Method for transition from traditional internet to universal identifier network
A technology for identifying networks and the Internet, which is applied in transmission systems, network interconnections, digital transmission systems, etc., and can solve the problems of difficulty in supporting terminal mobility and security, inability to support voice, video real-time requirements, and difficulty in supporting broadband streaming media services and other issues to achieve the effect of location privacy protection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
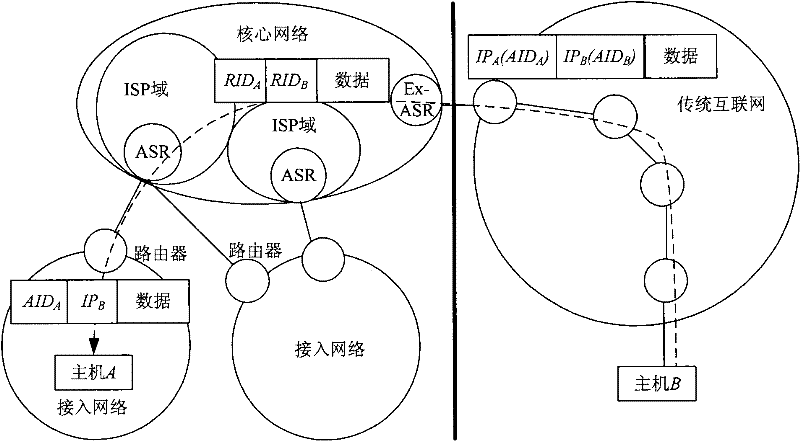
[0031] An example of when a user node located in the traditional Internet sends data to a user node in the integrated identification network, such as figure 1 shown.
[0032] exist figure 1 In , the sending process of the data packet is:
[0033] 1) When host B located in the traditional Internet sends data to host A located in the integrated identification network access network, the source of the data packet is the 32-bit IP address IP of host B B , the purpose is the access identifier AID of host A A (Traditional Internet considers it to be the IP address of host A);
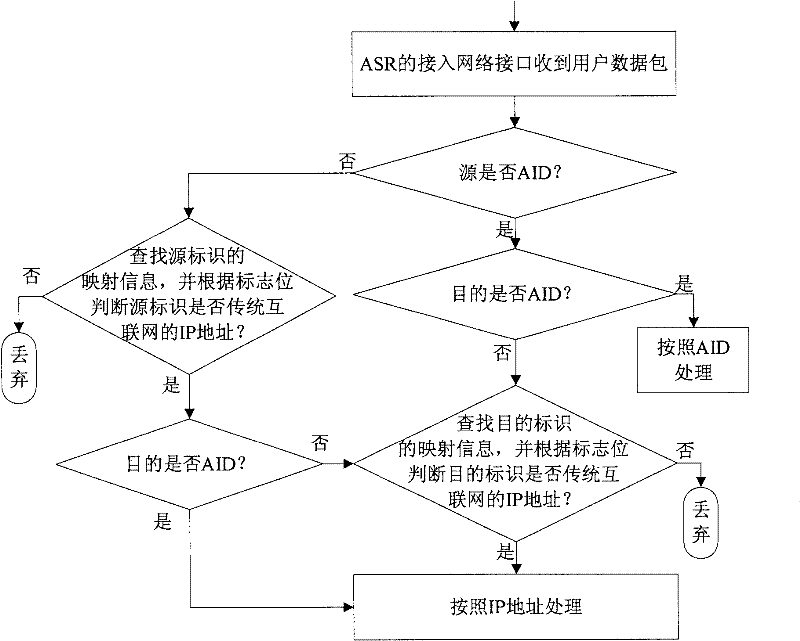
[0034] 2) When the data packet arrives at the Ex-ASR, it is judged whether the data packet is legal, and the illegal data packet is discarded. If the data packet is legal, the IP address of host B is replaced by the 128-bit switch routing identifier RID of host B B (RID B is the IP address of host B plus a 96-bit extended prefix), and the access identifier AID of host A A is replaced by host A's exchan...
Embodiment 2
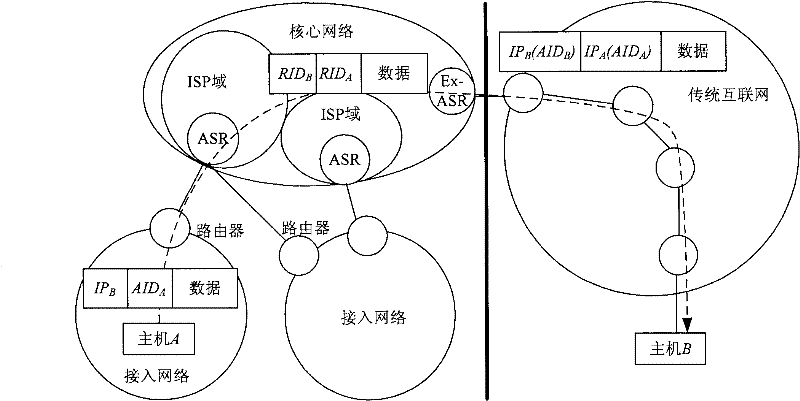
[0038] In the transition method from the traditional Internet to the integrated identification network, an example of a user node in the integrated identification network sending data to a traditional Internet node, such as figure 2 shown.
[0039] exist figure 2 In , the sending process of the data packet is:
[0040] 1) When host A on the access network sends data to host B in the traditional Internet, the source of the data packet is the access identifier AID of host A A , the purpose is the access identifier AID of host B B (that is, the IP address of host B IP B );
[0041] 2) After the data packet arrives at the core network access switch router to which the host A is connected, it is judged whether the data packet is legal, and the illegal data packet is discarded. Access identifier AID of host A A is replaced by host A's exchange routing identifier RID A , host B access identifier AID B is replaced by host B's exchange routing identifier RID B (RID B is the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com