Compositions and methods for treating traumatic brain injury
A traumatic, post-brain injury technique for use in the field of agents to reduce necrotizing neuronal cell death, addressing issues such as short treatment time windows
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
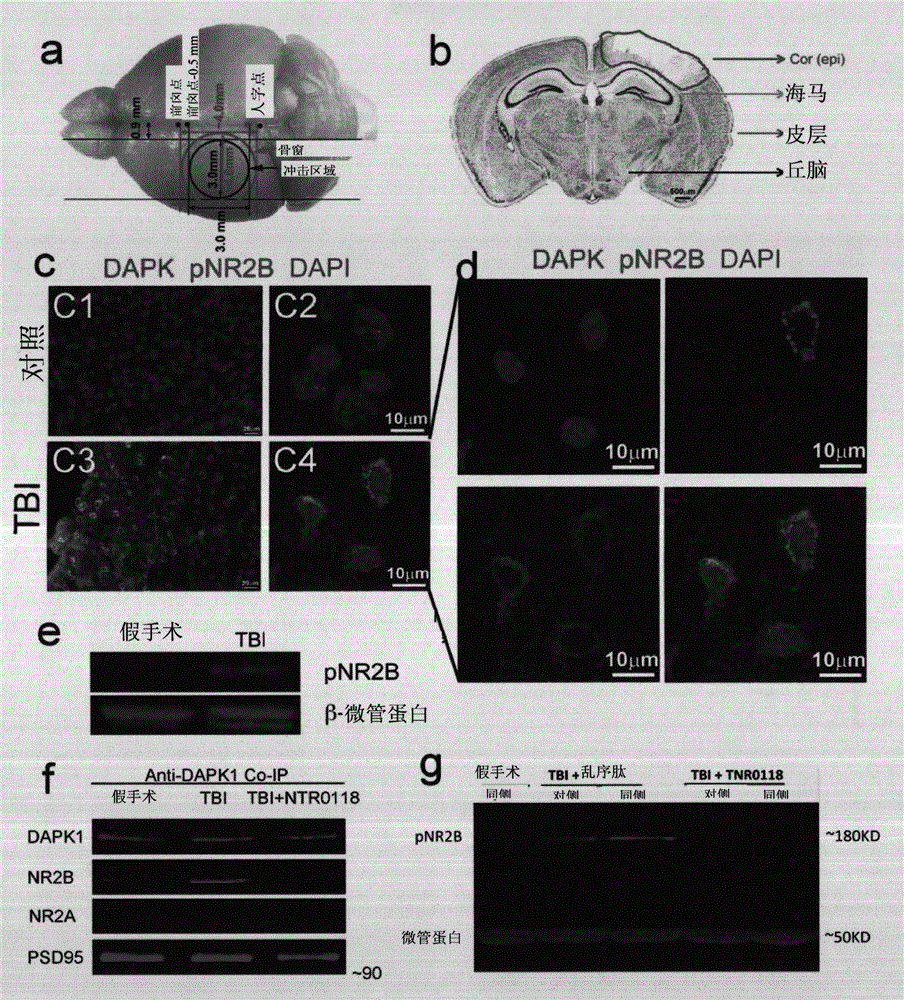
[0095] Example 1 - Death-associated kinase (DAPK) 1 phosphorylates NMDA receptor 2B subtype (NR2B) at S1303 in neurons after traumatic brain injury
[0096] Adult mice received a moderate level of impact on the left side of the brain, producing moderately traumatic CCI TBI. The location and parameters of impact are shown in the schematic diagram ( figure 1 described in a). In the sham-operated control mice, no loss of brain tissue was seen. 24 hours after a moderate level of CCI injury, the ipsilateral cortex exhibited typical tissue loss ( figure 1 b). In sham-operated control mice, immunostaining ( figure 1 In c, C1-C2), the levels of phosphorylated NR2B S1303 (pNR2B) and DAPK kinase are barely detectable. However, at 24 hours after injury, the levels of pNR2B and kinases were significantly upregulated in cells adjacent to the injury ( figure 1 c, C3-4). DAPI staining showed their nuclear condensation. The activated kinase is present in the cytoplasm, while pNR2B is ...
