Microkeratome cutting blade assembly and method for making the same
A microkeratome and cutting blade technology, applied in ophthalmic surgery and other directions, can solve problems such as difficulty, difficulty in adequately correcting patients' vision, and difficulty in detecting corneal flap thickness.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
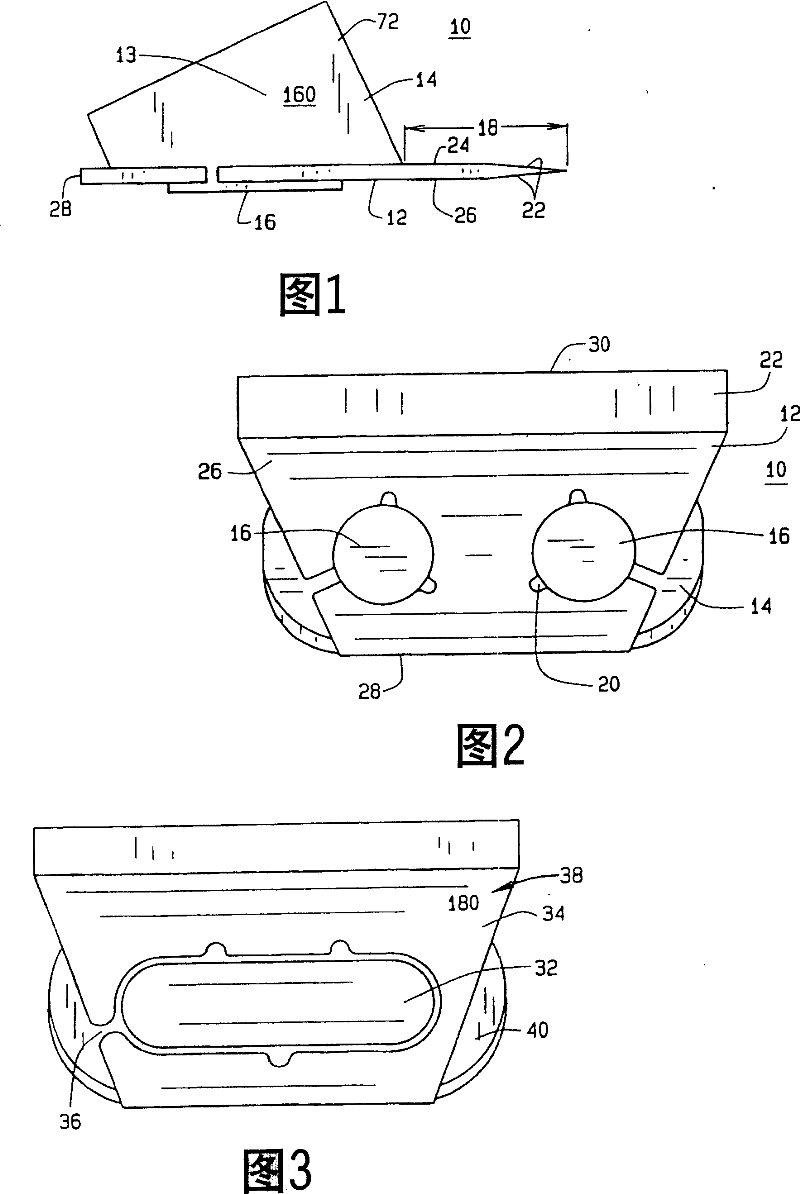
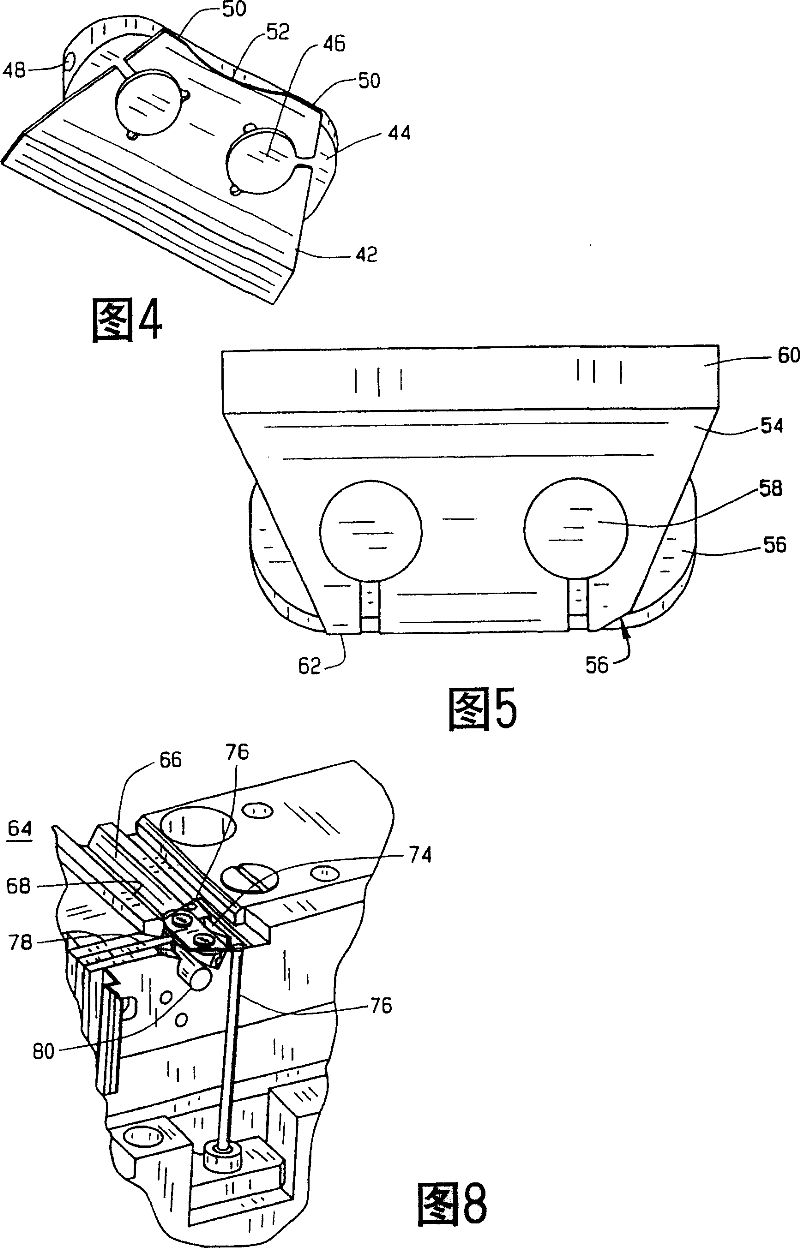
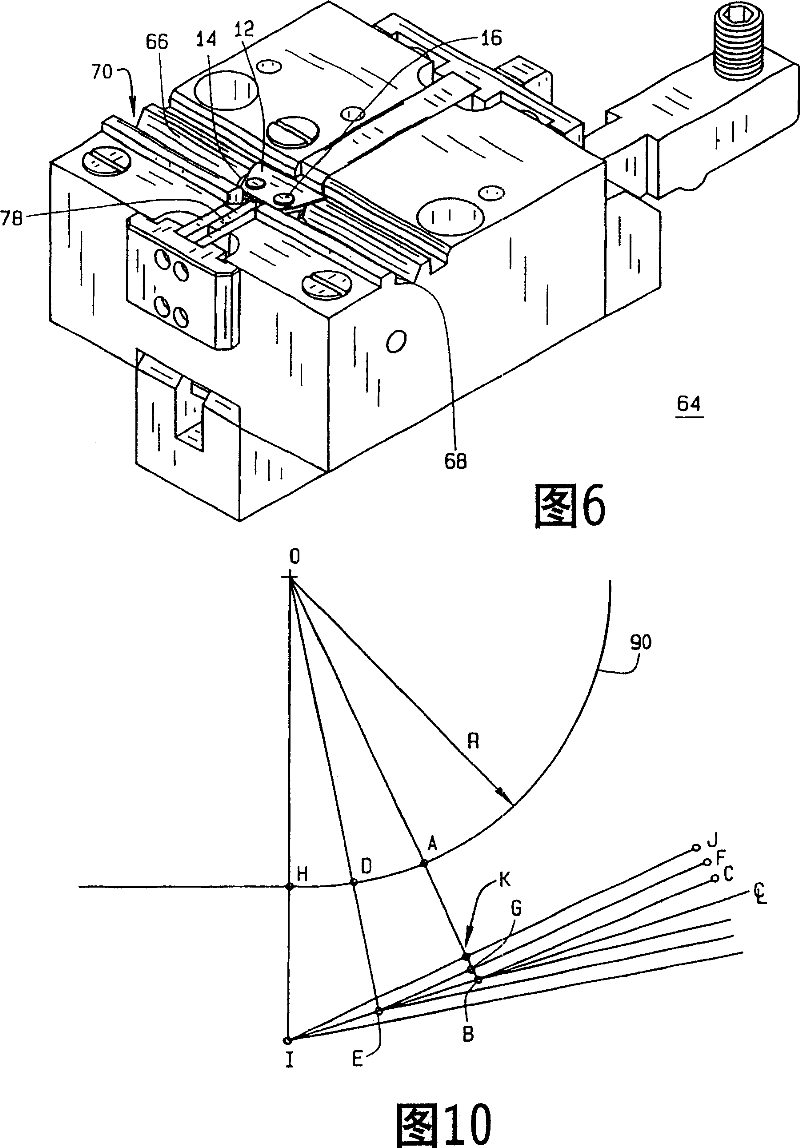
[0039] Figure 1 shows a microkeratome cutting blade assembly 10 of the present invention. The assembly 10 includes a cutting blade 12 and a blade holder 14 connected to the cutting blade 12 . Cartridge 14 is preferably attached to cutting blade 12 by post members 16 passing through apertures or through holes (not shown) in cutting blade 12 using known methods such as heat staking. However, other joining means such as cold staking, use of adhesives or other means are also possible. Also, the apertures need not be through holes as is known, but can be matching indentations and protrusions in the cartridge and blade. The difference between this assembly 10 and prior art assemblies is that the blade extension indicated by numeral 18 is controlled within a tolerance of at least 0.016 millimeters (six ten thousandths of an inch) to help and provide consistent, precise flap thickness. Such tight tolerance and blade extension have hitherto been unknown. For example, in the prior a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com