Data packet network
a data packet network and data packet technology, applied in the field of data packet network, can solve the problems of inability to immediately determine the appropriate transmission rate at which data packets may be sent, congestion feedback can become useless in a very short amount of time, and congestion feedback can quickly become outdated
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
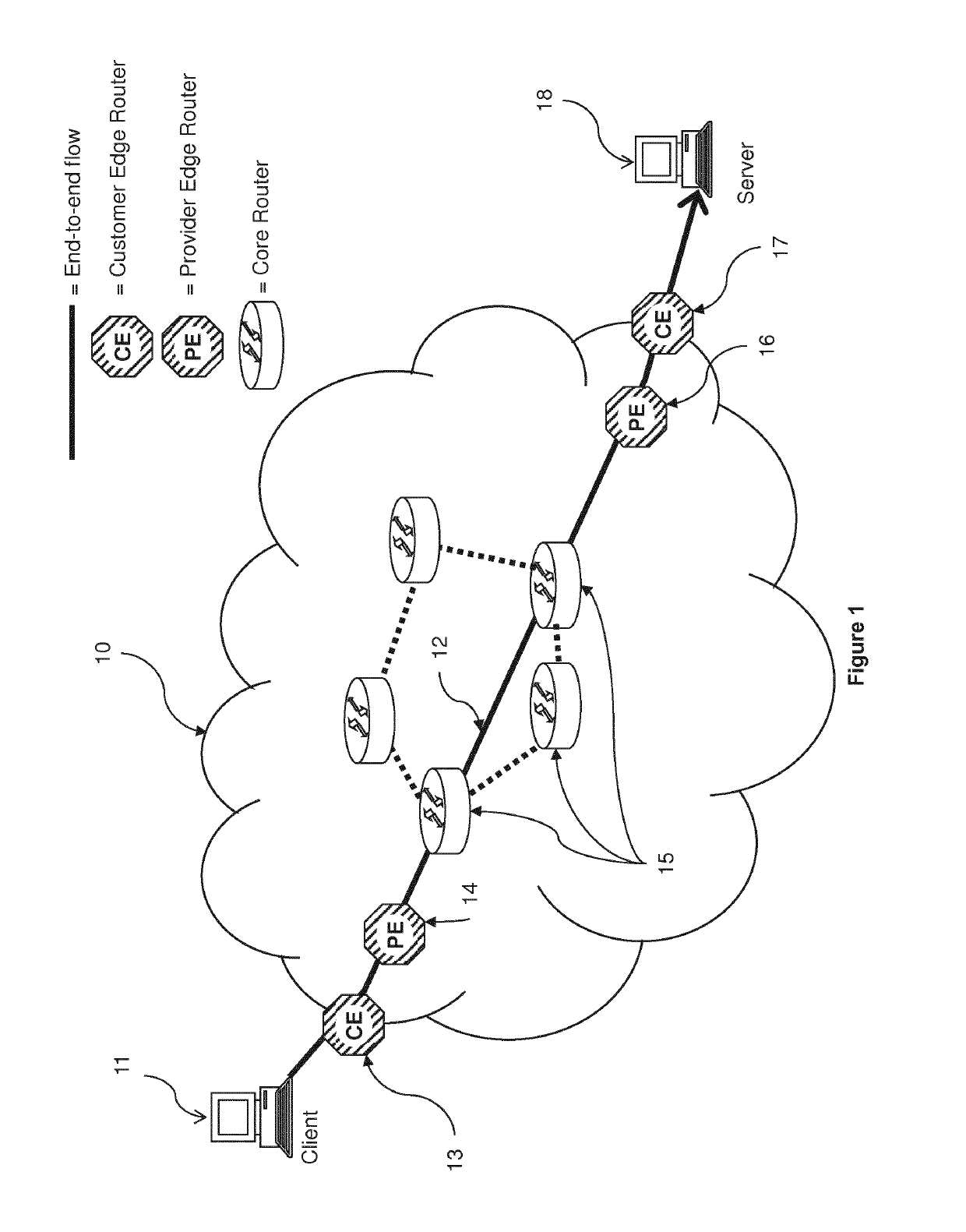
[0040]a communications network 10 of the present invention will now be described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 2b. The communications network 10 is a data packet network having a client 11, a server 18, a plurality of customer edge routers 13, 17, a plurality of provider edge routers 13, 16, and a plurality of core routers 15. The client 11 sends data packets to the server 18 via path 12, which traverses a plurality of customer edge, provider edge and core routers. The skilled person will understand that other clients and servers may be connected to the customer edge routers, and other customer edge routers may be connected to the provider edge routers.
