In vitro activity assay for human hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA polymerase, and its use for screening inhibitors of HBV DNA polymerase
A technology of hepatitis B virus and polymerase, applied in the field of the N-terminal of the enzyme, can solve problems such as inability to implement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Polymerase Activity Test of HBV Surface Antigen Mutants
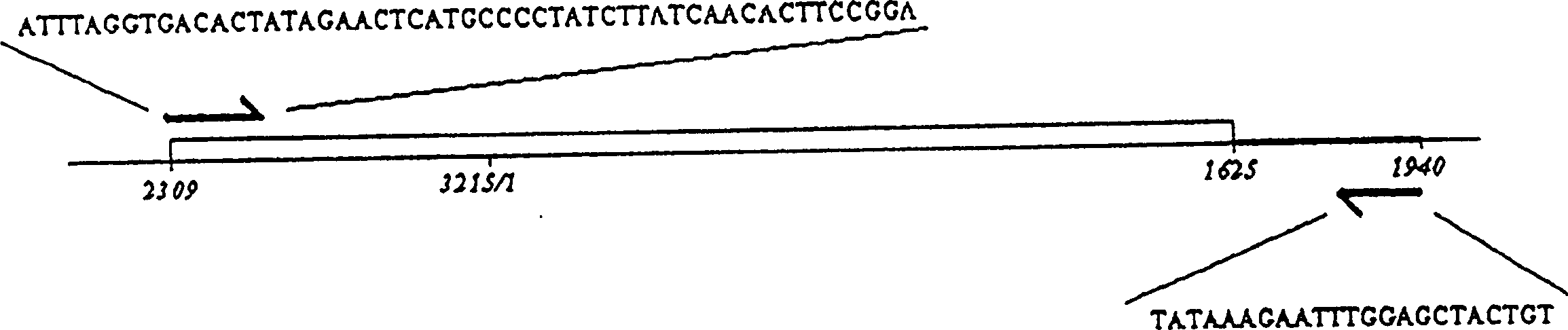
[0058]An immediate application of the facile activity assay of human HBV DNA polymerase reported in the present invention is the assessment of HBV variants with major surface antigen mutations, especially those induced by vaccination (i.e. 'S'145). active. Viral DNA was extracted from serum samples containing such HBV variants as described above. The mutants involved in the present invention include 'S'145 (glycine to arginine mutation) and 'S'146 (threonine to alanine mutation), which can evade existing immune detection systems and replicate independently. Using the viral DNA as a template, with the same oligonucleotide primers, use Taq polymerase (Promega, U.S.A.) on a DNA thermal cycler (Perkin-Elmer, Cetus) to carry out 35 cycles of PCR, each cycle including 1.5 minutes at denaturation temperature (94°C), 2 minutes at annealing temperature (53°C) and 4 minutes at extension temperature (72°C).
