Methods and kits for the rapid determination of patients at high risk of death during severe sepsis and septic shock
A technology for septic shock and sepsis, applied in disease diagnosis, biological testing, material inspection, etc., can solve problems such as useless life support, difficult and expensive for clinicians
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
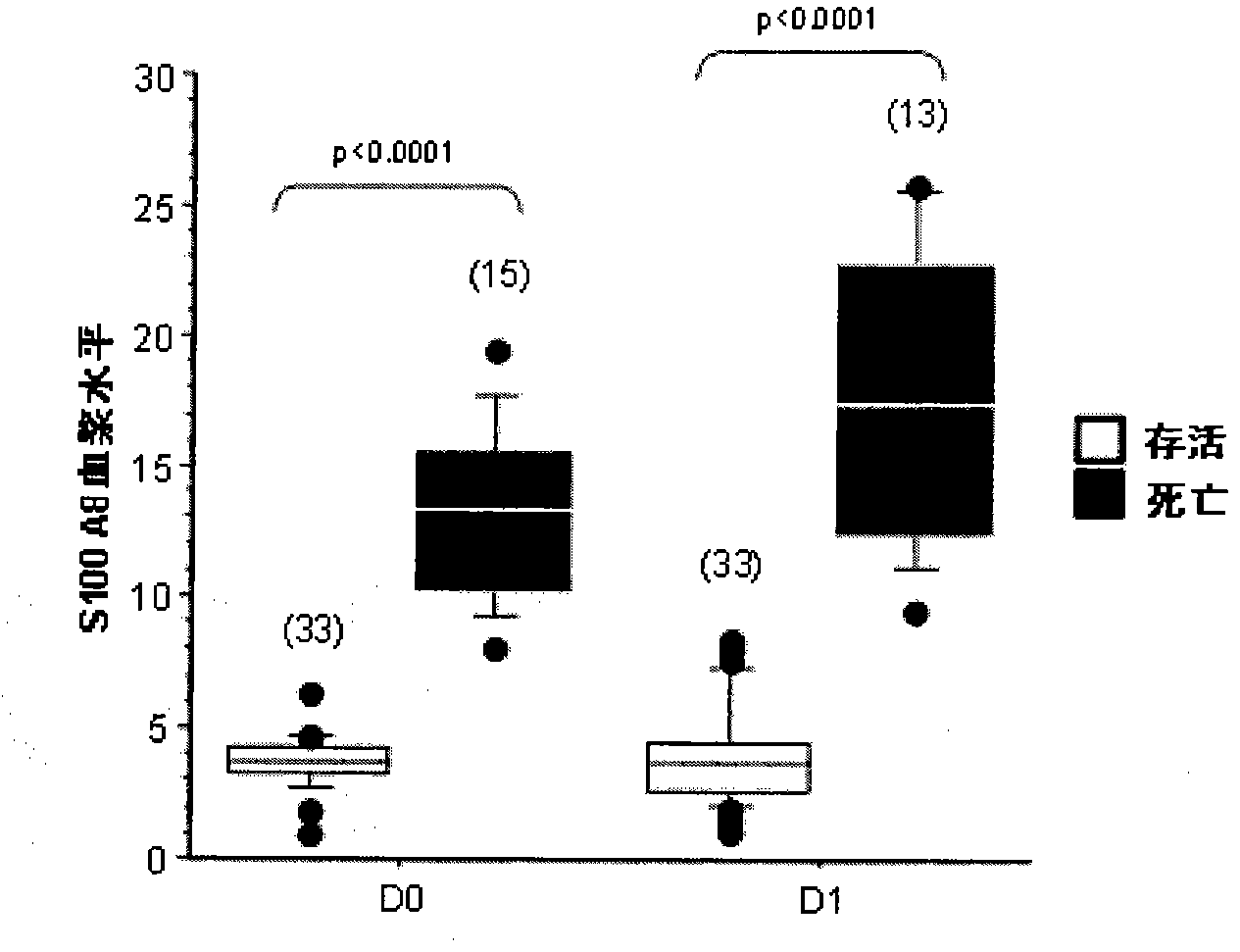
[0084] Example 1: Multicenter Evaluation of Plasma S100A8 / A9 Complex as an Early Prognostic Marker in Septic Shock
[0085] Materials and methods
[0086] All experiments reported below were performed using the materials and methods described below.
[0087] patient
[0088] This multicentre study was approved by the Cochin Hospital Ethics Committee (#CCPPRB 2061) and patients were recruited from 4 intensive care units (two medical, two surgical). Only patients meeting the criteria for septic shock as defined by the ACCP / SCCM joint meeting (Bone et al., 1992) were selected. Inclusion criteria required patients with septic shock to have at least two organ failures as defined by SOFA (Vincent et al., 1998). The first blood sample was collected on day 0 (D0), defined as within 24 hours of the onset of second organ failure.
[0089] Blood samples were obtained from these patients recruited to the training cohort who met the inclusion criteria for the determination of gene ...
