Method for the detection of potential toxicity of gastrotoxic insecticides or genetically modified insecticidal proteins to larvae of Apis mellifera
A technology of Italian honey bee and insecticidal protein, which is applied in biological testing, material inspection products, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in inspection methods, imperfect inspection methods, and researchers have not found improvement basis and instructions, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
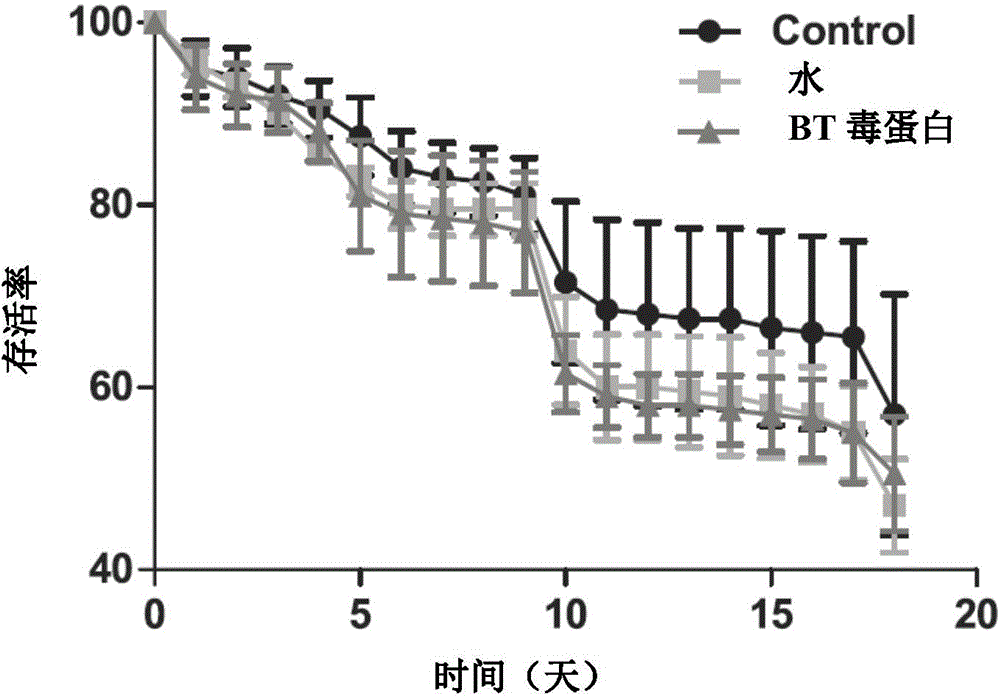
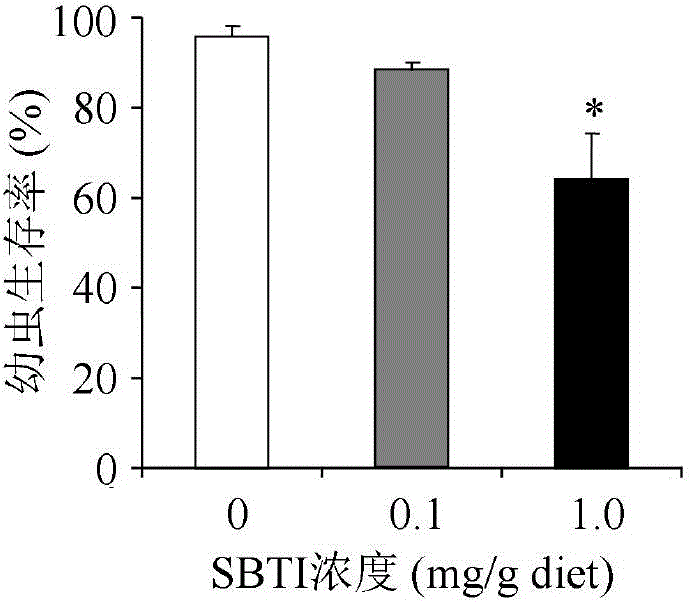
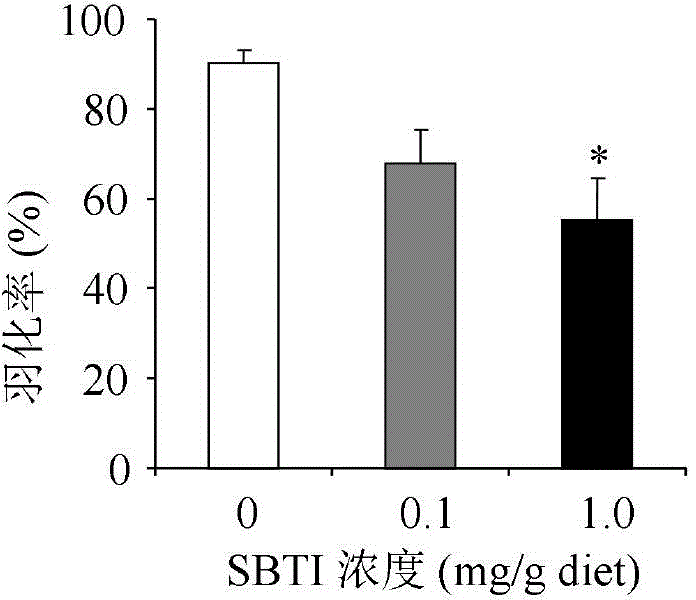
[0037] The invention provides a simple and sensitive detection method for detecting the direct toxicity of gastric toxicity insecticides or transgenic insecticidal proteins on Italian honeybee larvae. In this method, the tested insecticidal compounds are evenly mixed into artificial feed and fed directly to Italian bee larvae, and the artificial feed with a concentration of 0.1% (w:w) soybean trypsin inhibitor SBTI is used as a positive control. The feed was a blank control, and the potential toxicity of the tested insecticidal compounds to the Italian bee larvae was determined by comparing and analyzing important life indicators such as the survival rate, development period, mature larval weight and emergence rate of Italian bee larvae in the treatment group and the control group. This method was used to determine the toxicity of different concentrations of SBTI to Italian bee larvae. The results showed that the different life parameters of Italian bee larvae and the concentrat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com