Encoding apparatus and decoding apparatus
A technology of an encoding device and a decoding device, applied in the fields of encoding devices and decoding devices, can solve problems such as reducing encoding efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0033] [Overview of Encoding Device and Decoding Device]
[0034] refer to Figures 1A to 1C The outline of the encoding device and the decoding device according to the first embodiment of the present invention will be described. Figures 1A to 1C Outlines of the encoding device and the decoding device according to the first embodiment are depicted.
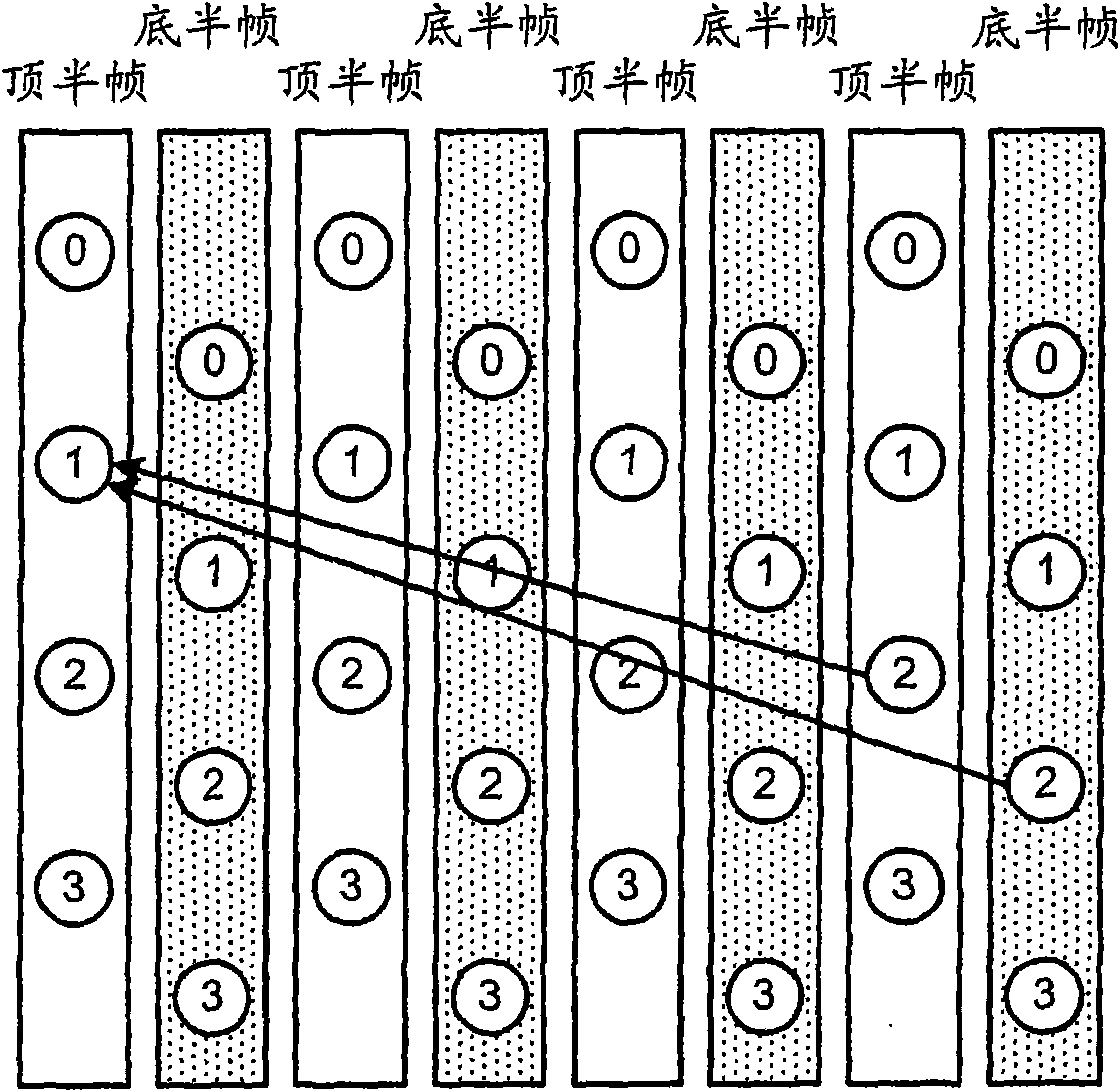
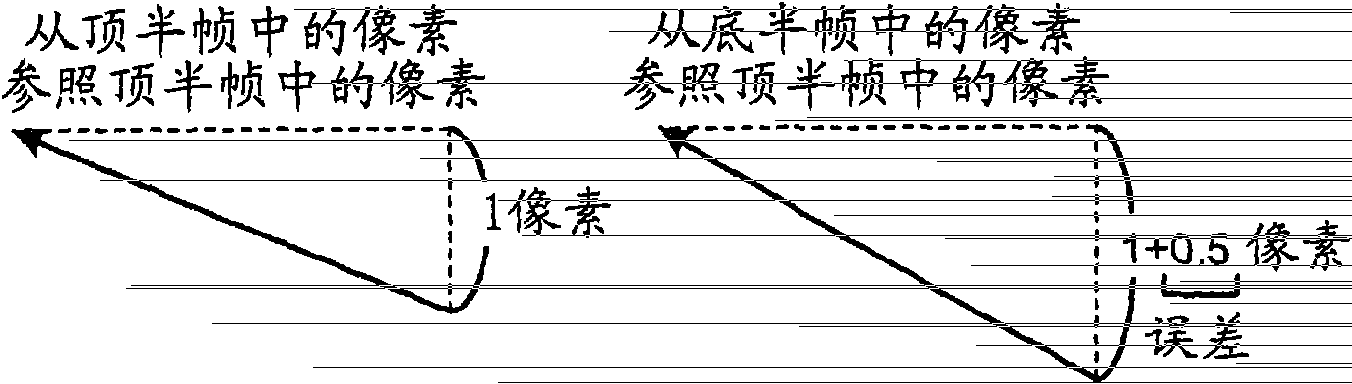
