Method for channel information feedback, basestation device and mobile station device
A technology of channel information feedback and channel information, which is applied in the field of wireless communication and can solve problems such as limited uplink bandwidth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
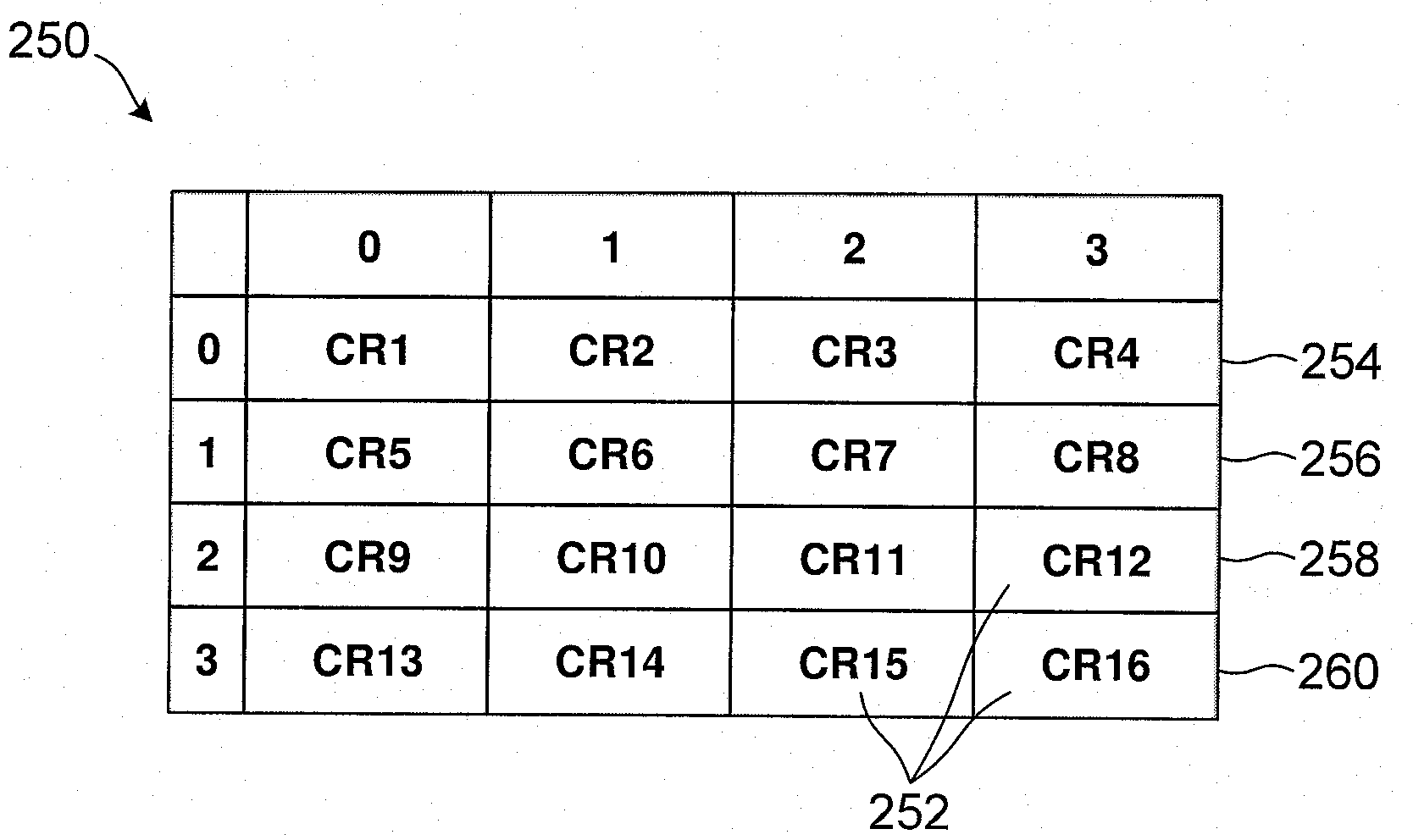
[0126] According to a first example, the base station 14 may schedule transmission of the primary identifier during a first transmission time period and may schedule transmission of the differential identifier during a second time period, wherein the second time period is subsequent to the first time period. The time period may be based on the uplink subframe data transmission rate between the mobile station 16 and the base station 14 . In one embodiment, each T subframes periodically schedule the transmission of the primary identifier (i.e. separated by the first predetermined time interval T ). The mobile station 16 invokes the channel estimation function 96 in response to the schedule provided by the base station 14 and in the codebook 250 ( Figure 15 shown in ) to determine which cluster best matches the channel response provided by the channel estimation function. The primary identifier corresponding to the selected cluster is then transmitted back to the base station...
