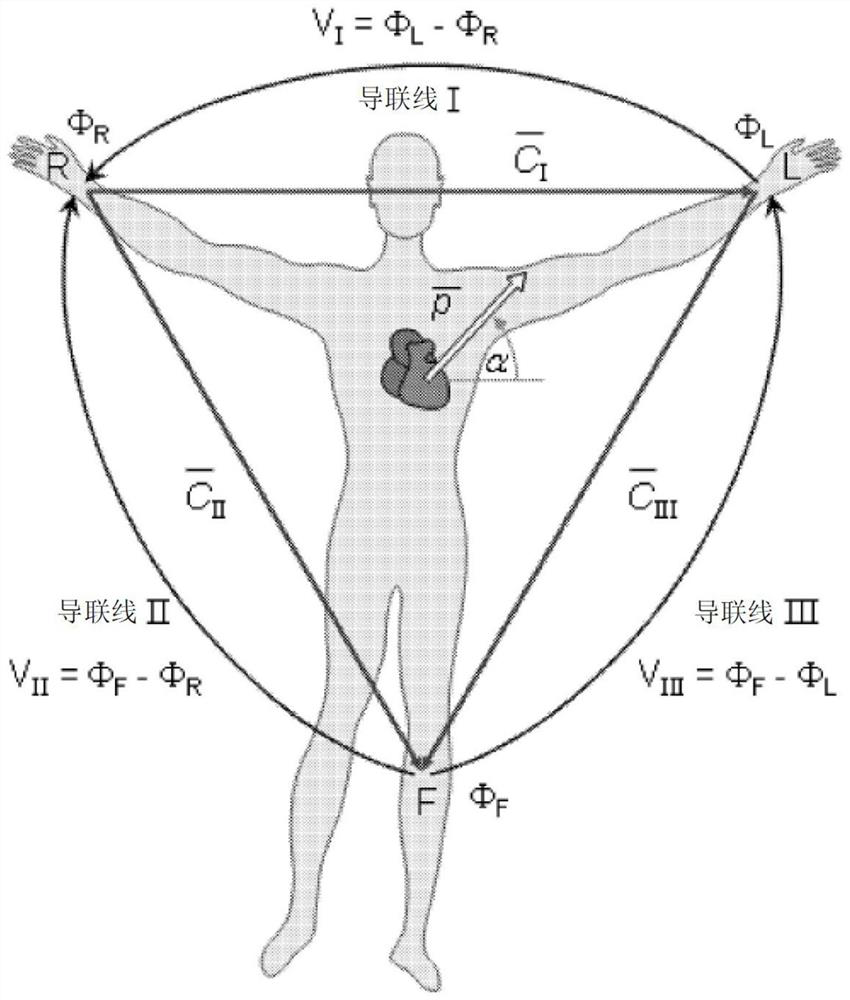
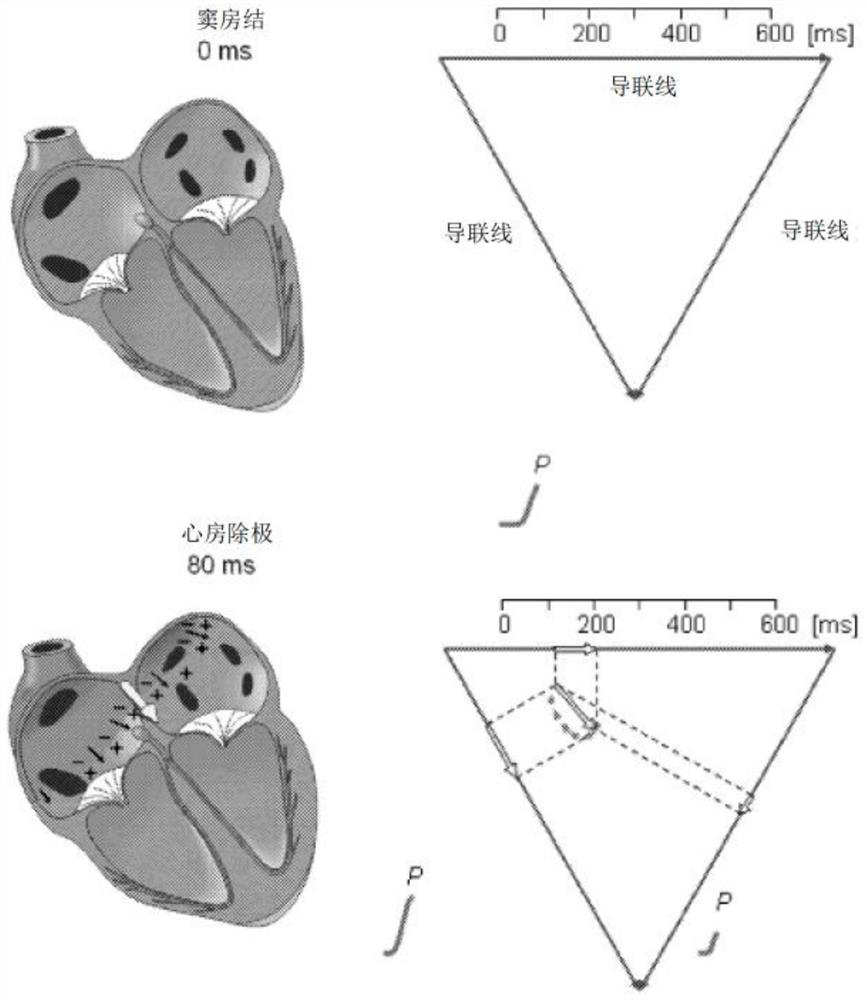
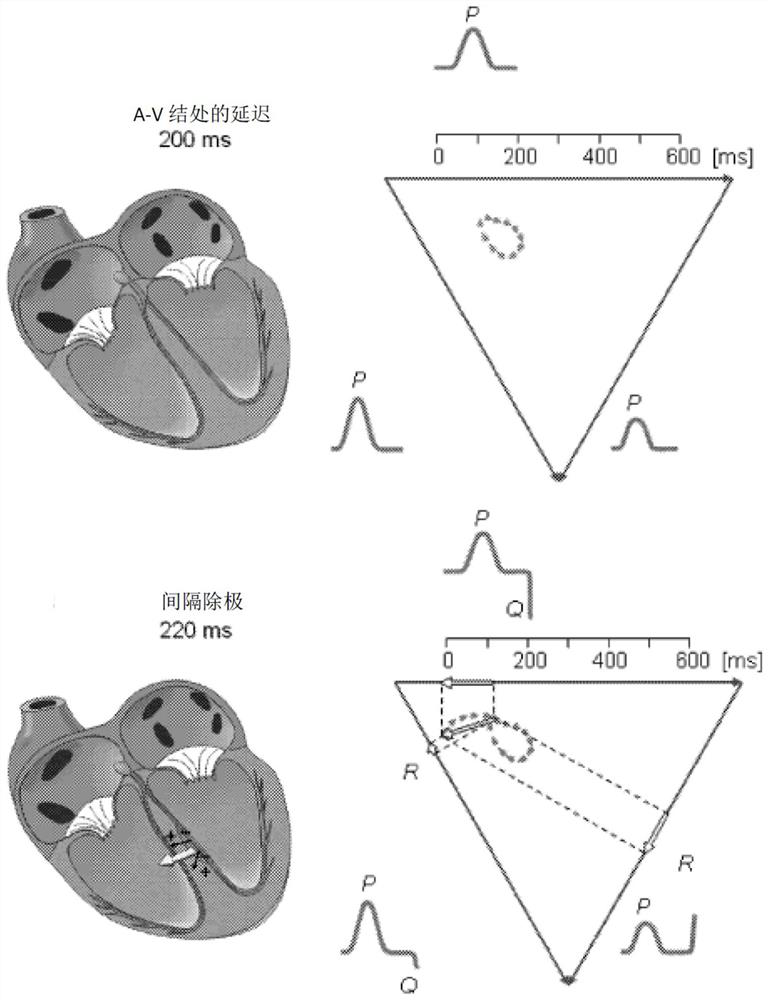
Microelectronic sensors for non-invasive monitoring of physiological parameters
A physiological parameter, non-invasive technology, applied in the direction of micro sensor, sensor, humidity sensor, etc., can solve the problem of sacrificing the switch-on performance of the device
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0273] Example 1: Charge Sources for Single Point PC-HEMT Signals
[0274] At the onset of the pulse arrival time (PAT) cycle in the chest, there are different ways to detect the primary cardiac activity signal that can be used for blood pressure calculations. The inventors of the present invention demonstrated that, in some embodiments, single point PC-HEMT signals actually arise from cardiac electric dipole field changes rather than mechanical changes in the heart / body.
[0275] In applied biomedical research, heart vibrations are measured by techniques known as ballistocardiography (BCG of whole body movements) or vibrocardiography (SCG of mainly thoracic movements). The mechanical BCG signal follows the electrical signal, with a delay of approximately 30-40 ms. In BCG, the mechanical motion of the heart is detected by measuring force or acceleration from the chest. Alternatively, using remote BCG recordings, the pumping activity of the heart can be monitored. It is usua...
example 2
[0279] Example 2: Cardiovascular and Lung Monitoring Using PC-HEMT Sensors