Embodiment 2
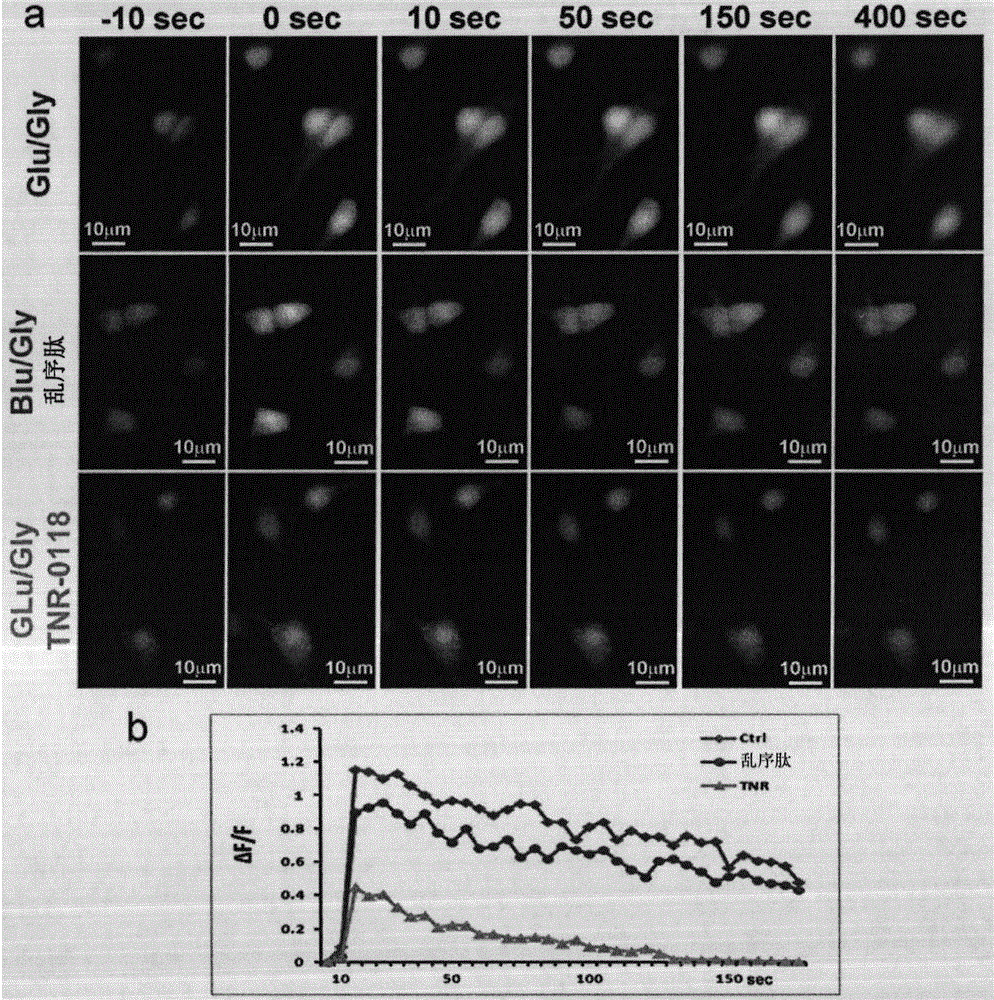
[0098] Example 2 - Treatment of neurons with TNR0118 reduces glutamate-induced Ca2+ influx and protects glutamate-induced neuronal hyperexcitatory death in vitro
[0099] It has been demonstrated that DAPK1 kinase can bind to the C-terminus of NR2B and phosphorylate NR2B at Ser-1303, thereby enhancing the response of NMDA receptors to Ca 2+ the permeability. Excess Ca 2+ Influx further activates DAPK1, which in turn enhances the response of NMDA receptors to Ca by phosphorylating NR2B 2+ The permeability of the nerves forms a harmful vicious circle, which leads to the excessive excitatory death of the nerves. In a variety of neurological diseases, including traumatic brain injury, neuronal cell death is due to glutamate receptor-associated excess Ca 2+ Caused by inflow [35, 36, 67].
