Method and apparatus for noninvasive inhibition of deep vein thrombosis
a deep vein thrombosis and non-invasive technology, applied in the field of electric stimulation of the foot muscles, can solve the problems of bringing on thrombosis, affecting cardiovascular circulation, and affecting the recovery of individuals, so as to reduce the pooling of blood, and enhance venous blood flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
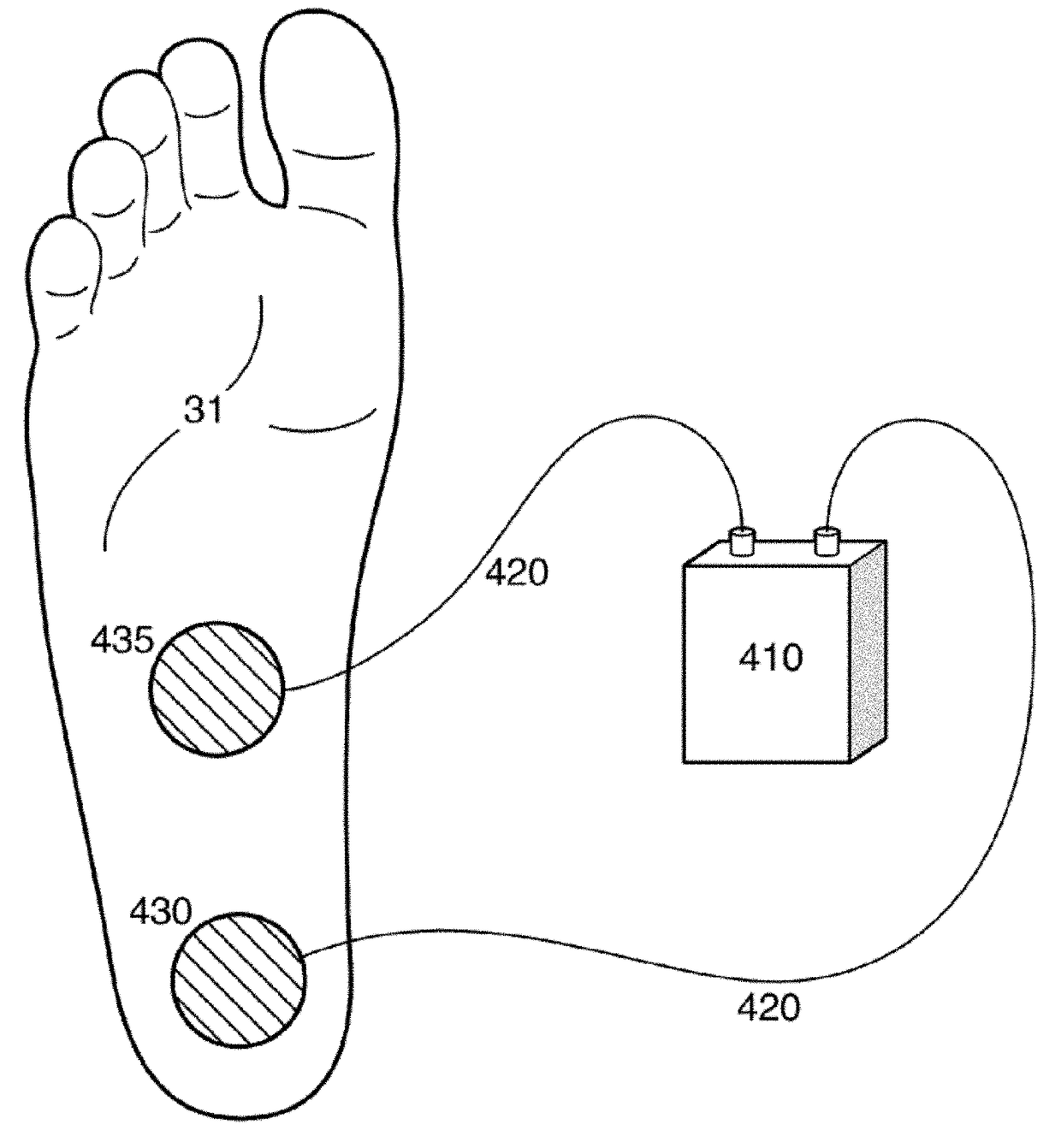
[0090]Aspects of the present invention provide an improved system, device, and method of administering electrical stimulation to the muscles of the foot.
