Non-linear procedure fault identification method based on kernel principal component analysis contribution plot
A nuclear principal component analysis and fault identification technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, instruments, adaptive control, etc., can solve problems such as unknown nonlinear mapping functions and failure to directly identify fault variables
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
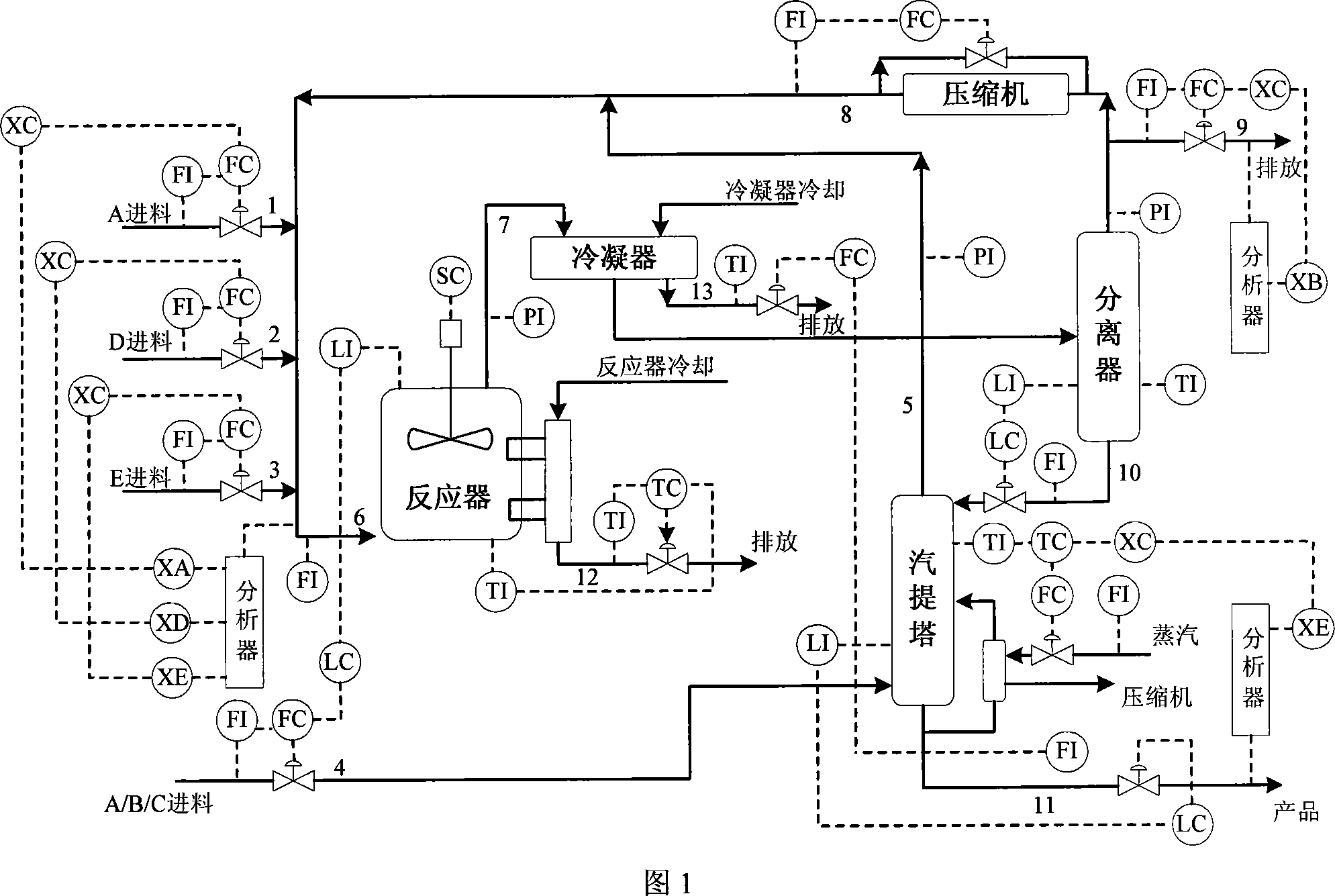
[0174] Tennessee-Eastman Process
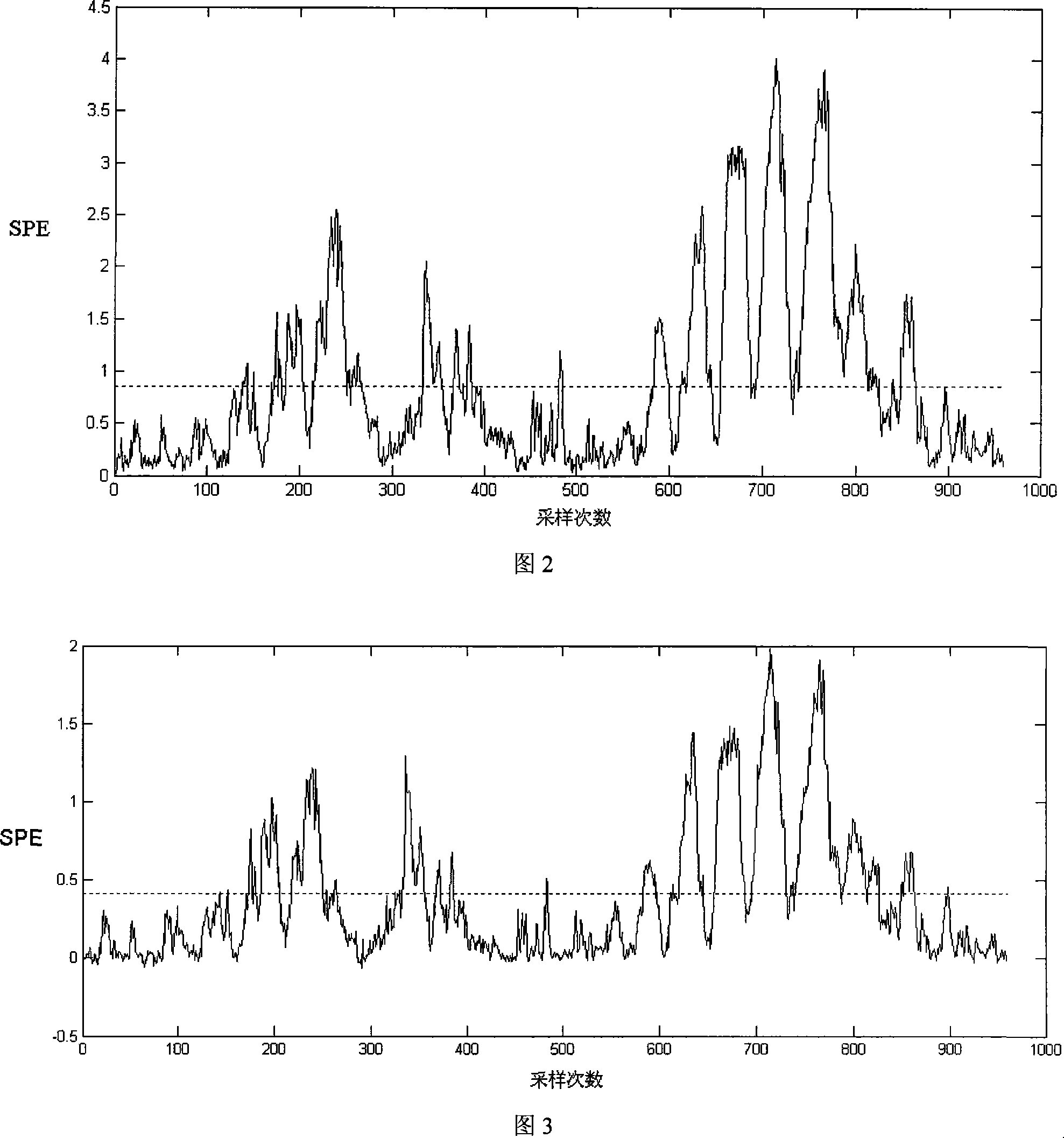
