Method used for evaluating frangibility of underground water
An evaluation method and vulnerability technology, applied in the field of environmental science and environmental risk, can solve problems such as inapplicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
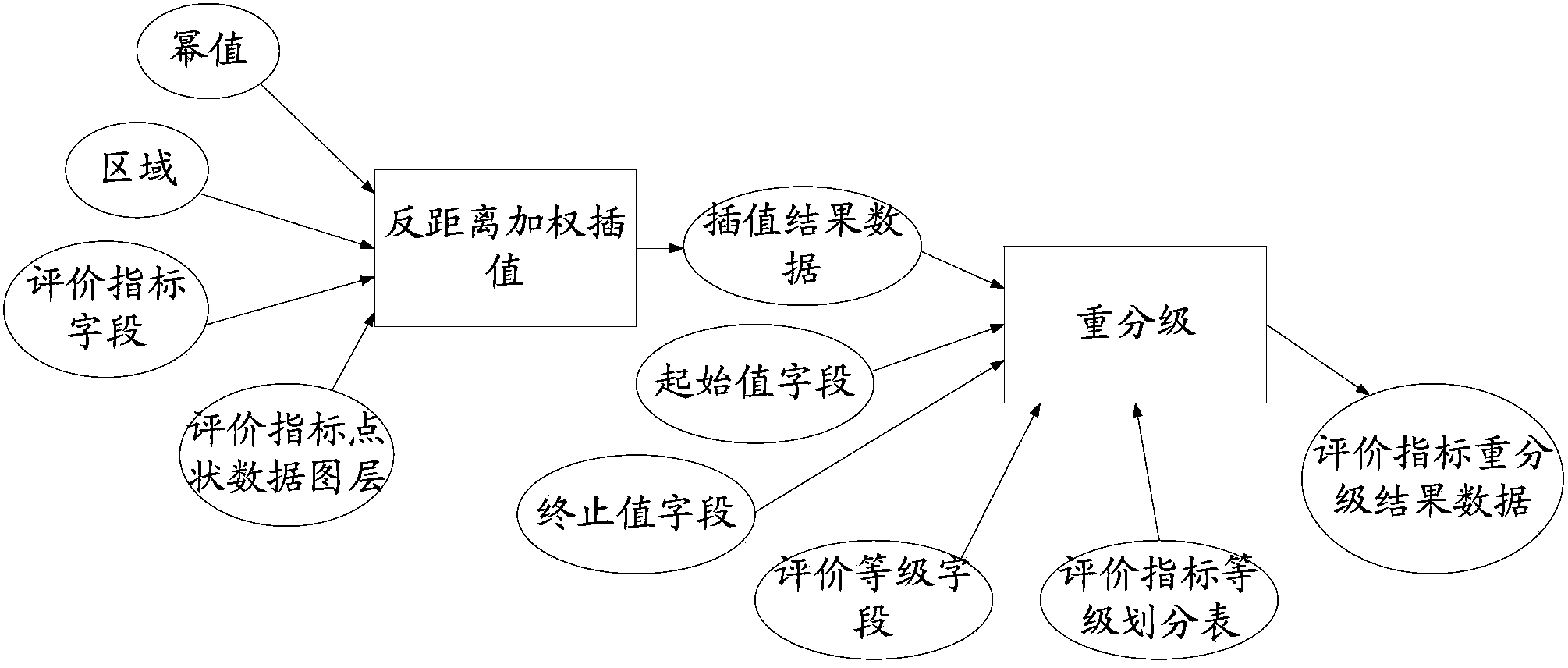
[0017] like figure 1 As shown, the groundwater vulnerability assessment method provided by the embodiment of the present invention includes:
[0018] Step 101: Obtain groundwater types, vulnerability evaluation indicators and parameters according to boreholes, empirical values or field pumping tests.