example 2
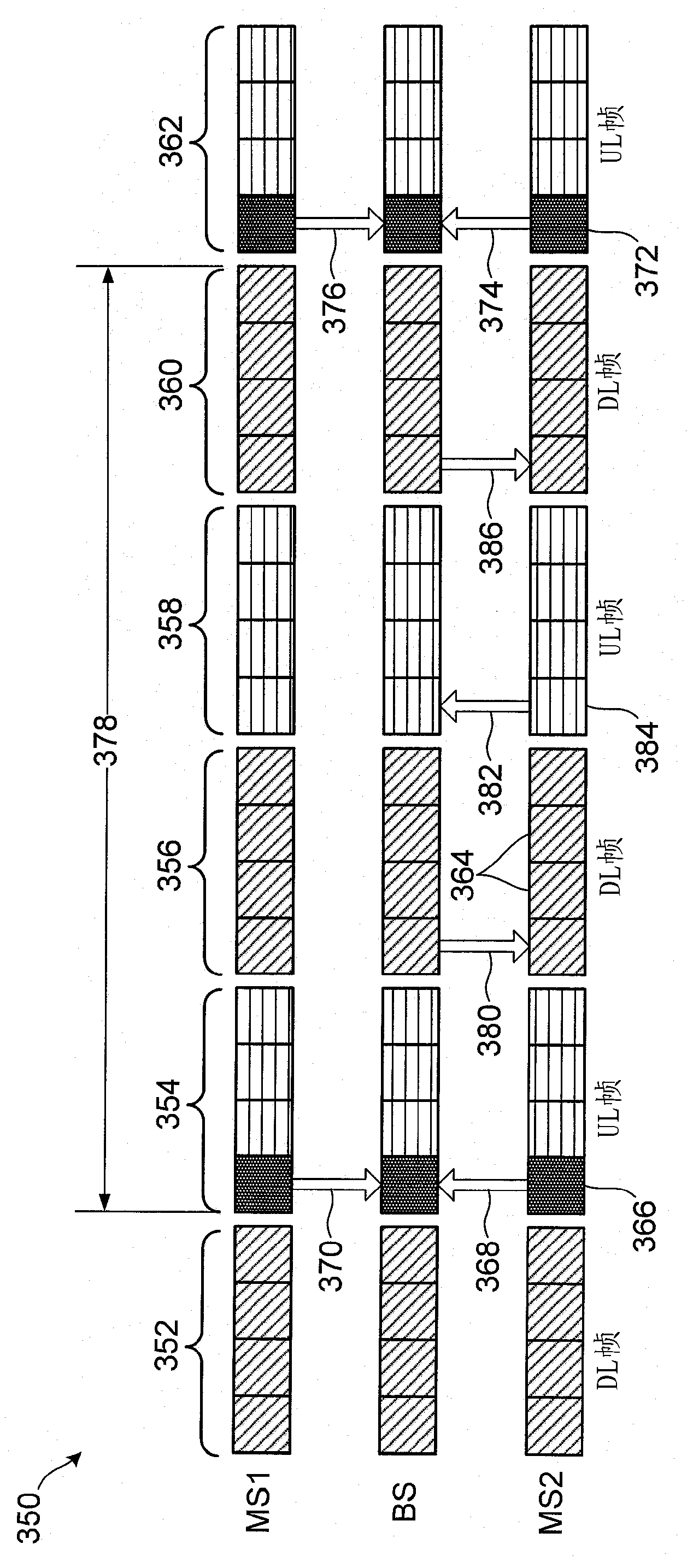
[0132] According to a second example, the base station 14 may schedule the periodic transmission of the primary identifier as described above in example 1, while only transmitting the differential identifier back to the base station when the base station 14 requests it. refer to Figure 18 , is generally shown at 350 an exemplary transmission between a base station (BS) and first and second mobile stations (MS1 and MS2). Data transmission is shown as a plurality of alternating uplink (UL) frames 354 , 358 , 362 and downlink (DL) frames 352 , 356 , 360 . Each downlink or uplink frame 352-362 includes a number of subframes 364. An uplink frame is a transmission from the mobile station 16 to the base station 14, and a downlink frame is a transmission from the base station to the mobile station.
[0133] In the first subframe 366 of the uplink frame 354, both MS1 and MS2 are scheduled by the base station to feed back primary identifiers as indicated by arrows 368 and 370. Simil...
example 3
[0137] According to the third example, using the Figure 19 The codebook shown generally at 400 in implements aperiodic feedback of both primary and differential identifiers to the base station 14 . refer to Figure 19 , the codebook includes 2 N1 x 2 N2-1 channel response, in this case for N1 =4 and N2 =4 is CR1-CR128. Group the channel responses according to the correlation criteria into 2 N1 clusters 402-404 (ie for N1=4 for 16 clusters). Each cluster includes a header 406, a dummy codeword 408 and 2 N2-1 channel response members 410-412. Header 406 defines the primary identifier, while indices 0-7 define differential identifiers (codewords). A dummy codeword is used when the differential identifier identifying the channel response provided by the channel estimation function 96 no longer belongs to the cluster identified by the primary identifier.
[0138] refer to Figure 20 , a process for directing the mobile station 16 to determine a channel response cod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com