Immunogenic peptide carrier conjugates and methods of producing same
A peptide immunogen and carrier technology, which is applied in the field of immunogenic peptide carrier conjugates and their production, can solve the problems of sensitivity to the destructive effect of chemical treatment and destruction of the function of the conjugate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
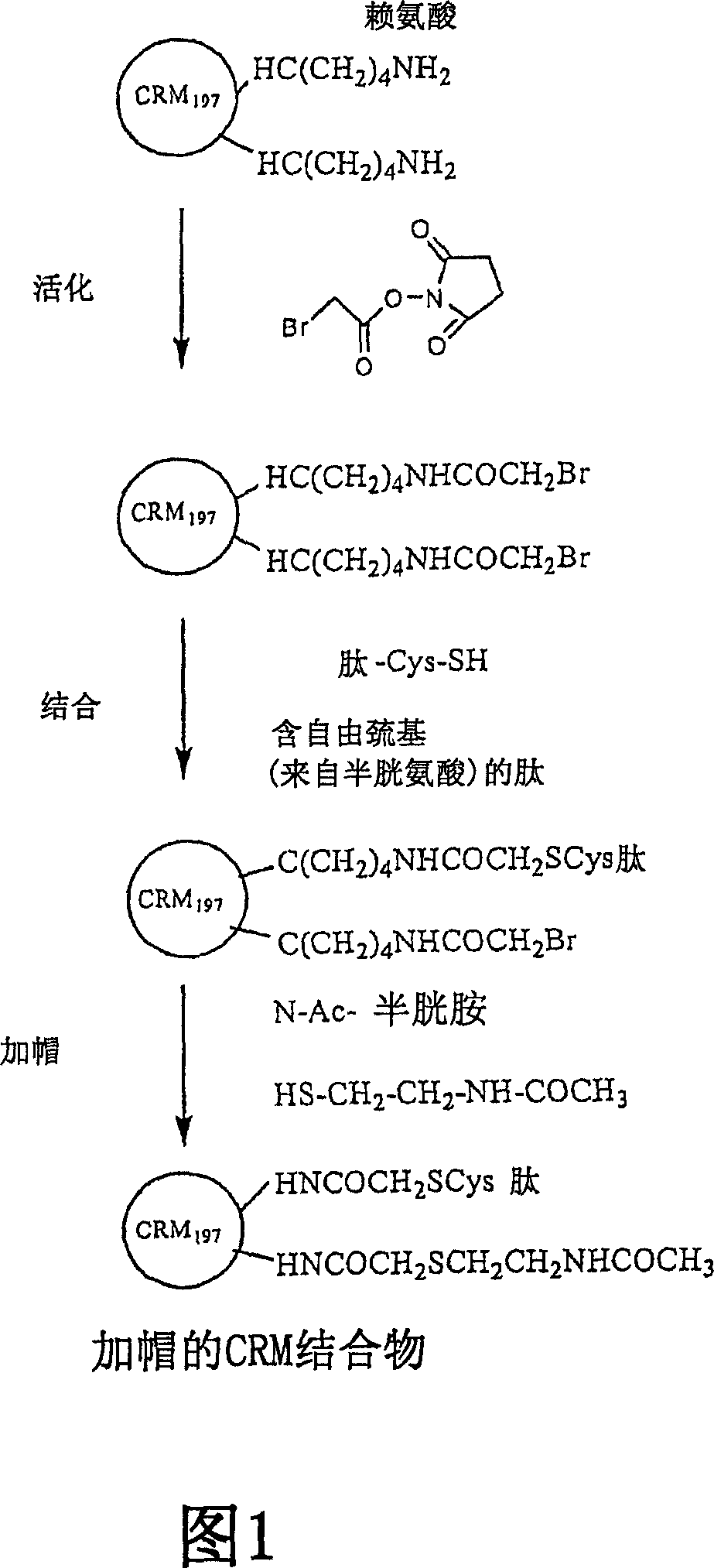
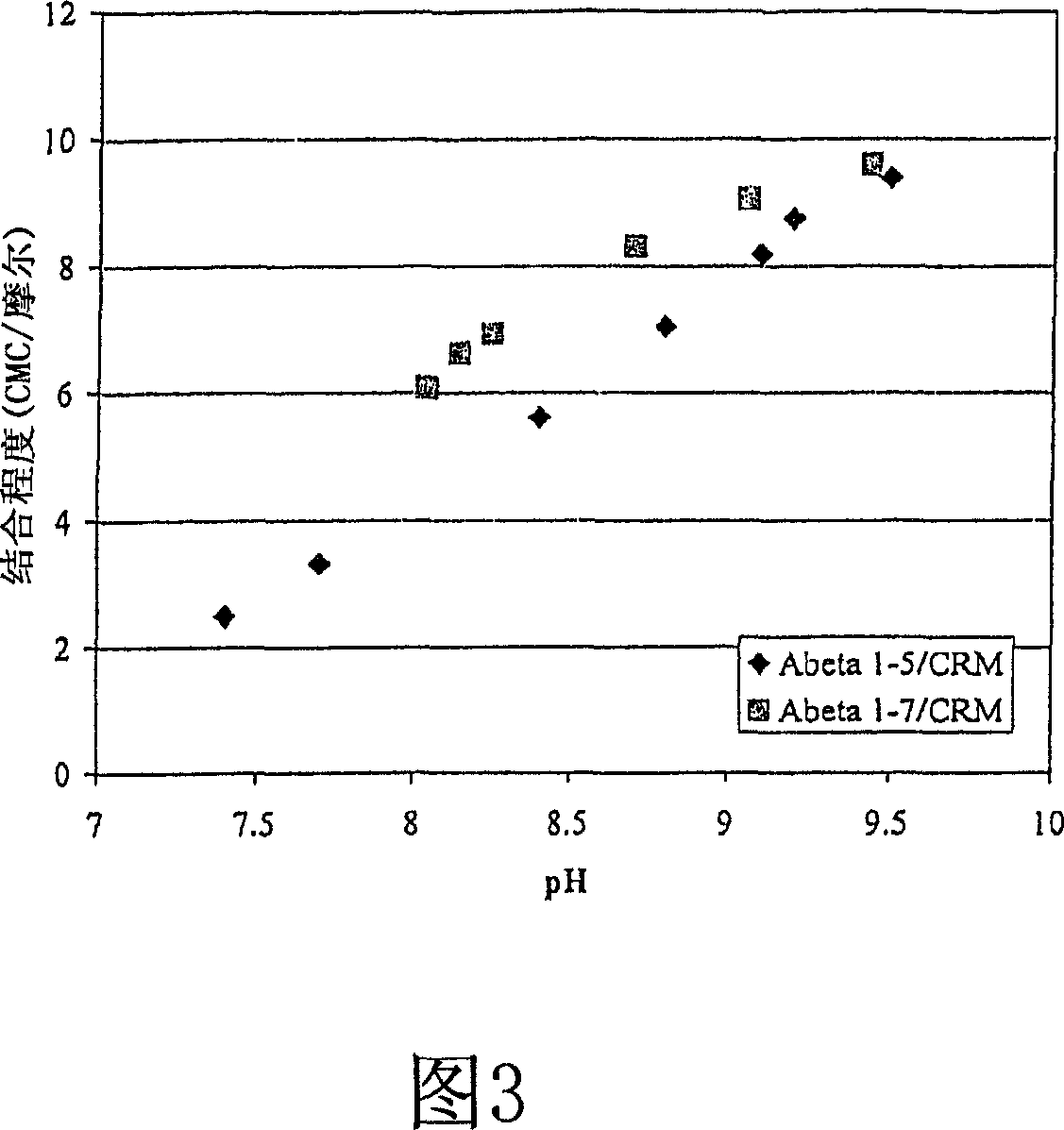
[0253] CRM 197 Binding to Aβ peptide
[0254] Activation vector CRM with 39 lysine residues 197 Hapten / antigenic peptide conjugation was carried out by reaction with a hapten / antigenic peptide having a pendant thiol group using the method described below (Fig. 1). All A[beta] peptides contain a cysteine residue at the carboxy terminus to facilitate conjugation of these peptides to carrier proteins via cysteinyl sulfhydryl groups. These peptides were produced by solid phase synthesis.
[0255] I. Activation
[0256] CRM 197 The free amino group of ® was bromoacetylated by reaction with an excess of N-hydroxysuccinimide bromoacetate (Sigma Chemical Co., St. Louis, MO) (Bernatowicz and Matsueda, 1986). To the cold CRM 197 (about 15mg) solution, add 