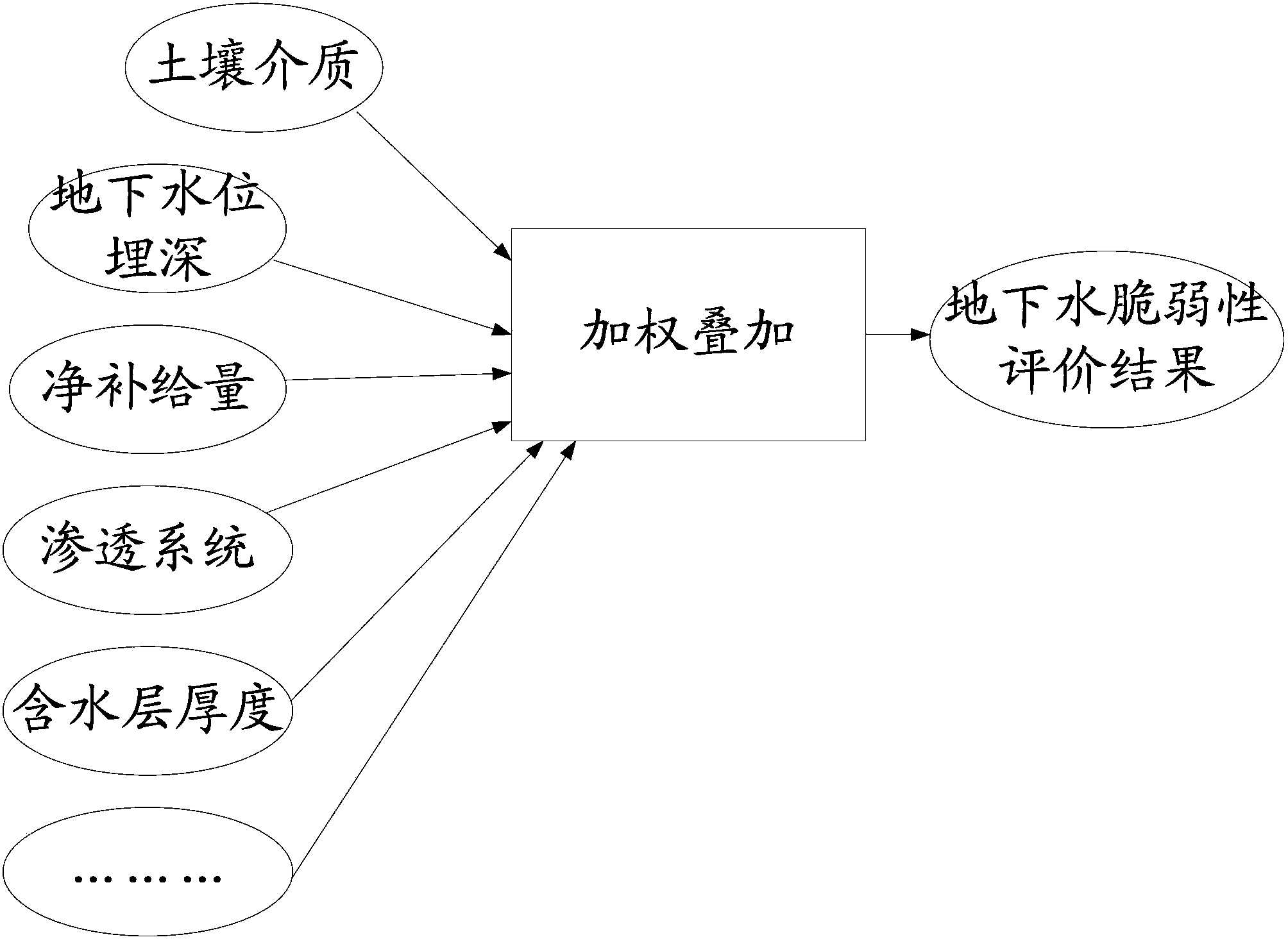
[0019] In this embodiment, the type of groundwater in step 101 may include: pore water, pore confined water or karst water; the vulnerability evaluation index may include: intrinsic vulnerability index and / or special vulnerability index; wherein, intrinsic vulnerability Indicators include: soil medium, buried depth of groundwater table, net recharge, thickness of cohesive soil layer in vadose zone, permeability coefficient, aquifer thickness and terrain slope; special vulnerability indicators include: pollutant migration and transformation One or more of regularity, density of river network, type of land use and extent of groundwater extraction.
[0020] Among them, the soil...
Embodiment 2
[0040] like Figure 4 As shown, the groundwater vulnerability assessment method provided by the embodiment of the present invention, the method and the figure 1 Similar to the one shown, except that it also includes:
[0041] Step 105, verify the groundwater vulnerability assessment map.
[0042] In this embodiment, the verification process in step 104 may include: verification according to a single-factor pollution evaluation model; and / or verification according to a single-point comprehensive evaluation model; and / or verification according to a tracer experiment.
[0043] Among them, the verification process according to the single-factor pollution model includes: obtaining the characteristic pollutant concentration of each single point in the study area and the corresponding groundwater vulnerability index; calculating the correlation degree of each single point characteristic pollutant concentration and the corresponding groundwater vulnerability index ρ, the
[0044] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com