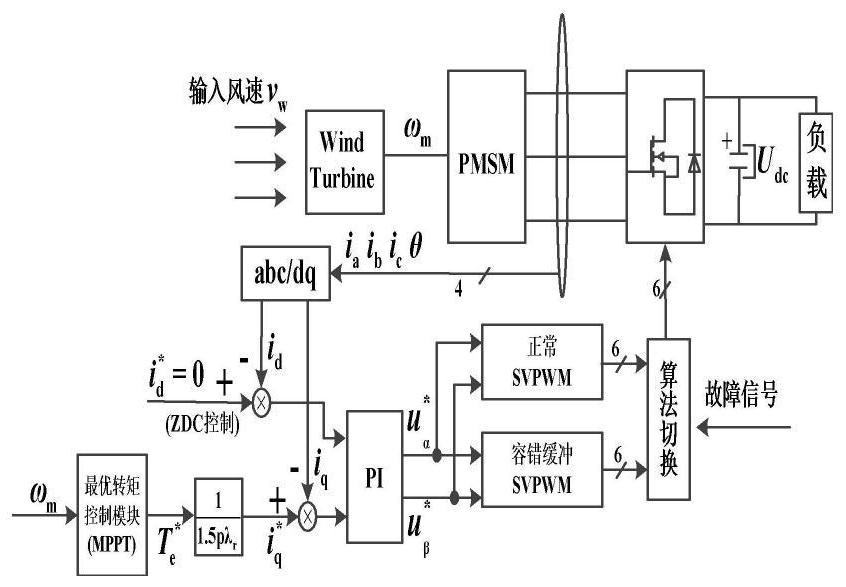
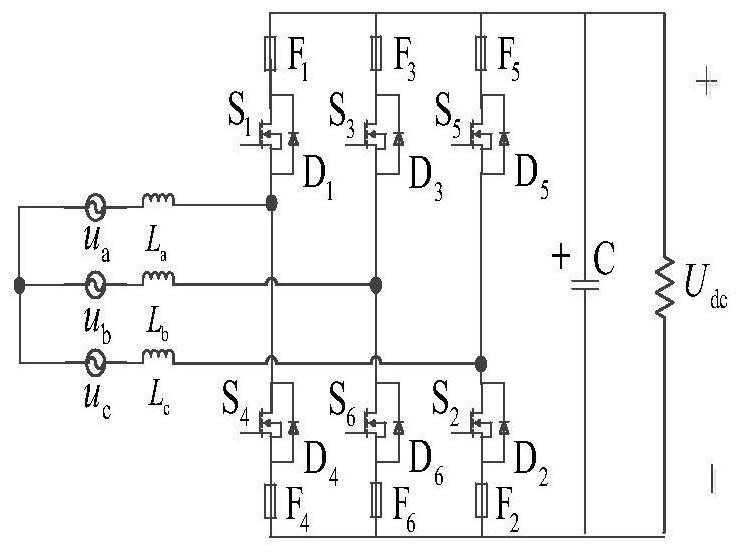
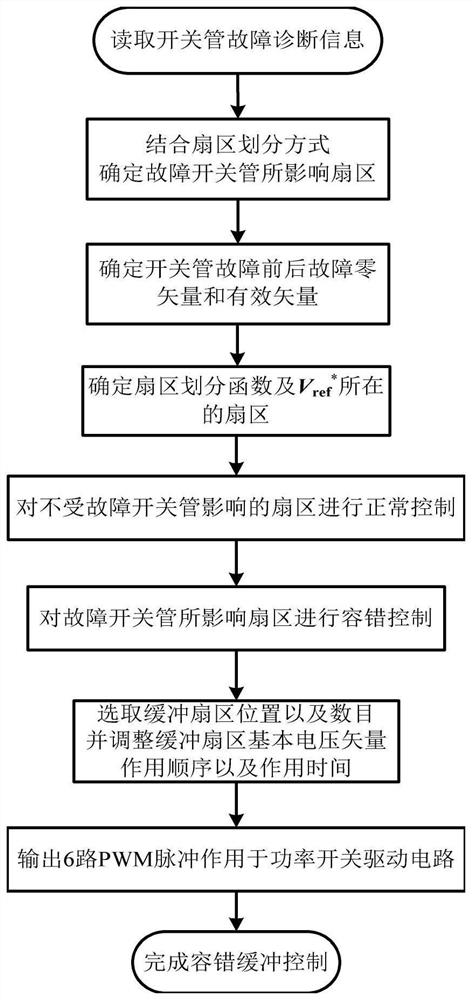
Fault-tolerant control method of two-level pwm rectifier based on sector buffer
A fault-tolerant control and rectifier technology, which is applied to electrical components, output power conversion devices, and AC power input to DC power output, etc. It can solve the problem of inability to realize fault-tolerant control, compensation, and undercompensation of multiple bridge arm switches.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0163] In this embodiment, the three-phase two-level PWM rectifier is divided into eight sectors to illustrate the single-tube fault S1. When a short-circuit fault occurs in the S1 tube, it will be converted into an open-circuit fault by the thermal fuse. When an open-circuit fault occurs in S1 According to Table 16, the fault-tolerant buffer control method is described by comparing the sector changes under the three states of fault-tolerant control, single-sector fault-tolerant buffer control, and double-sector fault-tolerant buffer control in a single cycle.
[0164] Table 16 Comparison of three-state sectors in a single cycle of eight sectors under S1 switch tube failure
[0165]
[0166] Schematic diagram of the sector and buffer sector distribution affected by the fault switch tube of the three-phase two-level PWM rectifier S1 tube fault in the eight-sector division mode is as follows Image 6 As shown, in the case of S1 tube failure, for the sector not affected by the...
Embodiment 2
[0168] This embodiment is described by taking a three-phase two-level PWM rectifier with multi-transistor faults in an eight-sector division mode.
[0169] When two switching tubes in the three-phase two-level PWM rectifier fail at the same time, such as figure 2 As shown, it will be divided into the following four situations:
[0170] a. The two upper and lower switching tubes of the same bridge arm fail at the same time;
[0171] b. Two upper tubes of different bridge arms fail at the same time;
[0172] c. Two lower tubes of different bridge arms fail at the same time;
[0173] d. One upper tube and one lower tube of different bridge arms are faulty.
[0174] Since the short-circuit fault can be converted into an open-circuit fault through the thermal fuse, after other fault diagnosis, the switching tube fault can also be converted into an open-circuit fault by turning off the controller. Here, the open-circuit fault is used for description.
[0175] For case a, the si...
Embodiment 3
[0179] In this embodiment, the three-phase two-level PWM rectifier is divided into twelve sectors with a single-tube fault S1 to illustrate. When a short-circuit fault occurs in the S1 tube, it will be converted into an open-circuit fault by the thermal fuse. When an open-circuit fault occurs in S1 At this time, according to Table 17, the fault-tolerant buffer control method is described by comparing the sector changes under the three states of fault-tolerant control, single-sector fault-tolerant buffer control, and double-sector fault-tolerant buffer control in a single cycle.
[0180] Table 17 Comparison of three-state sectors in a single cycle of twelve sectors under S1 switch tube failure
[0181]
[0182]
[0183] Schematic diagram of the sector and buffer sector distribution affected by the fault switch tube of the three-phase two-level PWM rectifier S1 tube fault in the twelve-sector division mode is as follows Figure 7 As shown, in the case of S1 tube failure, f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com