10% (v / v) of 1.0M NaHCO 3 (pH8.4). will be used with the CRM 197 An equal weight of N-hydroxysuccinimide bromoacetate was dissolved in 200 μL of dimethylformamide (DMF) and slowly added to the CRM 197 and stirred gently for...
Embodiment 2
[0272] Aβ peptide-CRM 197 Preparation of conjugates and purification by ultrafiltration
[0273] CRM 197 bromoacetylation
[0274] CRM 197 (100mg) of 0.01M sodium phosphate buffer, 0.9% NaCl, pH7.0 solution and N-hydroxysuccinimide bromoacetate (dissolved in DMSO to 20mg / mL) in an argon atmosphere at a weight ratio of 1:1 The next reaction. The reaction was titrated as needed to maintain the pH at 7.0. The mixture was stirred at room temperature in the dark for 1.5 hours. The reaction mixture was filtered through a 1.2 μm filter into the retentate reservoir of a UF / DF system (Millipore Labscale TFF, Billerica, MA). Purification was accomplished by diafiltration (30-fold) in 0.01 M sodium phosphate buffer / 0.9% NaCl, pH 7.0 using 10K or 30K UF membranes. Bromoacetylated CRM 197 Filtration was performed by passing through a 0.2 μm filter. The degree of bromoacetylation is determined by the activation of the CRM 197 Reaction with cysteine followed by determination by a...