[0100] To test whether the inhibition of glutamate-induced phosphorylation of NR2B by TNR0118 could prevent Ca 2+ Influx, reduce excess intracellular Ca 2+ To investigate the cytotoxicity i...
Embodiment 3
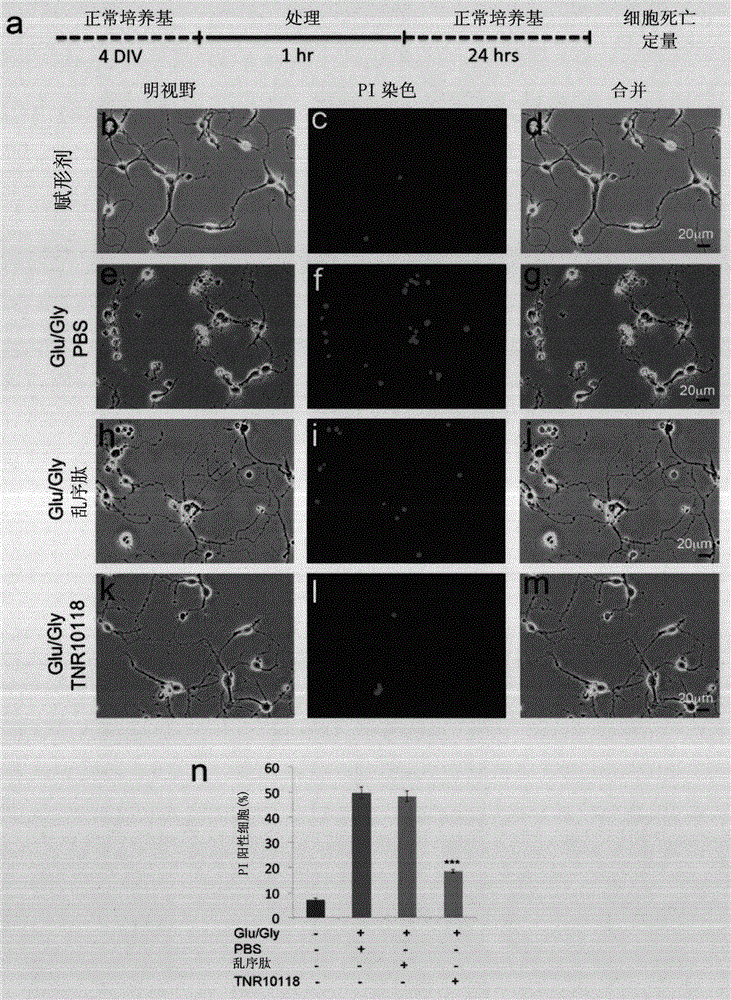
[0103] Example 3 - A single intravenous injection of TNR10118 after TBI reduces TBI-induced cerebral cortex damage
[0104] All animals received moderate traumatic brain injury (TBI) and were then randomly assigned to PBS control, scrambled control peptide and treatment groups [22, 48, 56, 68]. One hour after wounding, mice received intravenous injections of PBS, control peptide (10 mg / kg body weight), or TNR10118 (10 mg / kg body weight), respectively. Twenty-four hours after injection, mice were sacrificed and the size of their cerebral cortical lesion volumes were determined using the Cavalieri method.
[0105] Each animal suffered a moderate traumatic brain injury, and all showed obvious cerebral cortex defects at the traumatized site ( Figure 4 a-c). We first measured the volume of cortical lesions to assess the therapeutic effect of short peptides. Control animals that received PBS injection showed obvious cortical tissue defects ( Figure 4 a). Compared with the cor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com