Friction control device for railway vehicle
A technology for railway vehicles and control devices, which is applied to railway car body parts, measuring devices, and mechanical devices, etc., can solve the problems of inability to change the coating amount of friction modifier and difficulty in friction state.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0085] The present invention will be described more specifically below with reference to examples.
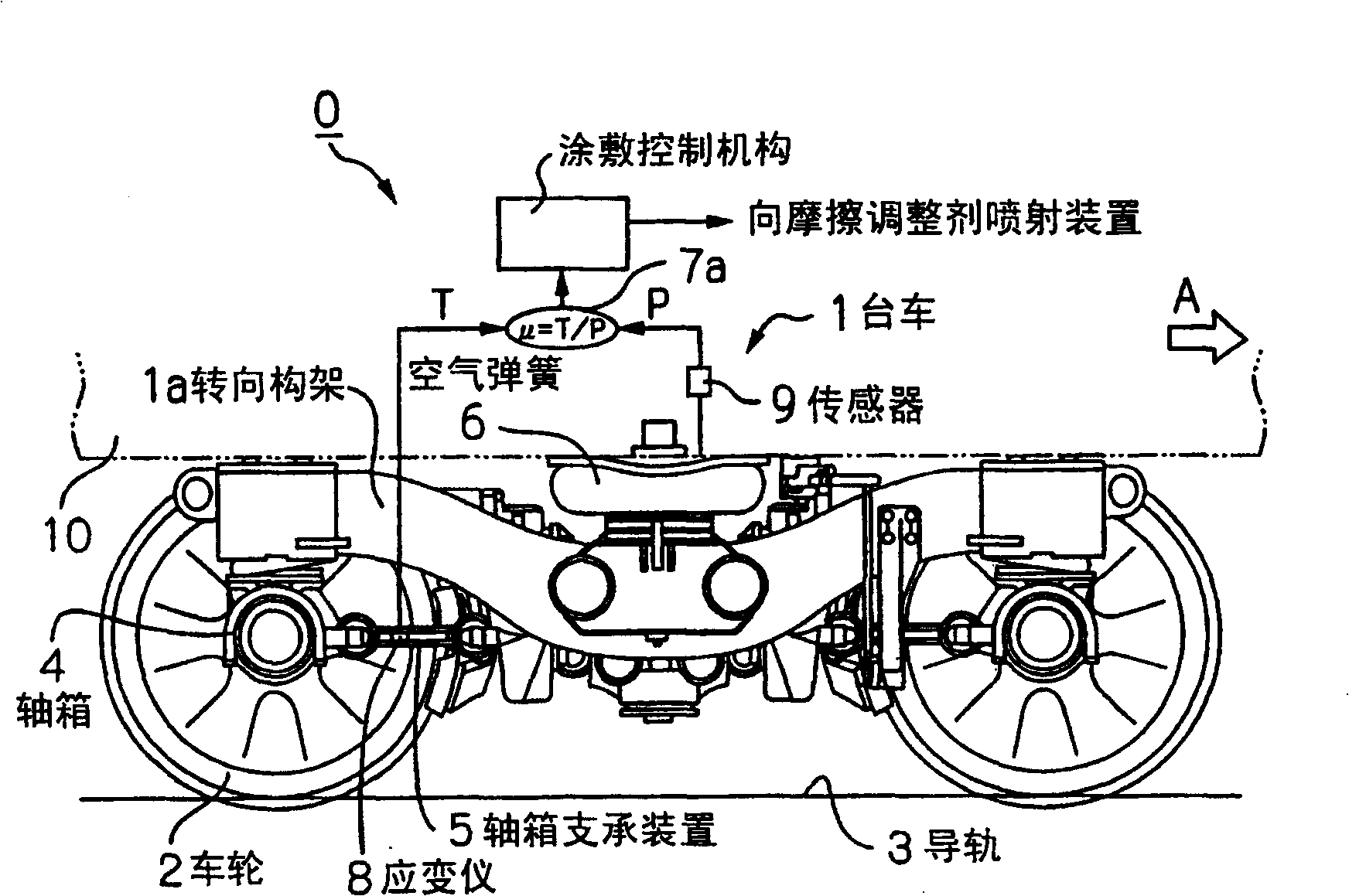
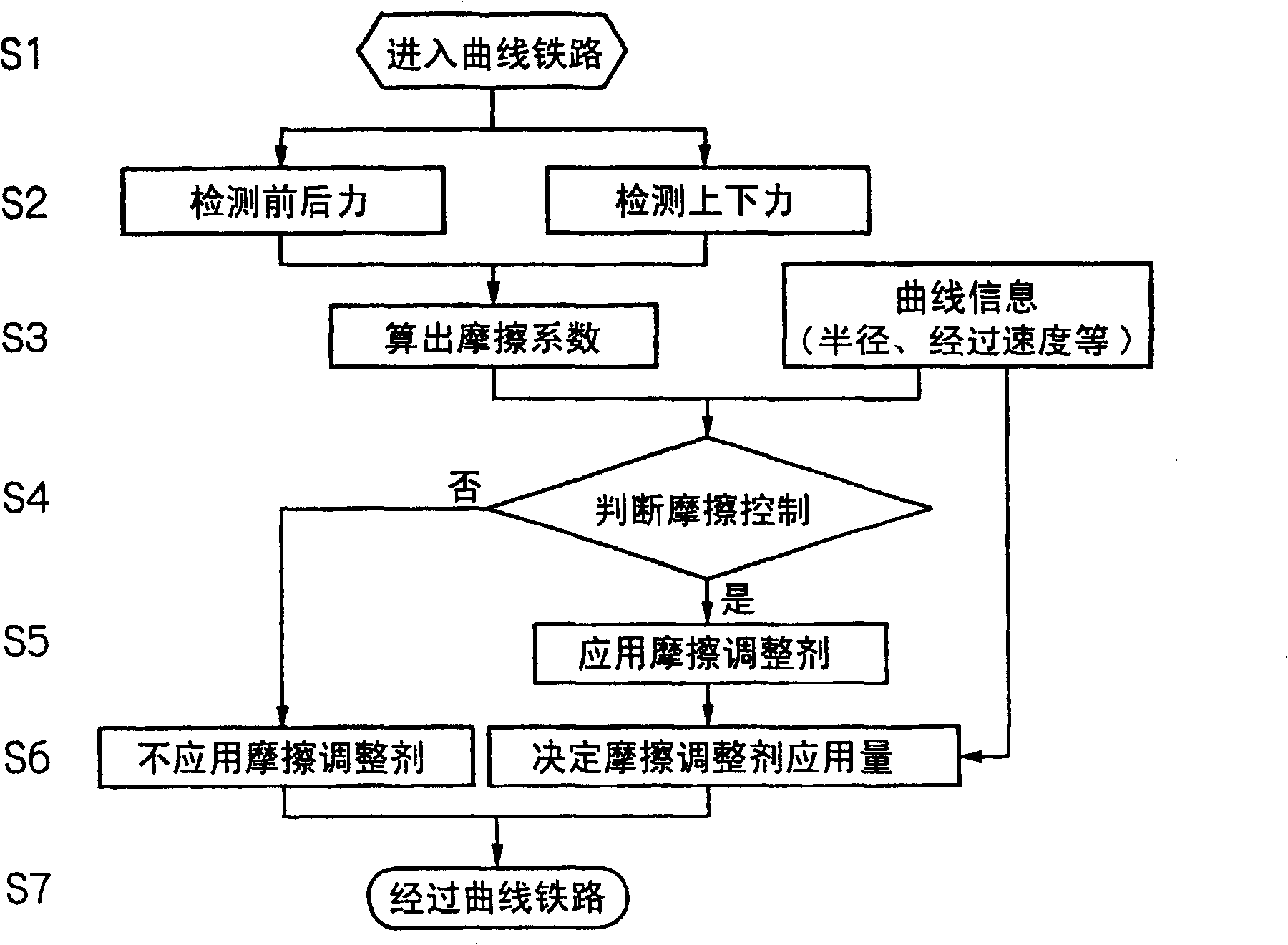
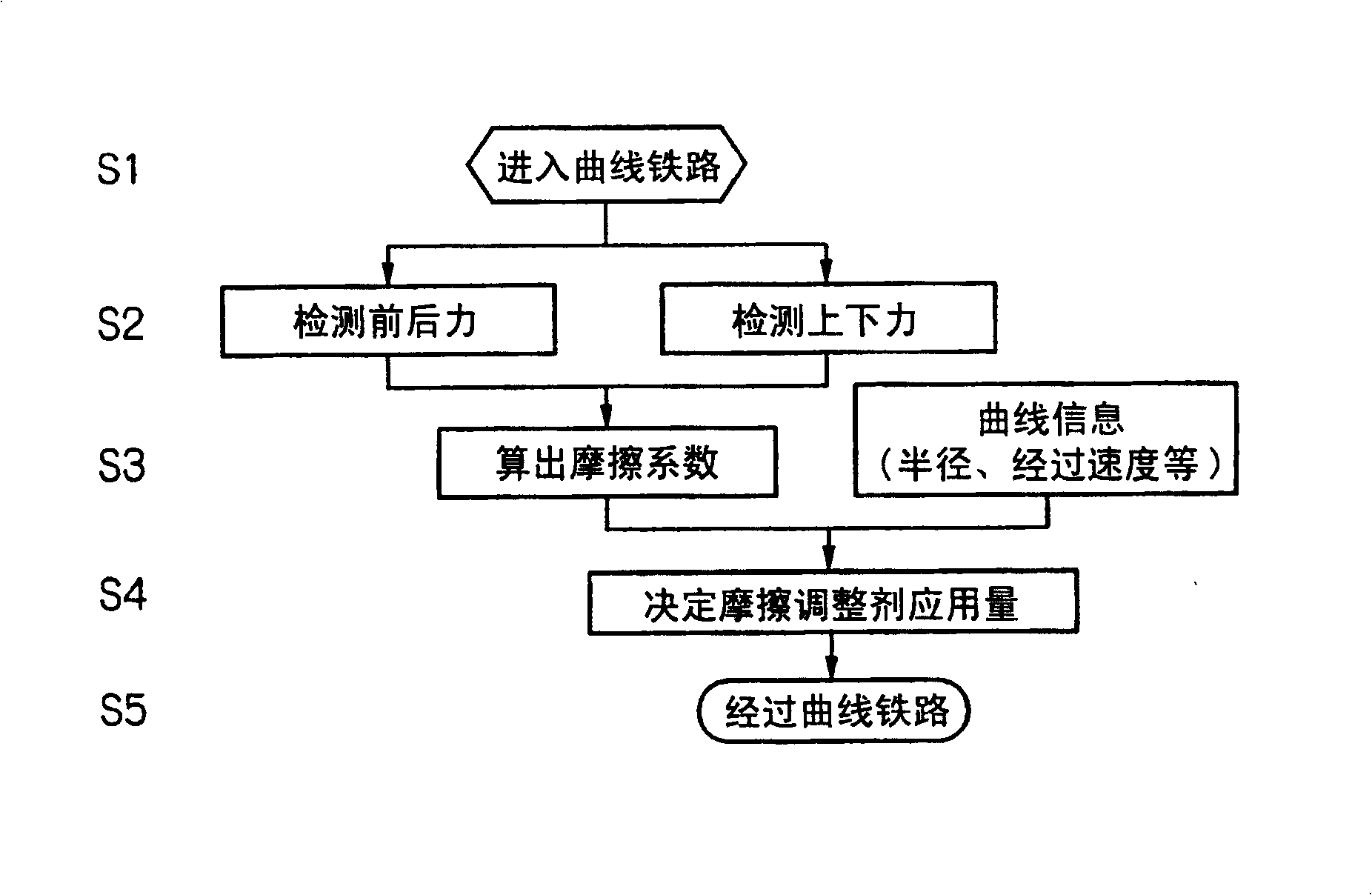
[0086] make it equipped with such figure 1 The railway vehicle of the railway vehicle trolley 1 of the friction control device 0 of the present invention shown travels on a curved guide rail 3 with a radius of 200 m or 130 m, respectively. Furthermore, based on