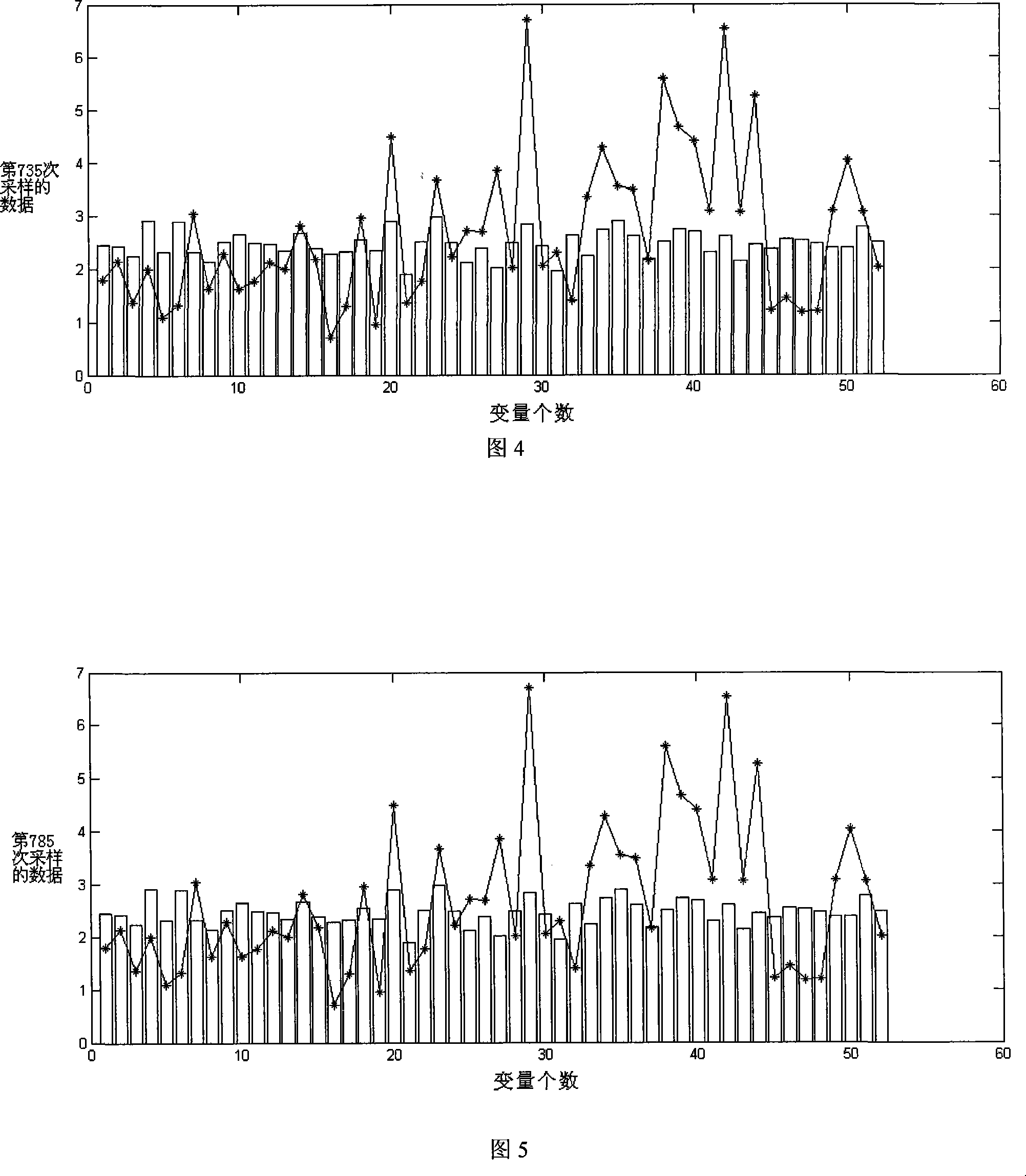
[0175] The method of the present invention is applied to the Tennessee-Eastman process simulation data and compared with the original KPCA detection result. The Tennessee-Eastman process is a complex and non-linear process. It was created by Eastman Chemical Company. Its purpose is to provide a real industrial process for evaluating process control and monitoring methods. The control structure is shown in Figure 1. The process includes five main units: reactor, condenser, compressor, separator, and stripper; moreover, it contains eight components: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H. The four reactants A, C, D and E are added to the reactor together with the inert component B to form products G and H, as well as by-product F. The Tennessee-Eastman process includes 22 continuous process measurements, 12 control variables, and 19 component measurements. As shown in Table 1. In addition to the stirring speed of the agitator of the reactor (because it was not...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com