Embodiment 3
[0279] Conversion to aminoacetyl by capping unreacted bromoacetyl group
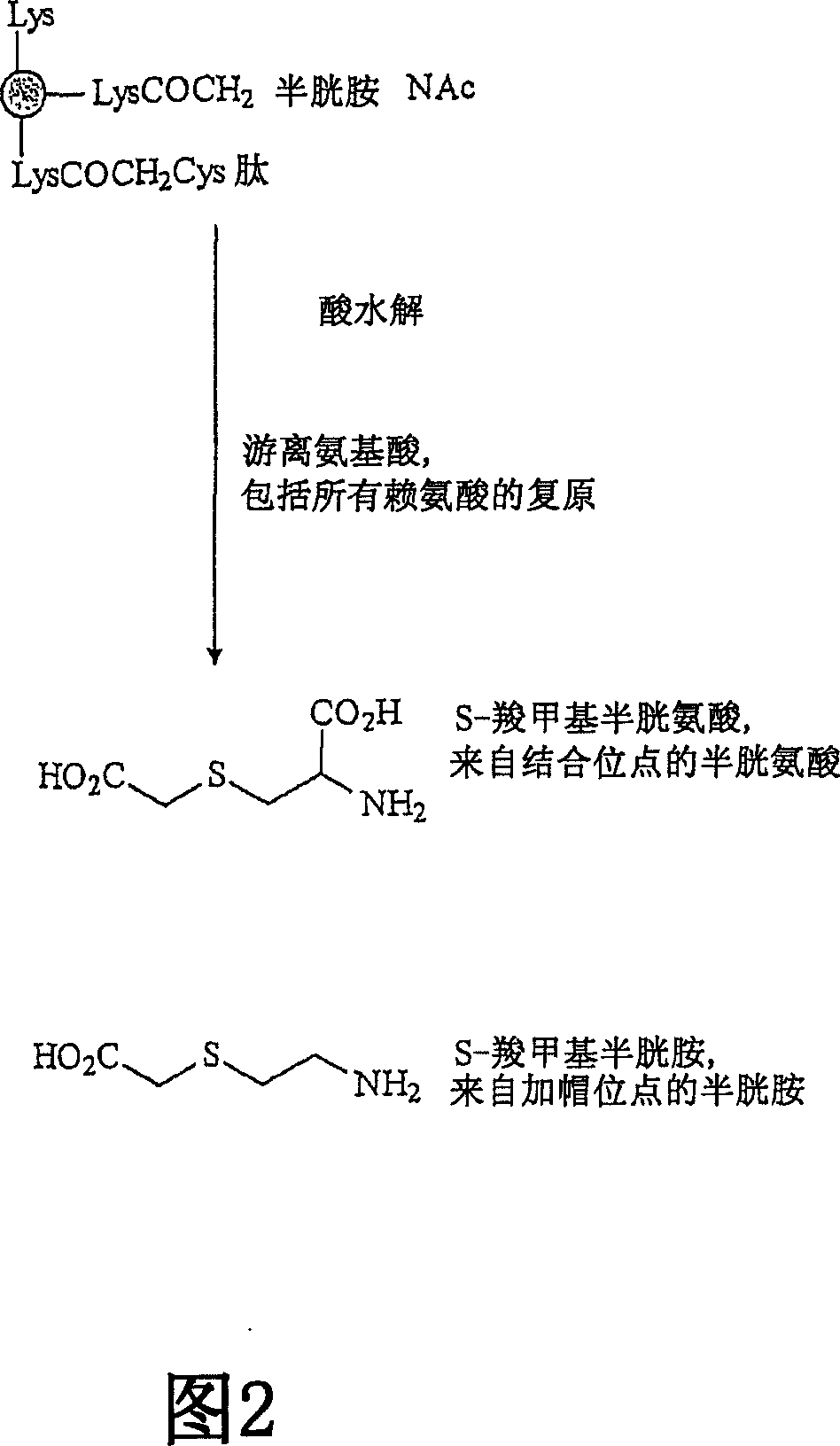
[0280] Bromoacetylated CRM prepared as described in Example 2 197 (50 mg) was transferred to a reaction vessel. To the stirred solution maintained at 2-8°C was added 1M sodium carbonate / sodium bicarbonate. Titration was performed under an argon atmosphere to achieve a target pH of 9.0. Weigh 50 mg of Aβ peptide individually and dissolve in WFI to 20 mg / mL. To this solution was added 1 M sodium carbonate / bicarbonate until pH 9.0 was obtained. CRM to bromoacetylation 197 To the solution was added the peptide solution and the mixture was stirred at 2-8°C for 14-18 hours. The remaining bromoacetyl groups were capped using 8% ammonium bicarbonate solution for 4 hours at 2-8°C.
[0281] The reaction mixture was filtered through a 1.2 μm filter into the retentate reservoir of the UF / DF system (Millipore XL), passed through 0.01M sodium phosphate buffer / 0.9% NaCl, pH7. The conjugate was purified by 30-fol...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com