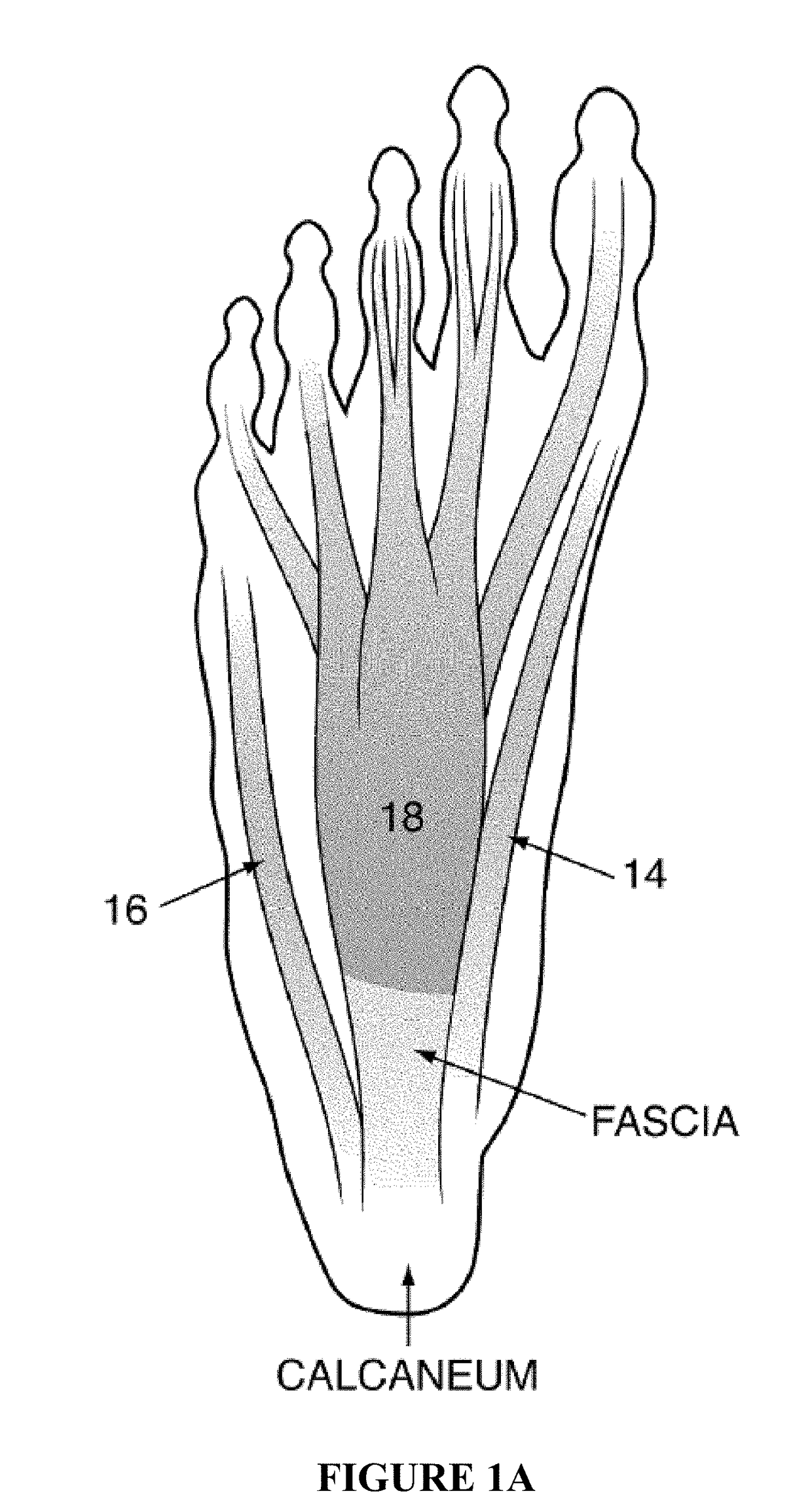
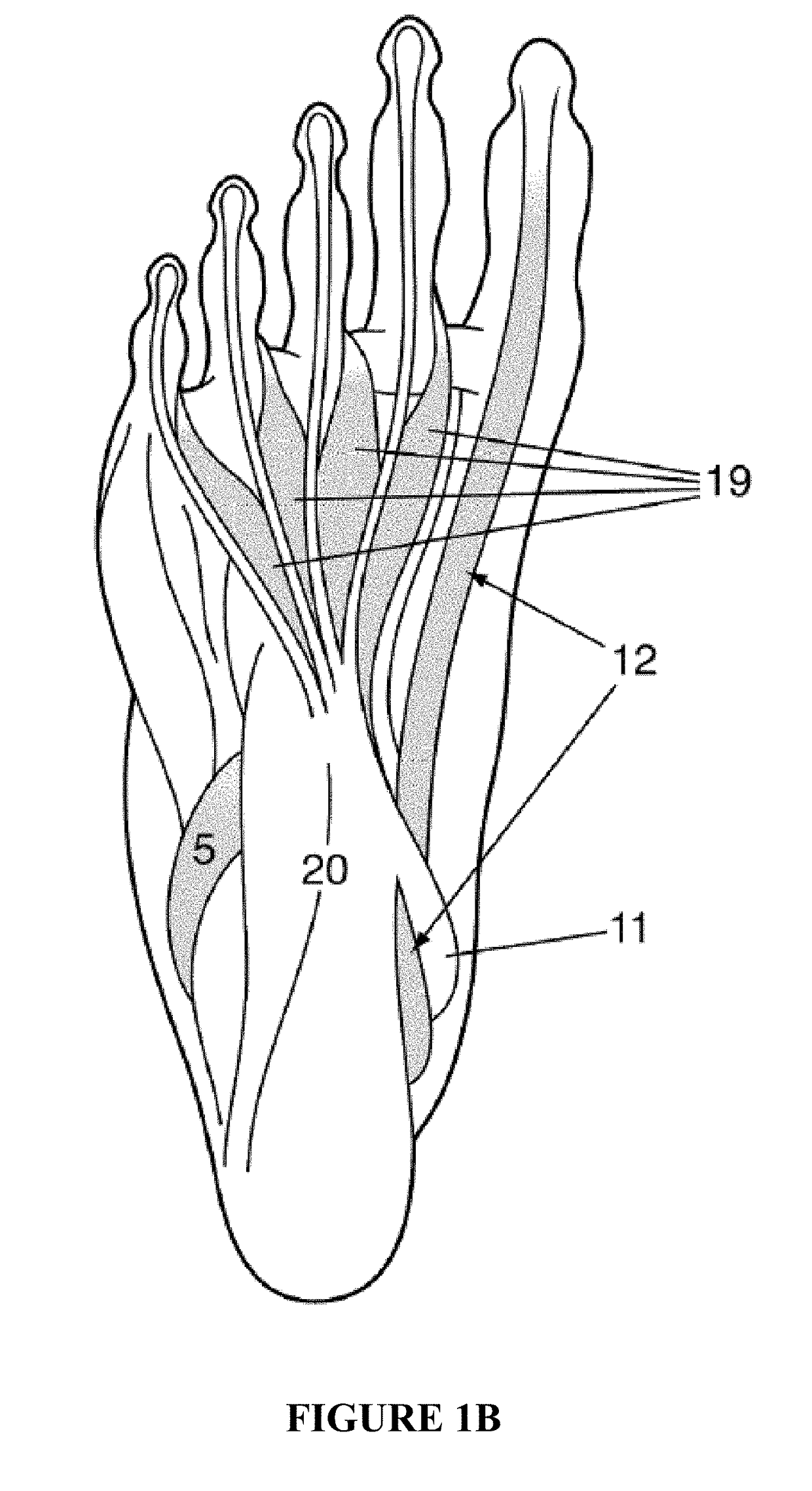
[0091]Aspects of the present invention provide a programmable electrical pulse generator for delivering an electrical current of mild and tolerable intensity to the muscles of the foot, which results in a mild contraction of the muscles. In various aspects of the present invention, the contraction may be accomplished by placing surface electrodes on the soles of the feet or at the ankles. When placed on the soles, the active surface electrodes are placed over the larger muscles of the first layer that are closer to the surface of the skin and in an area where callousing of the skin and the fat layer is minimal such as the mid-foot and arch area. The ground electrodes may be placed over or proximal to the heel. By stimulating the foot muscles in this manner, blood pooling in the calf veins is prevented. When placed on the side or top...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com