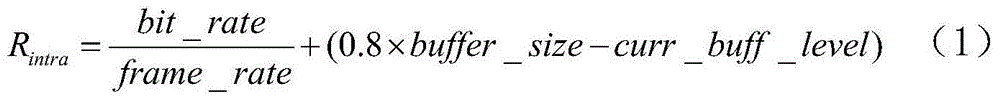I-frame code rate control method based on residual frequency domain complexity
A rate control and complexity technology, applied in the field of I frame rate control based on residual frequency domain complexity, can solve I frame complexity measurement and rate model inaccuracy, and limited improvement of I frame rate control effect And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0044] The invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
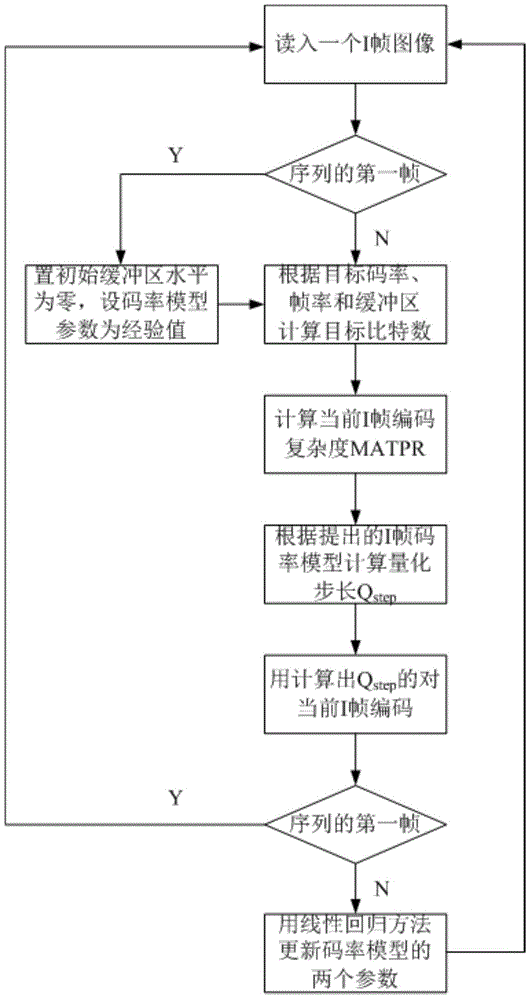
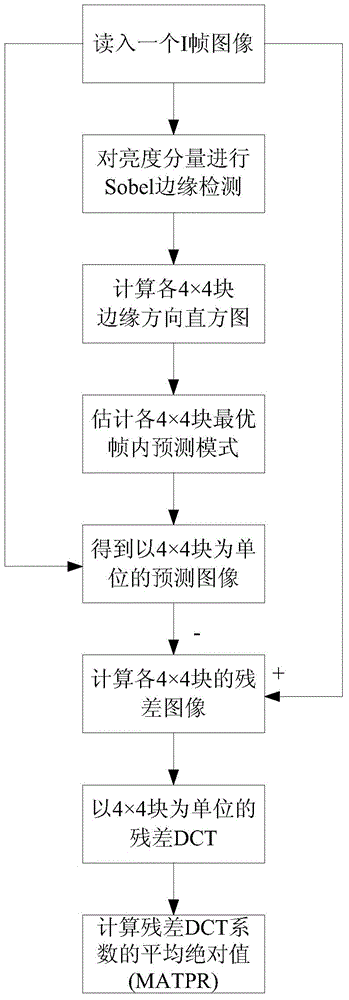
[0045] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the present invention provides a method for controlling the code rate of an I frame based on residual frequency domain complexity, which is specifically a method for controlling the code rate of an H.264 I frame, comprising the steps of:
[0046] 1) Read in the I-frame image to be encoded in the video sequence. If it is the first frame of the sequence, set the initial buffer level to zero, that is, curr_buff_level=0; and set the parameters c and d in the I-frame bit rate model as empirical values.
[0047] 2) Calculate the target number of bits allocated to the current I frame according to the target bit rate, the predefined frame rate and the current buffer level. The formula is as follows:
[0048] R intra = bit _ ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com