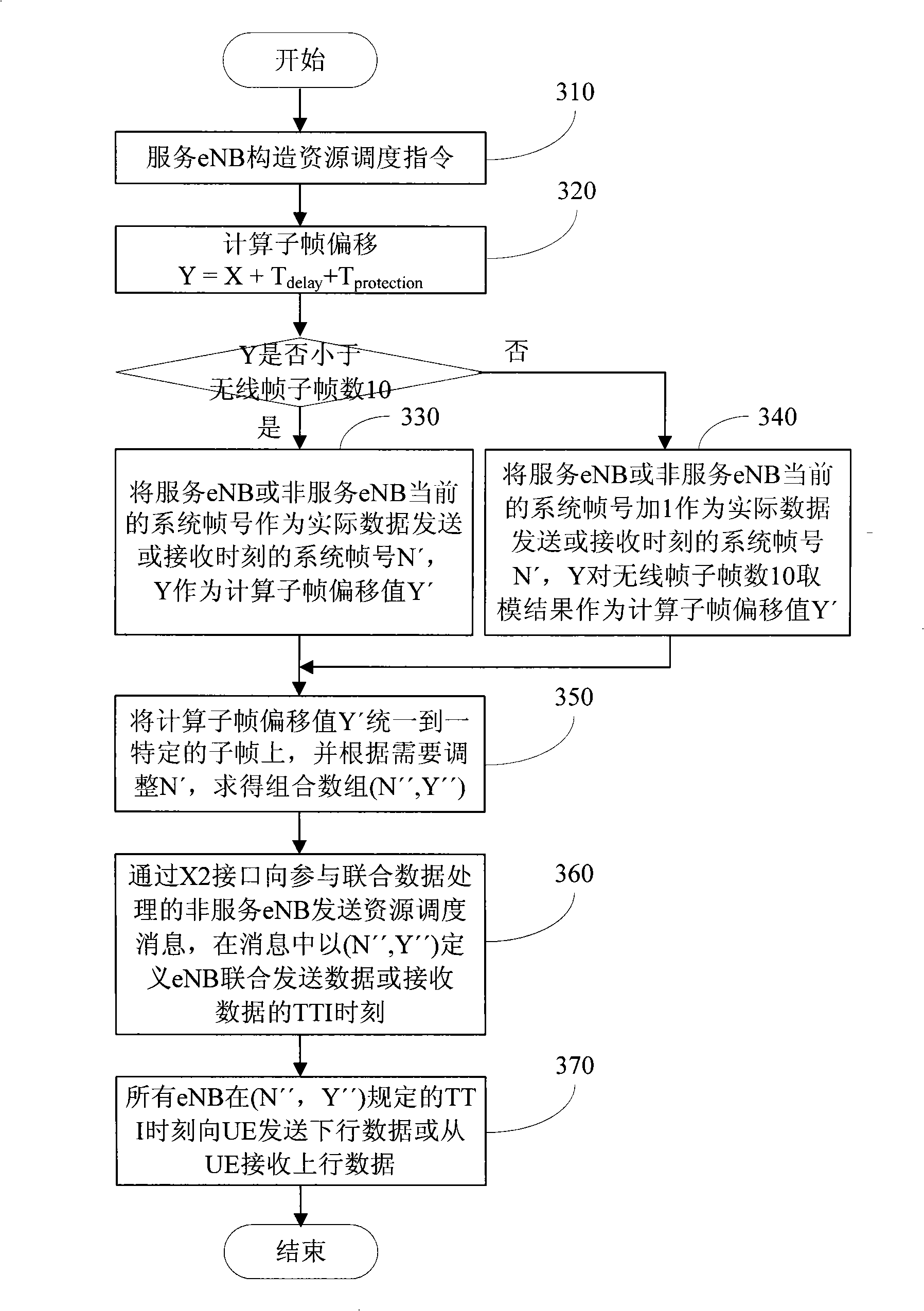
[0092] Such as Figure 4 As shown, each square in the figure represents a TTI width (1ms) in the timing. Each radio frame (10ms) includes 10 subframes (1ms), which are respectively labeled as 0-9. The system frame numbers and frame boundaries of the serving eNB and the non-serving eNB have been aligned synchronously. Assume that the serving eNB has been limited to only send downlink scheduling signaling on three predetermined subframes 1, 4, and 7.
[0093] The serving eNB is ready for downlink resource scheduling when the system frame number is N and the subframe offset in the frame is 3. According to the delay parameter and time protection parameter calculation, it should postpone 6 TTIs, that is, send the downlink in the 9th subframe scheduling.
[0094] However, since subframe 9 does not belong to the three scheduled subframes 1, 4, and 7, the delay is increased until...
Embodiment 2
[0097] Embodiment 2: A method for synchronously performing uplink resource scheduling between eNBs
[0098] Such as Figure 5 shown. Each square in the figure represents a TTI width (1ms) in the timing. Each radio frame (10ms) includes 10 subframes (1ms), which are respectively labeled as 0-9. The system frame numbers and frame boundaries of the serving eNB and the non-serving eNB have been aligned synchronously. The difference from downlink scheduling is that because uplink scheduling is synchronous, the scheduling of a specific uplink HARQ process is performed in a specific TTI, so there is no need to specify several specific processes like downlink scheduling. TTI.
[0099] The serving eNB is ready to perform uplink resource scheduling for the uplink HARQ process when the system frame number is N and the intra-frame subframe offset is 3. According to the delay parameter and time protection parameter calculation, it should be delayed by 6 TTIs, that is, in the ninth subf...
Embodiment 3
[0102] Embodiment 3: A method for synchronously performing semi-persistent resource scheduling (SPS, Semi-Persistent Scheduling) between eNBs
[0103] Such as Figure 6 shown. Each square in the figure represents a TTI width (1ms) in the timing. Each radio frame (10ms) includes 10 subframes (1ms), which are respectively labeled as 0-9. The system frame numbers and frame boundaries of the serving eNB and the non-serving eNB have been aligned synchronously. For SPS scheduling, since the serving eNB no longer transmits resource scheduling instructions to non-serving eNBs within a certain period of time, all eNBs automatically send data according to the SPS cycle, so the synchronization alignment of the first scheduling is particularly important, so in the case of SPS, the scheduling The instruction is delayed for a period of time to ensure the synchronization between eNBs. Assume that the serving eNB has been limited to only send downlink scheduling signaling on three predete...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com