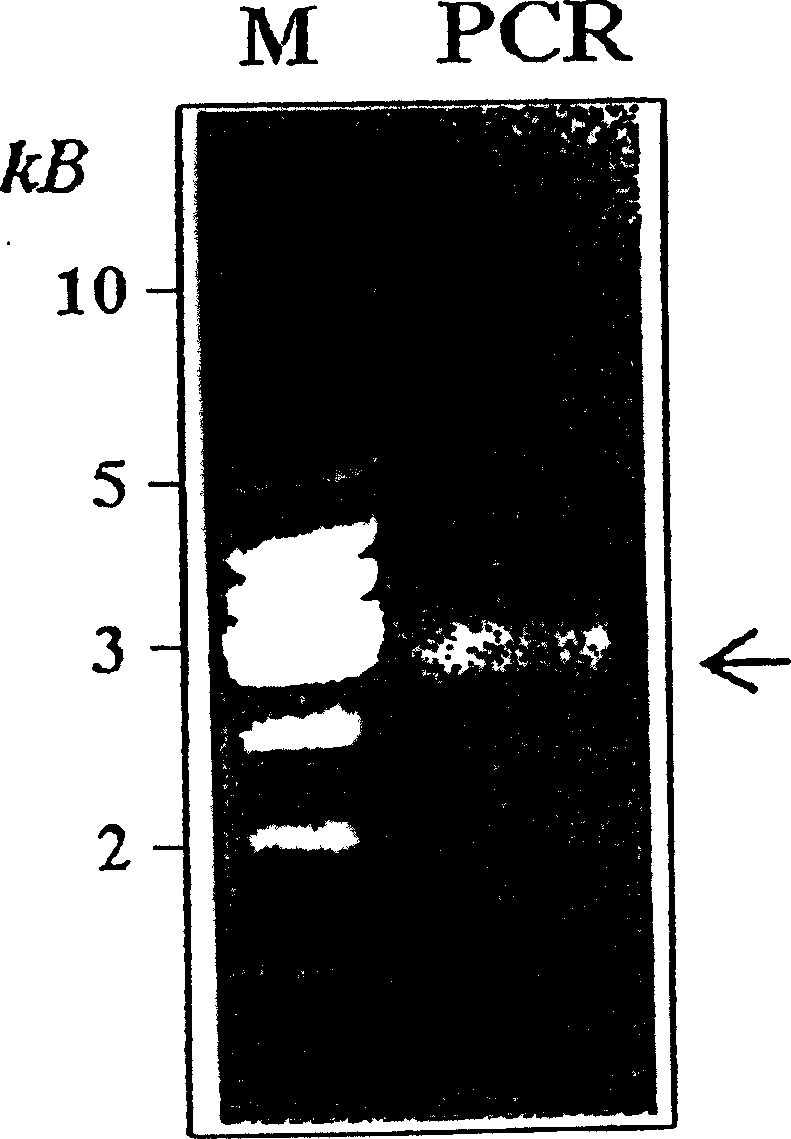
[0059] PCR ...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Detection of inhibitors of human HBV DNA polymerase
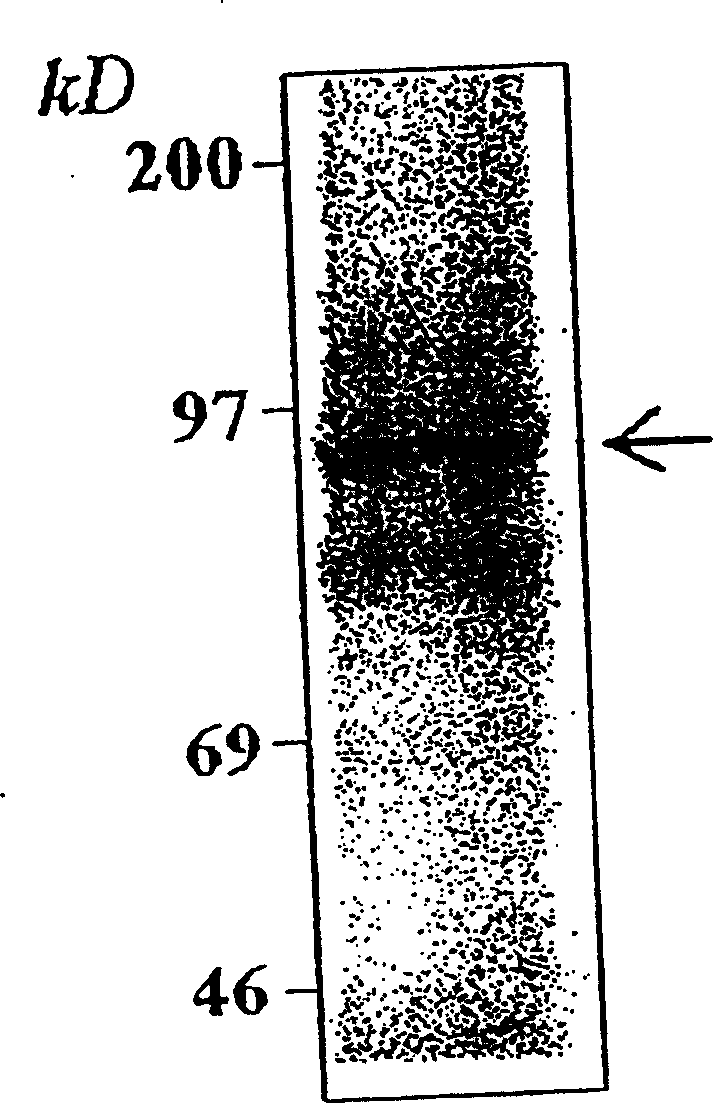
[0062] Screening for inhibitors of human HBV DNA polymerase will provide new therapeutic agents for HBV infection, since effective inhibition of polymerase activity will lead to inhibition of HBV viral replication. The simplified activity assay reported in the present invention enables more rapid analysis of the inhibitory effect of newly discovered molecules on the DNA polymerase of HBV variants carrying major surface antigen mutations. Briefly, candidate inhibitors were first incubated with wild-type human HBV DNA polymerase that was PCR amplified and translated in vitro as reported in the present invention. There is [α- 32 P]dTTP and the other conditions mentioned above are present. The inhibitory effect can be determined by laser densitometry followed by SDS-PAGE analysis, or by measuring the amount of radiolabeled HBV DNA polymerase bound to the nitrocellulose membrane after filtration. Obviously, analysis of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com