Semantic and label difference fused named entity identification field self-adaption method
A technology for named entity recognition and labeling, which is applied in the Internet field and can solve the problems of not fully considering the large difference of sentence semantic vectors, not considering the influence of label differences, and label set differences.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
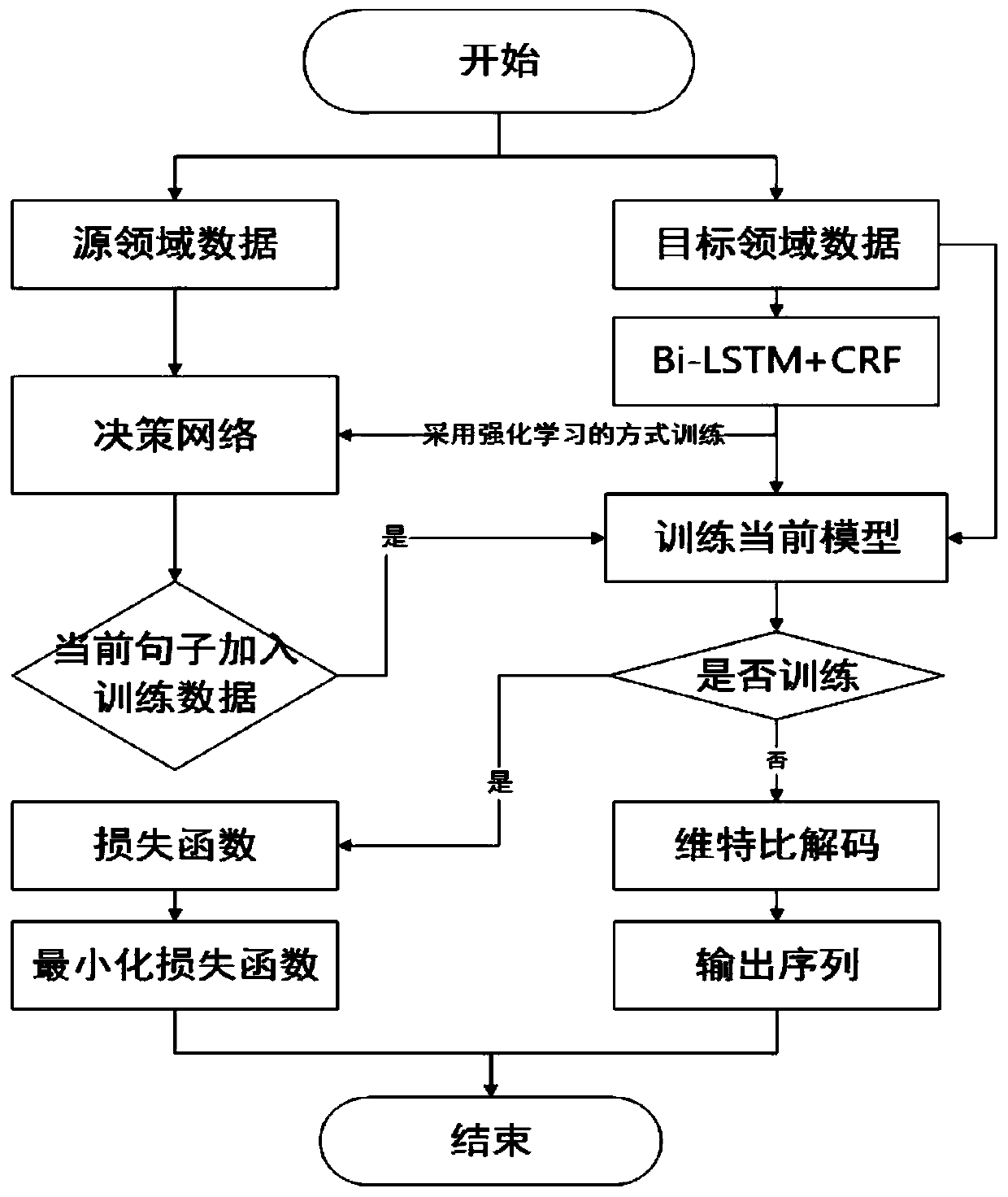
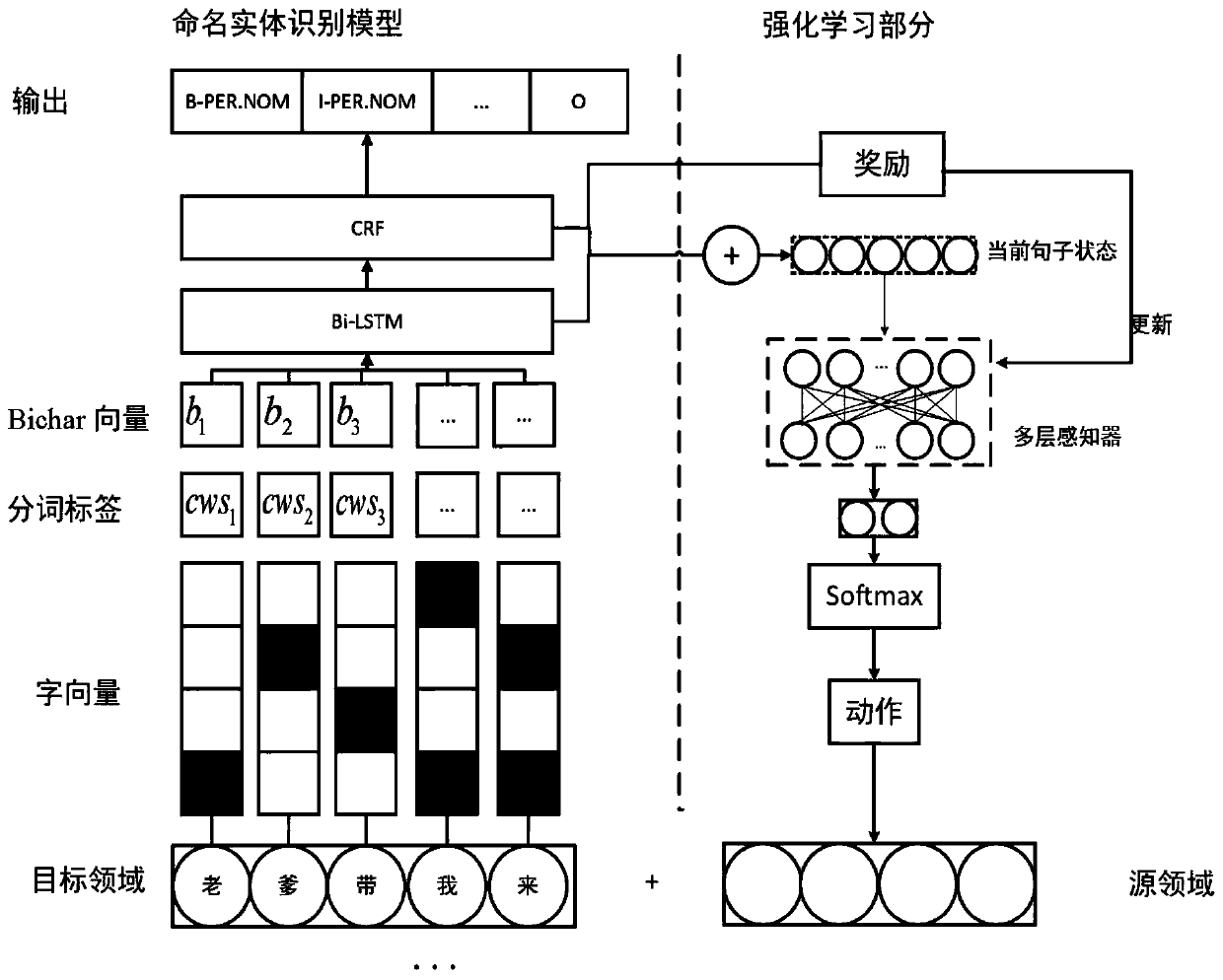
[0069] refer to figure 1 , 2 As shown, the present invention provides a method for integrating semantics and label differences to perform domain transfer on named entity recognition tasks. Specifically, during training, the method includes:
[0070] Step 1. Preprocess the sentences in the source domain and the target domain corpus, remove URLs and special symbols, and perform traditional and simplified conversion to convert all sentences in the corpus into simplified Chinese.
[0071] Step 2: Process the labels of the sentences in the source domain corpus to unify the entity label sets of the source domain and the target domain. Specifically, the PER tag in the source domain is changed to PER.NAM, the LOC tag is changed to LOC.NAM, and the ORG tag is changed to ORG.NAM, while the O tag remains unchanged.
[0072] Step 3: The sentences in the source domain and the sentences in the target domain are mapped into vector representations according to the same dictionary, and are u...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com