[0041]When the client 11 sends a data packet along path 12, it is initially forwarded to a first customer edge router 13, which forwards it on to the first provider edge router 14. The first provider edge router 14 forwards the data packet to a core router 15, which in turn forwards it on to a second provider edge router 16 (which may ...
second embodiment
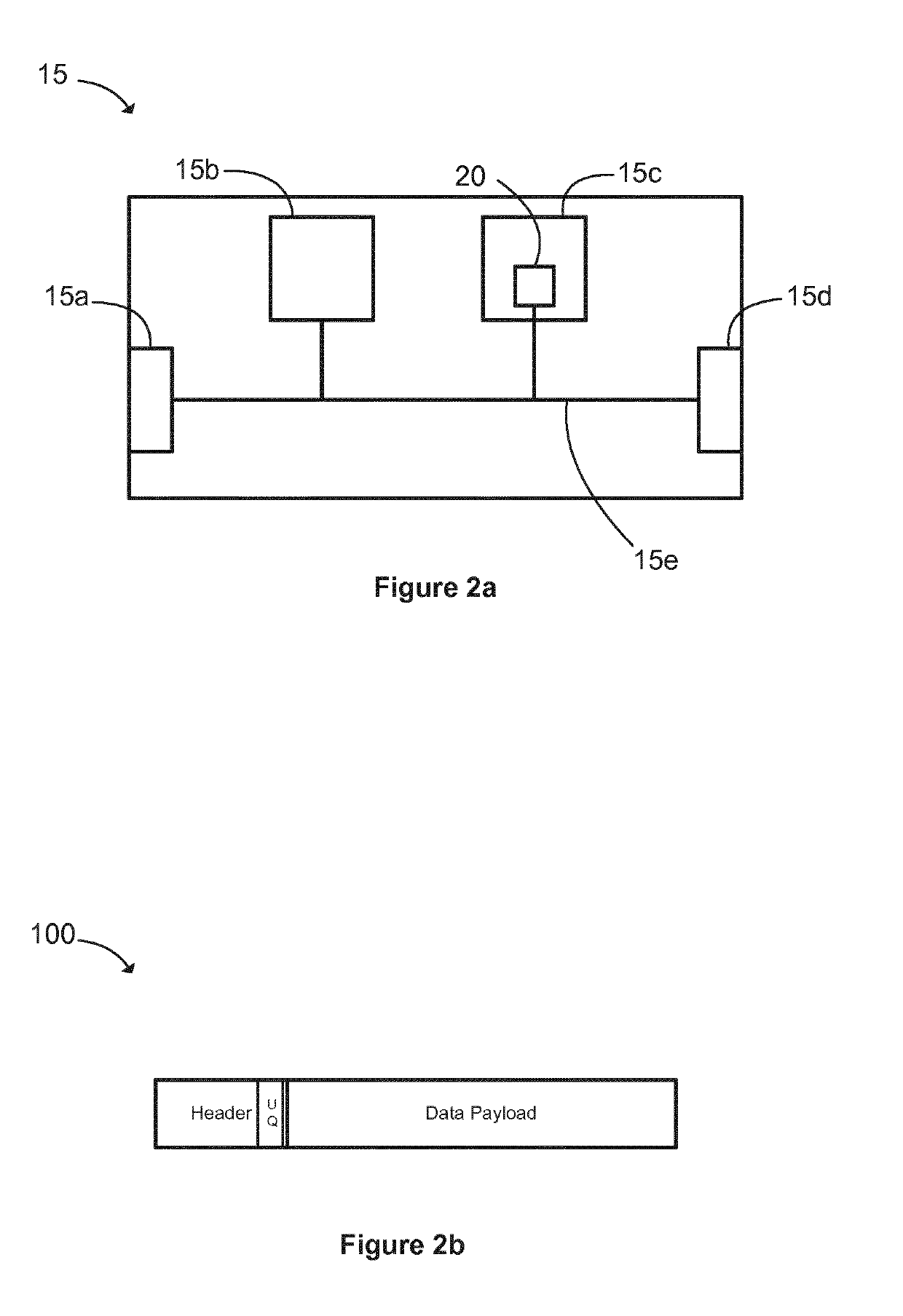
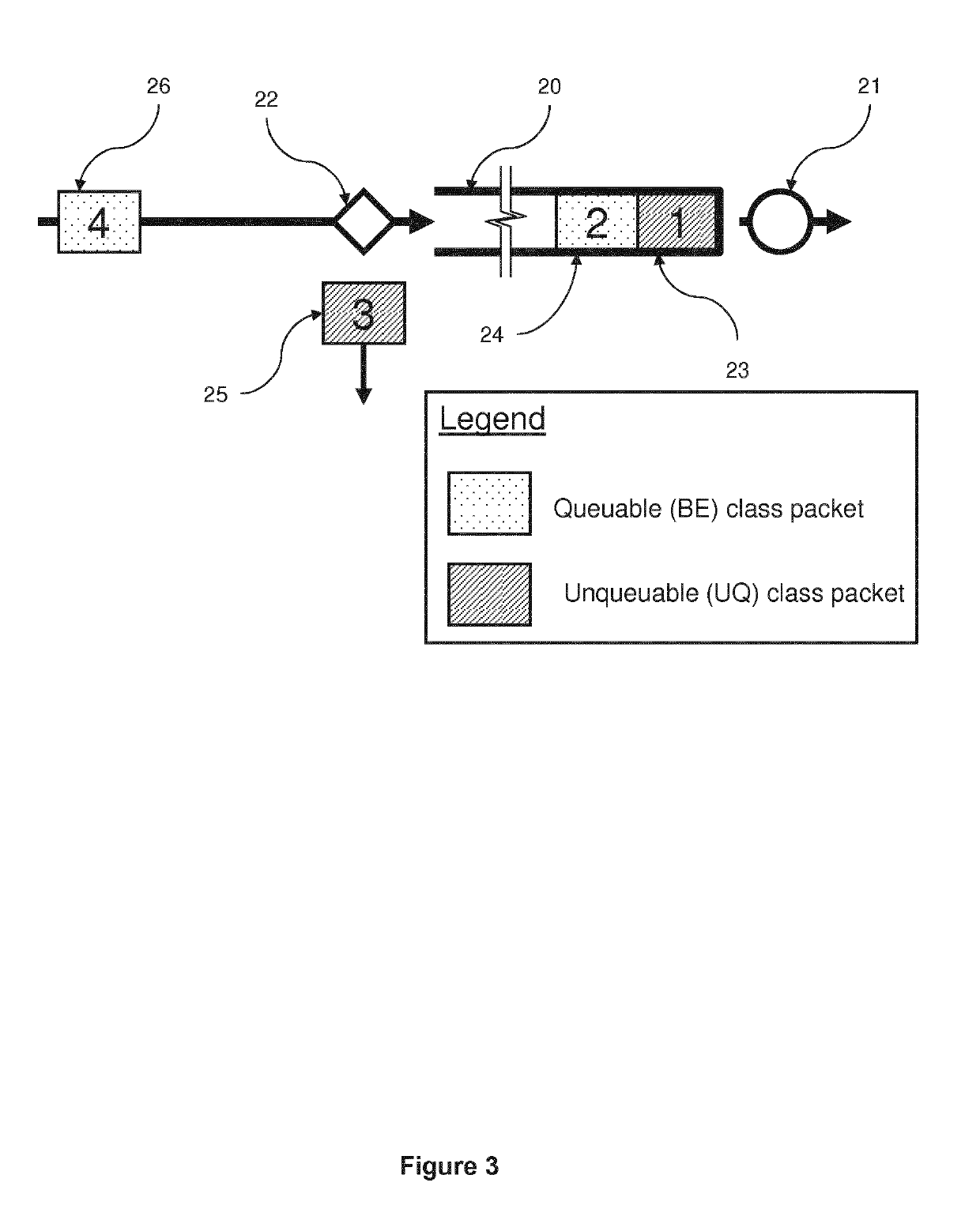
[0051]A flow diagram illustrating the management function 22 of the processor 15b is shown in FIG. 5b. In this embodiment, the steps of determining whether the buffer is empty and determining whether the packet is unqueuable are reversed.
[0052]The unqueuable class of service can be exploited by a sender / receiver node 11, 18 pair in order to determine an appropriate transfer rate to use in the communications network 10 (i.e. the maximum rate at which data can be transmitted without causing any packets to be dropped or causing packets on data flow sharing part of the same transmission path to be dropped). Before an embodiment of this algorithm is described, an overview of the conventional TCP Slow-Start process and its corresponding timing diagram will be presented with reference to FIG. 6.
[0053]FIG. 6 is a timing diagram in which two time axes extend downwardly from a client (e.g. client 11) and a server (e.g. server 18). Various data packets are represented by arrows extending betwe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com