the cases where the friction modifier between the wheels 2 and the curved guide rail 3 is controlled by spraying the friction modifier on the curved guide rail 3 and the case where the friction control is not performed, the effects on the wheels 2 located on the rear side in the direction of travel are analyzed. The relationship between the front and rear force T and the up and down force P and the friction coefficient μ.
[0087] In addition, the front-rear force T is obtained by attaching the strain gauge 8 to the axle box supporting devices 5, 5 of the left and right wheels 2, 2 on the rear side of the trolley 1 in t...
Embodiment 2
[0094] In general, it is known that when the coefficient of friction between the wheel and the curved guide becomes high, noise, vibration, and wear of the curved guide increase. Conventionally, the evaluation of the frictional state between the wheel and the curved guide rail is generally evaluated using the ratio (Q / P) of the wheel weight Q of the front axle located on the front side in the traveling direction to the lateral pressure P. That is, if the ratio (Q / P) exceeds 0.4, the noise, vibration, and wear will all become excessive. Therefore, in the present invention, the relationship between the above-mentioned friction coefficient μ and the ratio (Q / P) used as a control factor is analyzed. relationship between.
[0095] Figure 7 It is a graph showing the relationship between the ratio (Q / P) of the wheel load Q to the lateral pressure P of the front axle located on the front side in the traveling direction and the coefficient of friction (T / P) specified in the present i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com