Elastomeric nonwoven laminates and process for producing same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] The method, material, and the apparatus of the present invention are designed to provide a more cost effective and / or consumer desirable elastomeric laminate suitable for use in a variety of articles including disposable absorbent articles.
Definitions
[0033] The following terminology is used herein consistent with the plain meaning of the terms with further details provided in the present specification.
[0034] The terms “activating”, “activation” or “mechanical activation” refer to the process of making a substrate, or an elastomeric laminate more extensible than the it was prior to the process.
[0035]“Basis weight” refers to the weight of a planar material for a given surface area. Basis weight is typically measured in grams per square meter (gsm). The basis weight of an elastomeric laminate is typically measured in an unstrained configuration.
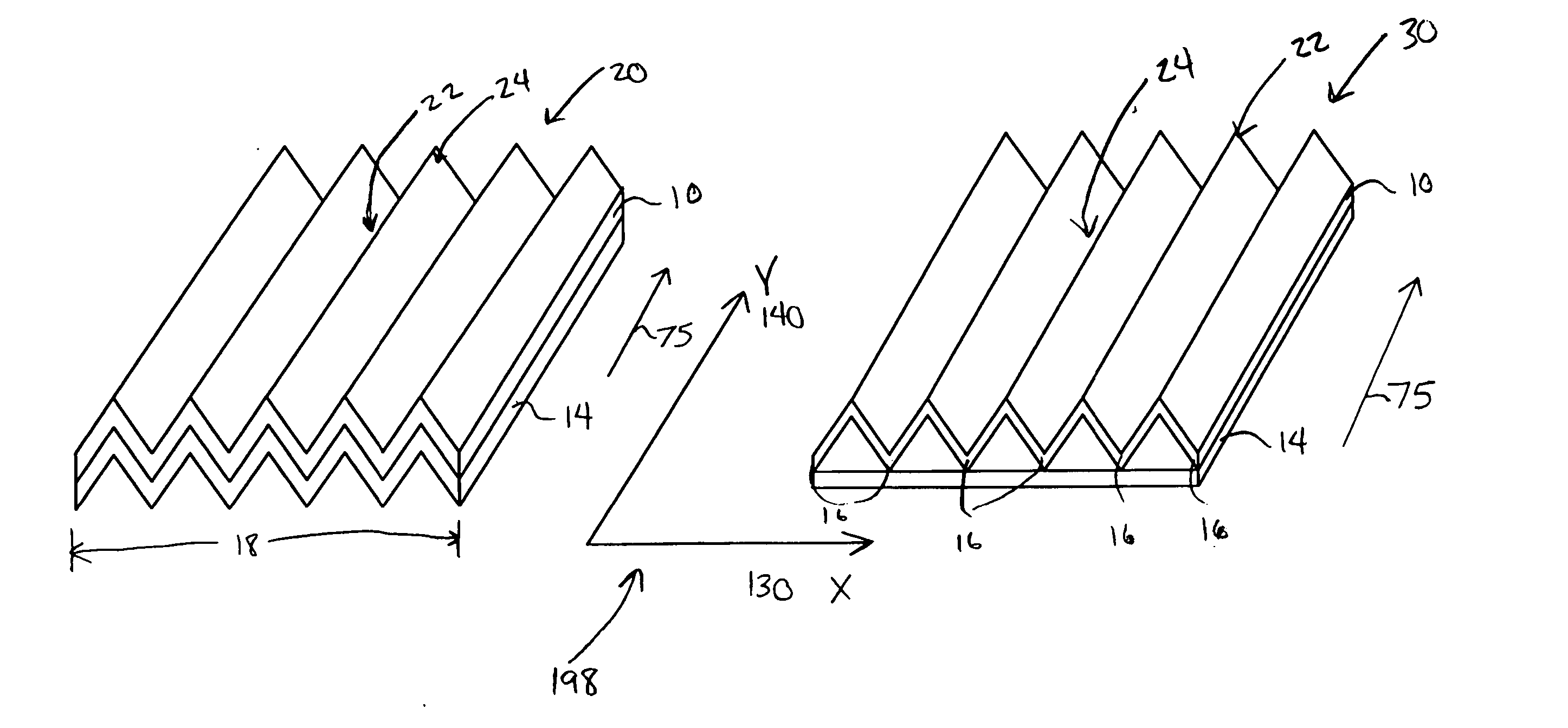
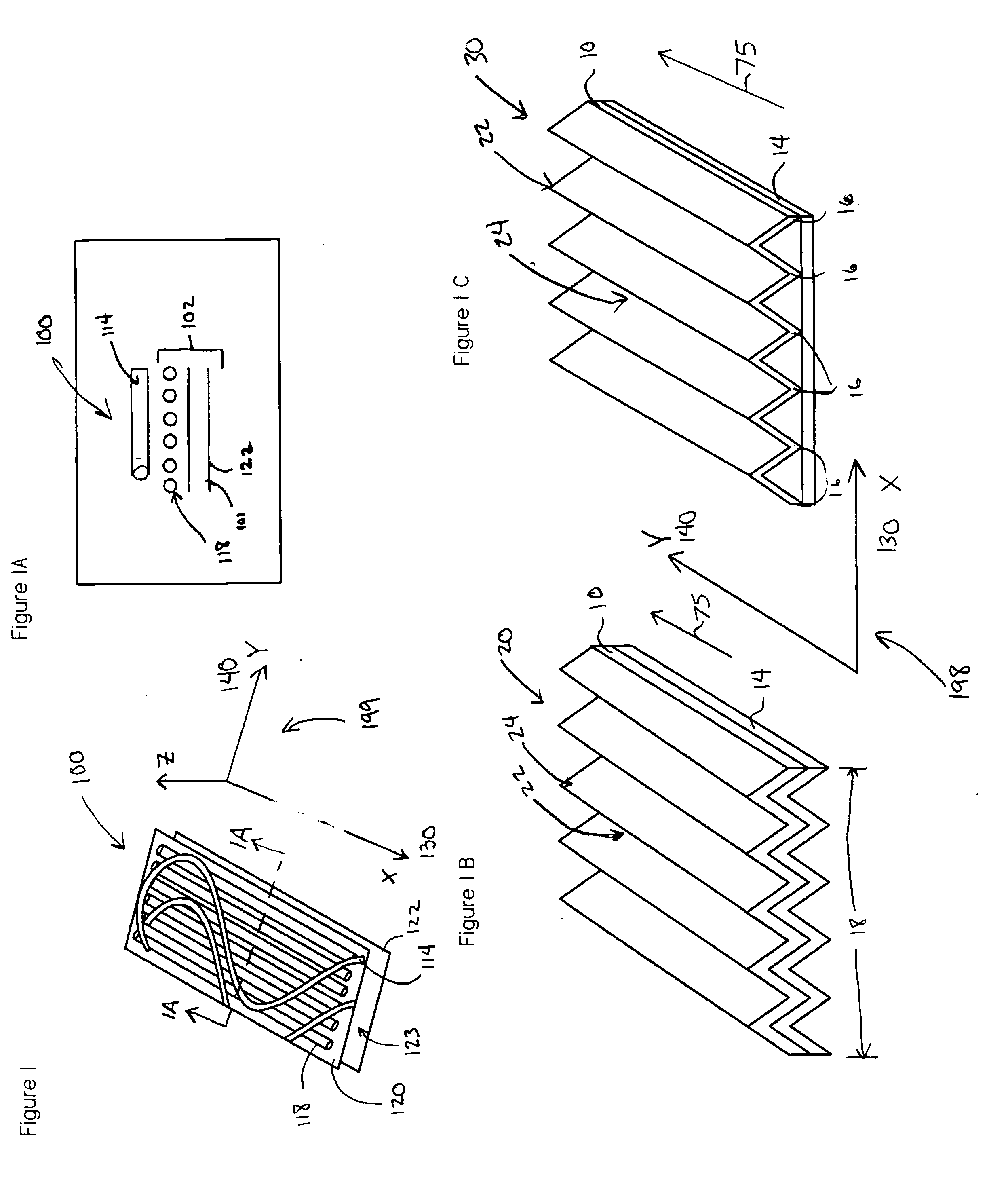
[0036] The terms “corrugations” or “ruggosities” are used to describe hills and valleys that occur in a substrate or in a laminate...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Elastomeric | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com