[0280] Referring now to Figure 22, which shows a heartbeat waveform (Wiggers diagram, cited from WikiCommons 2008) recorded using different conventional instruments. Figure 23 A heartbeat detected at the wrist with a single point PC-HEMT sensor and a pulse oximeter is shown compared to a standard signal. The oximeter signal follows the aortic pressure waveform with a time delay ΔΤ that is common with the device installed. Figure 24a Central venous pressure (CVP) data synchronized with ECG and cardiac signal data recorded with a PC-HEMT sensor are shown. Figure 24bThe first derivative of the ECG recording curve obtained from 100 combined measurements using the PC-HEMT sensor is shown. It is consistent with CVP readings, enabling non-invasive CVP to be performed using one embodiment of the sensor of the present application in conjunction with the ECG described above. Therefore, cardiac signals rec...
example 3
[0283] Example 3: Flow test
[0284] A prototype single-point measurement PC-HEMT sensor was used to perform a full cardiac cycle activity recording, including the physical motion of the left and right atria, in a real-time synchronized manner with the cardiac polarization / depolarization electrocardiographic dynamics. The technique described in this application allows non-invasive cardiac diagnostics to be performed, which can alternatively be performed only by invasive left and right atrial cardiac catheterization with simultaneously recorded ECG. Furthermore, the PC-HEMT sensor of some embodiments of the present application enables access to a single site on the patient's body where cardiac measurements need to be taken. This allows for the smooth integration of PC-HEMT sensors into wristwatch form, revolutionizing the entire approach to cardiovascular and pulmonary diagnostics and therapy monitoring. Furthermore, with the integrated PC-HEMT sensor, cardiac telemedicine in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com