Embodiment 2
[0138] Example 2: Trend of plasma S100A8 / A9 complex levels over time in septic shock patients
[0139] As in example 1, for experiments performed on day 0 and day 1, it has been completed in 28 days (days 0, 1, 7, 14, 28)
[0140] Results from 111 patients (49 training group, 62 test group in Example 1) showed that plasma protein levels decreased over time in survivors but not in non-survivors ( Figure 5 ). Plasma S100A8 / A9 was still high at day 28 in survivors compared to controls (median 2.65 μg / ml (IQR 2.60)).
[0141] Only one patient with a good final outcome showed surprisingly high levels of the S100A8 / A9 complex at day 14. In this patient, the S100A8 / A9 values were 4.7 μg / ml on day 0, 4.0 μg / ml on day 1, 4.5 μg / ml on day 7, and 20.1 μg / ml on day 14, although its progression was smooth And had a good final outcome (discharged by day 28). But S100A8 / A9 levels at day 14 were not controlled, and this surprising outcome may be a measurement artifact.
[0142] Both...
Embodiment 3
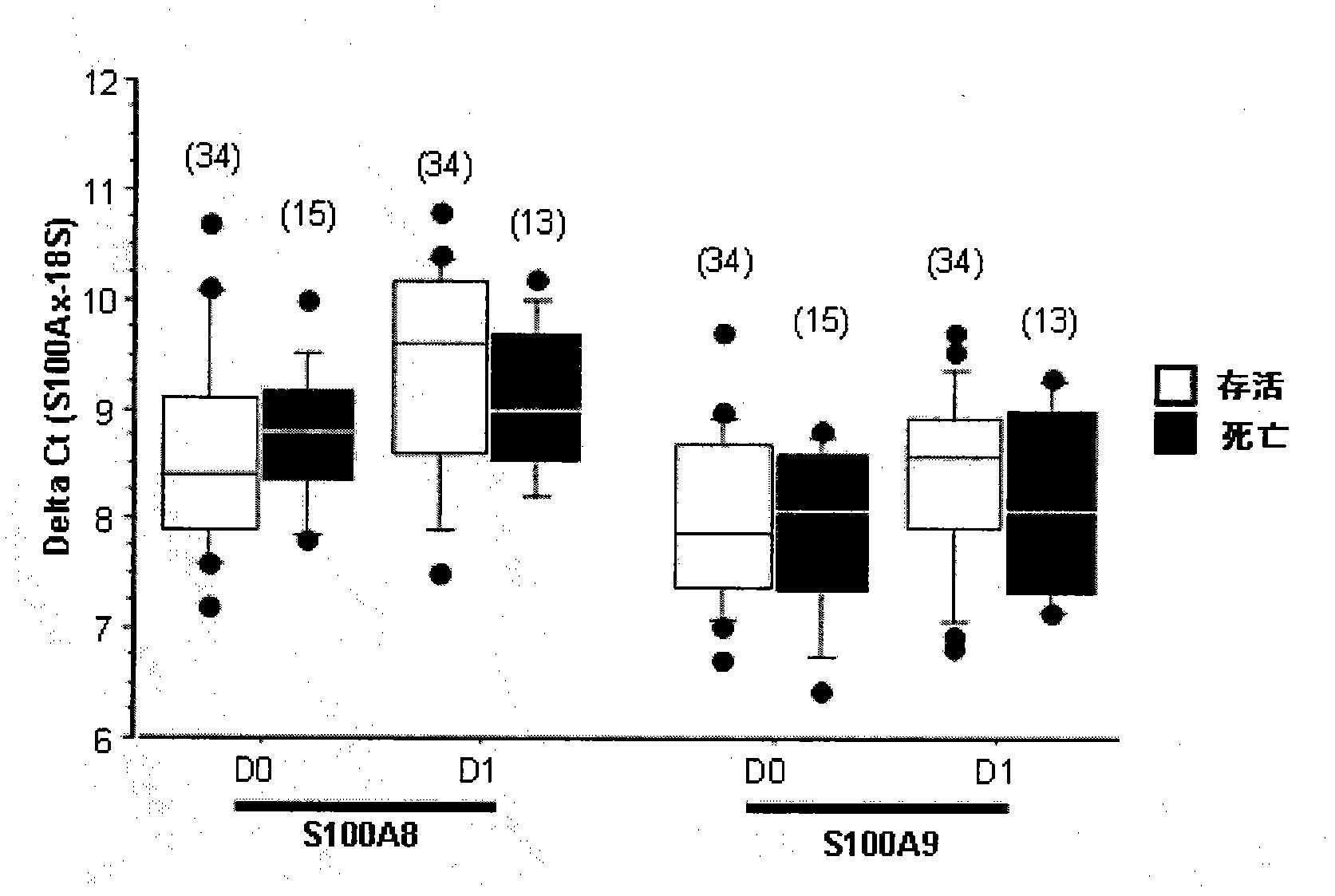
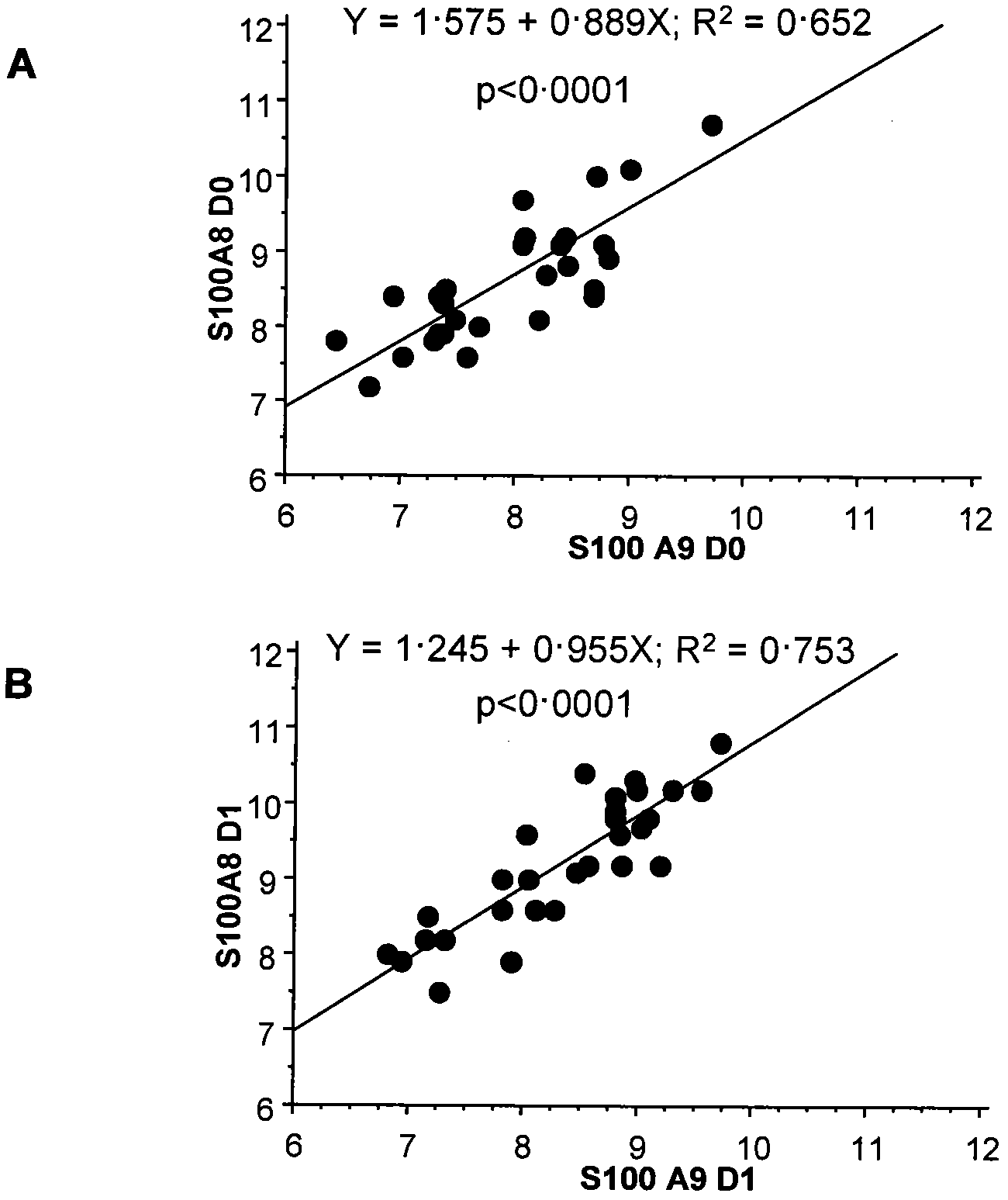
[0150] Example 3: Trends of S100A8 and S100A9 gene expression levels over time in patients with septic shock
[0151] Image 6 and Figure 7 Gene expression of S100A8 and S100A9 in 32 patients is shown. These data were collected from microarray analysis performed on an Affymetrix HG-U133 Plus 2.0 array using the same method as described in EP 2085486A1.
[0152] There was a slight decrease in S100A8 gene expression among survivors between day 0 and day 7, even though it was not significant as 28 days passed. This trend was not observed in the non-survivors. S100A8 gene expression statistics are as follows:
[0153] Friedman's test among survivors, Day 0-Day 28, n=11: not significant
[0154] Day 0-Day 7, n=18: p=0.0421
[0155] Wilcoxon test among survivors, day 0-day 1, n=17: not significant
[0156] Wilcoxon test among non-survivors, day 0-day 1, n=9: not significant
[0157] Mann Whitney test, Survivors vs. Non-survivors: Significant at day 1, p=0.035.
[0158] S...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| intra-assay coefficient of variation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com