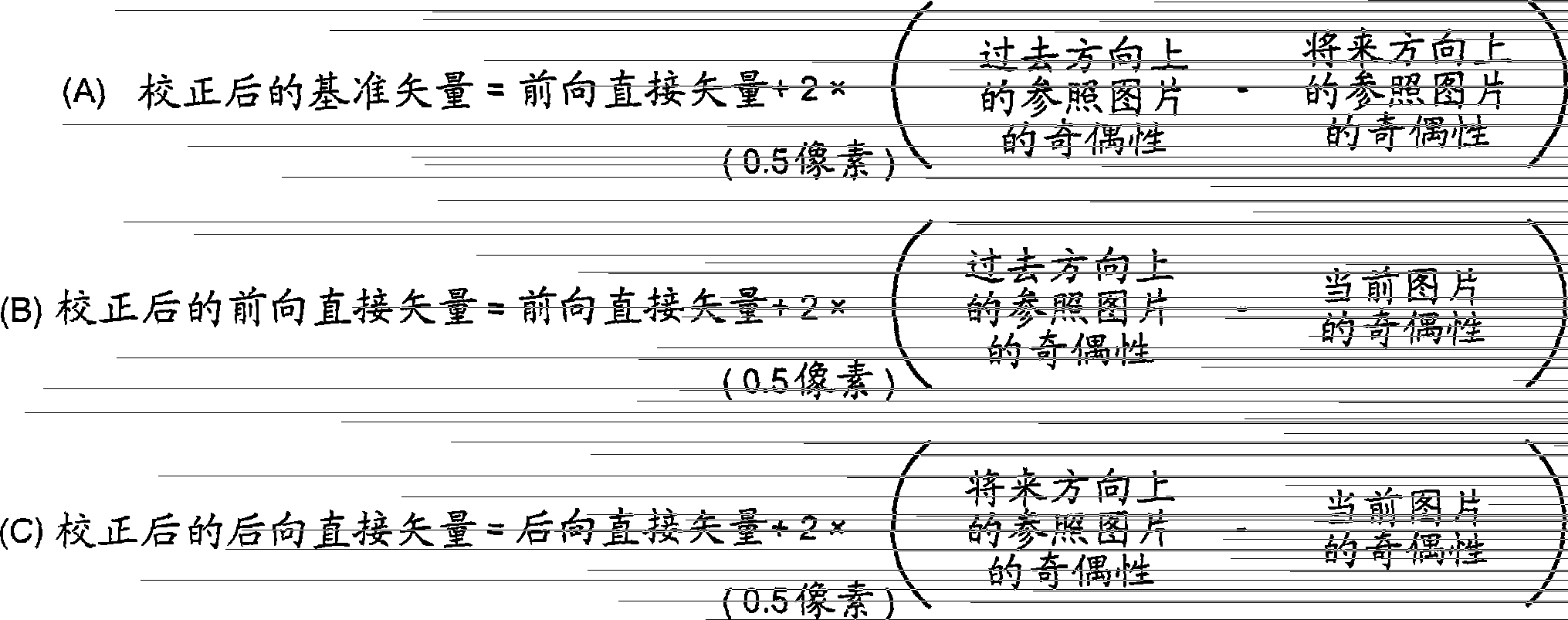
[0035] Such as Figure 1A As shown, if a picture with a field structure is coded in direct mode with reference to pixels with opposite parity, an error corresponding to this difference in parity occurs in the vector. For example, if Figure 1A As shown in , if pixel "2" in one top field (Top_field) refers to pixel "1" in another top field (Top_field), the vertical component of the vector is derived from "2" - "1" "one pixel" (see Figure 1B ), while the value of the vertical component of this vector is correctly calculated as "-4 (1 pixel / 0.25 pixel)".
[0036] For example, if Figure 1A As shown, if pixel "2" in a bottom ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com