Traveling wave network positioning method based on dynamic virtual fault
A technology of network location and virtual fault point, which is applied in the field of traveling wave network location based on dynamic virtual fault, and can solve the problem of too large fault location error.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] 1. Analysis of Time Difference of Arrival Characteristics of Fault Traveling Waves
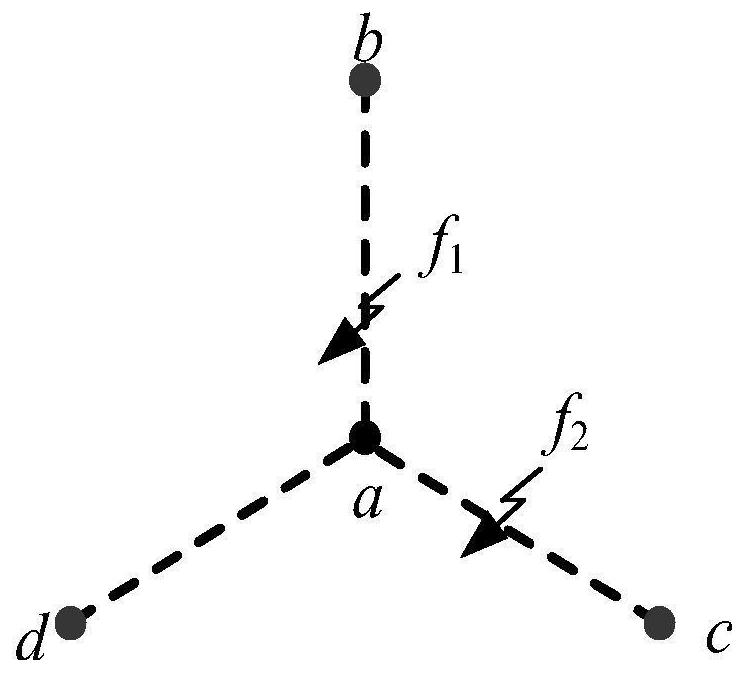
[0071] by figure 1 The structure shown is taken as an example for analysis, and the three lines are all connected to node a. After a fault occurs on the transmission line, the initial traveling wave propagates along the shortest path to three measurement points b, c, and d respectively.
[0072] Assume f in line ab 1 A fault occurs at , and the initial traveling wave of the fault starts from f 1 The time required to propagate to measurement points b, c, d at for
[0073]
[0074] In the formula, v b , v c , v d Respectively represent the wave velocity of the fault initial traveling wave propagating to the measurement point b, c, d; Indicates the line length from the fault point to the measurement point. Traveling wave velocity can generally be regarded as a fixed value, so we can set v b =v c =v d =v. Then the time difference of the fault initial traveling wave arriv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com