Optimizing method for wireless sensor network node laying oriented to area monitoring
A wireless sensor and area monitoring technology, applied in the direction of data exchange network, transmission system, digital transmission system, etc., can solve problems such as inability to guarantee convergence, poor operability, and unusability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0065] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
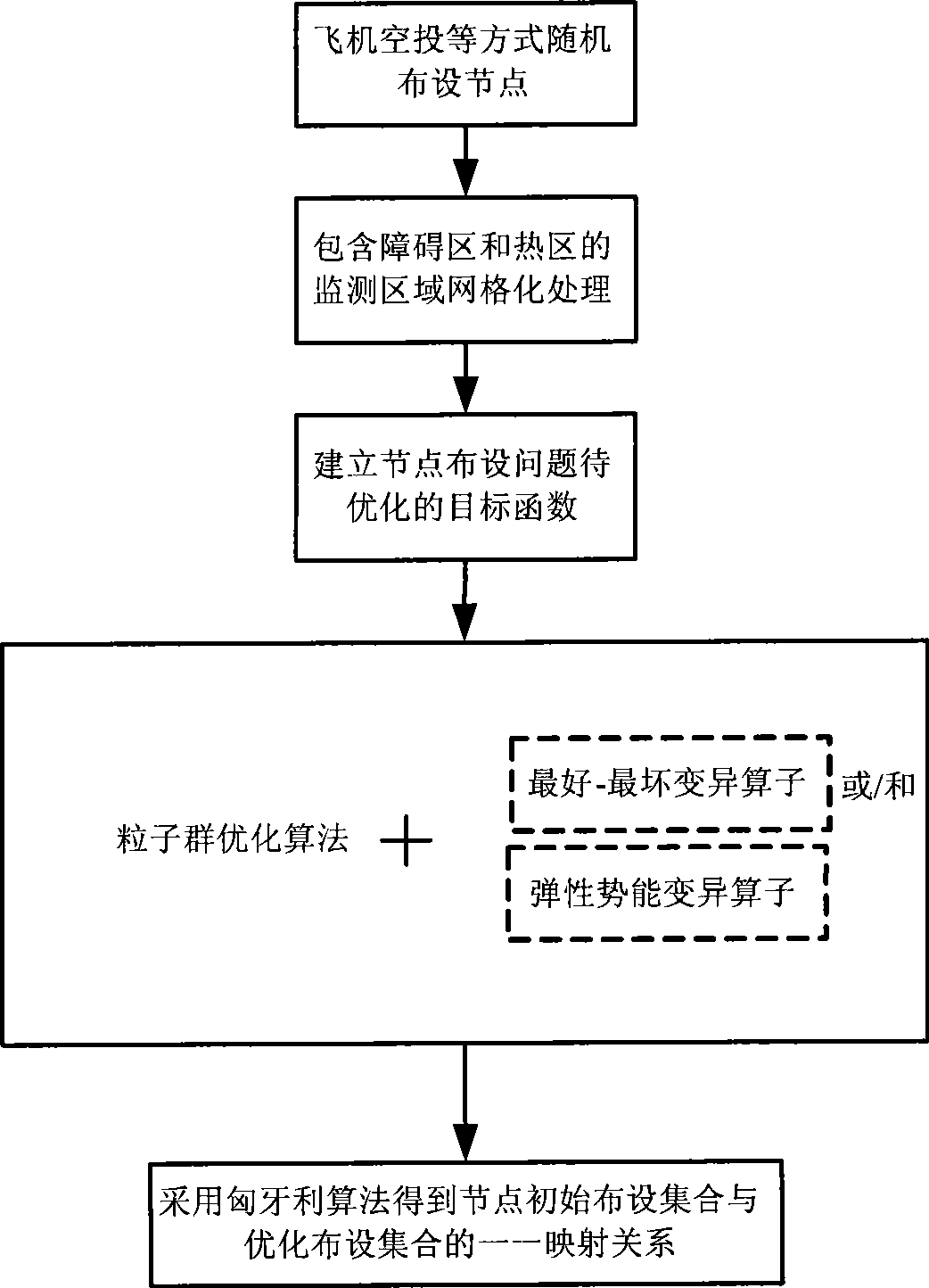
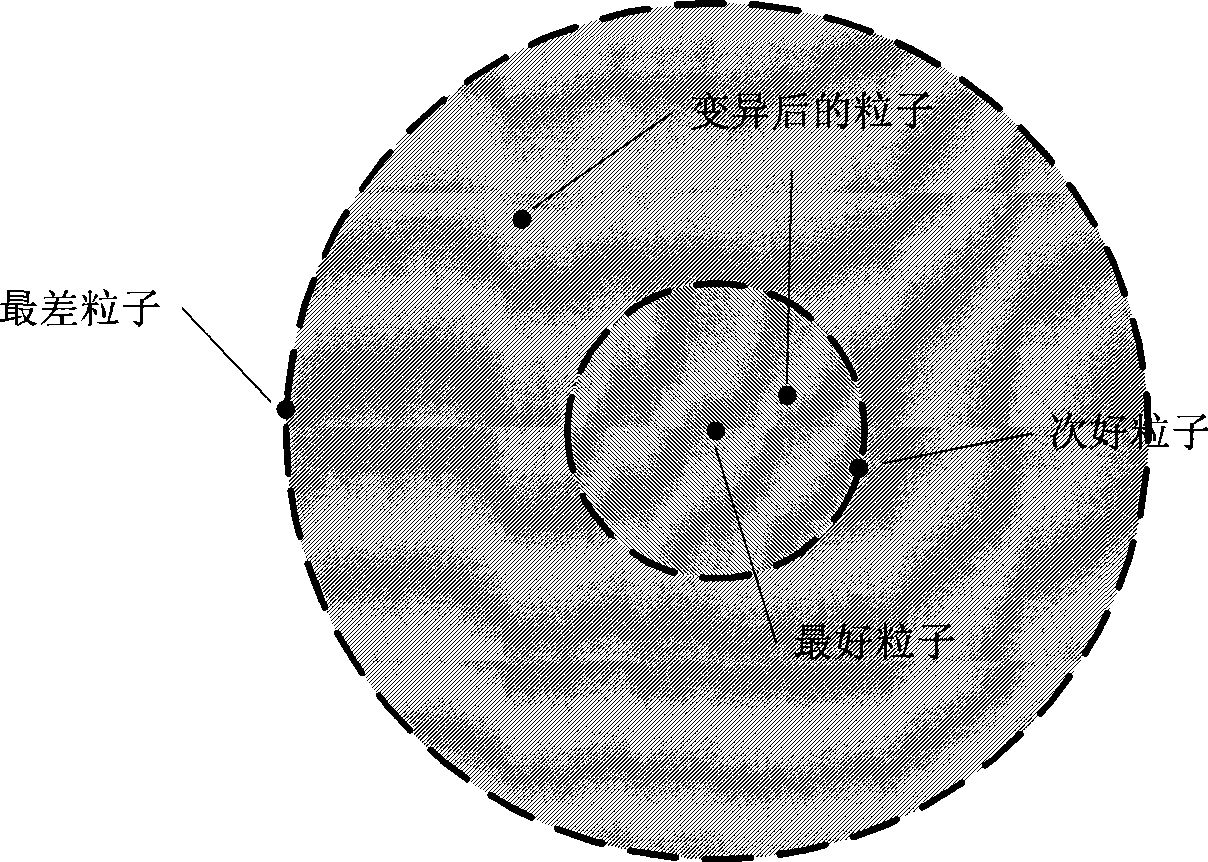
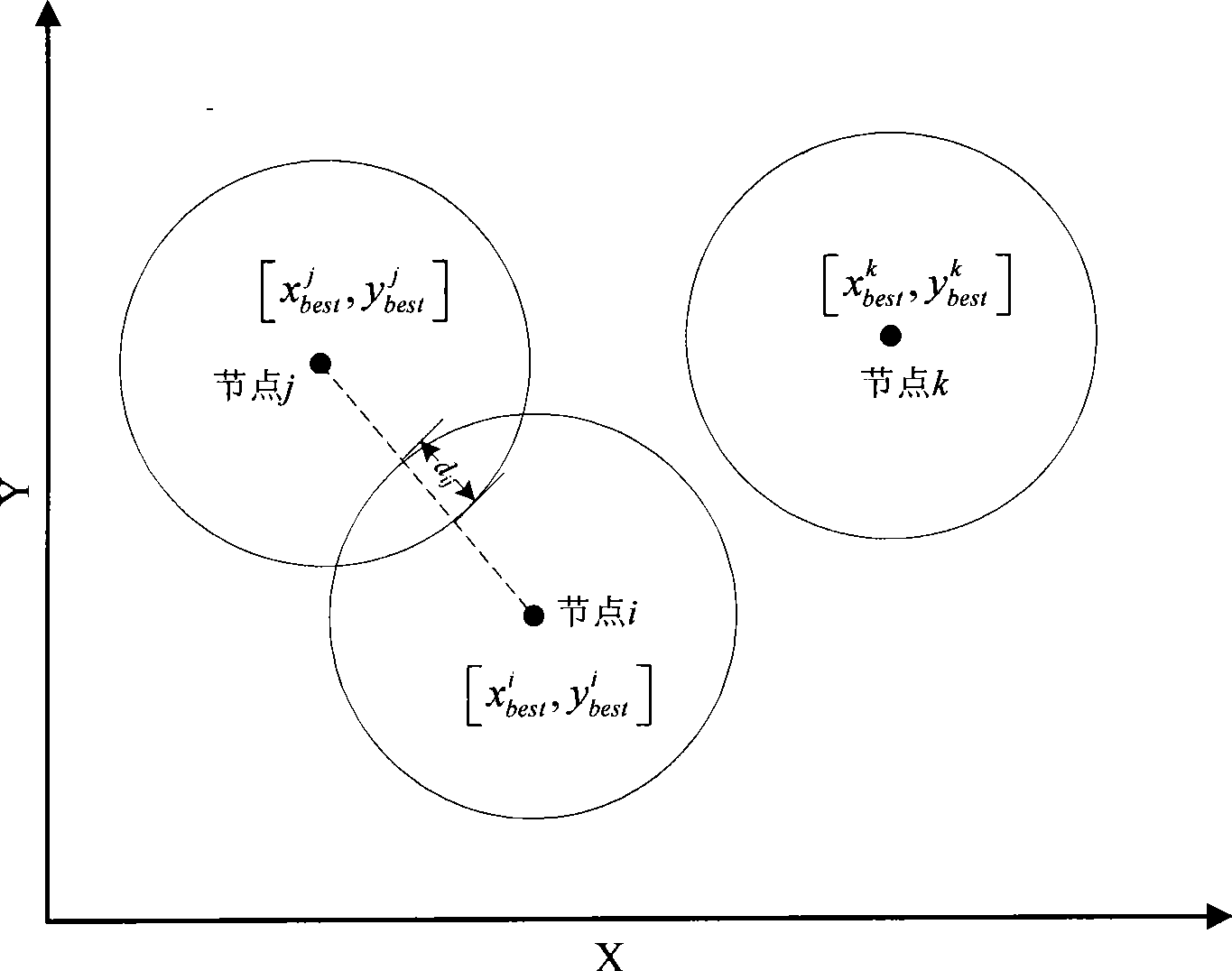
[0066] Assuming that the monitoring area is a rectangular area of 50m×50m, the monitoring area includes a 10m×10m hot area and a 10m×10m obstacle area. The detection range of each sensor is a disc whose center is itself and the radius is r=5m. This embodiment is applied to the deployment stage of wireless sensor network nodes for regional monitoring applications, such as figure 1 As shown, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0067] 1) Determine the number N of sensors to be deployed. Take ε=0.25 in this embodiment, by
[0068] N = A A s ( 1 + ϵ )
[0069] N ≈ 40 is obta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com