Method for polishing semiconductor wafer
A semiconductor and wafer technology, applied in the field of double-sided polishing of semiconductor wafers, can solve problems such as unfavorable polishing machines and wafer fixing systems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
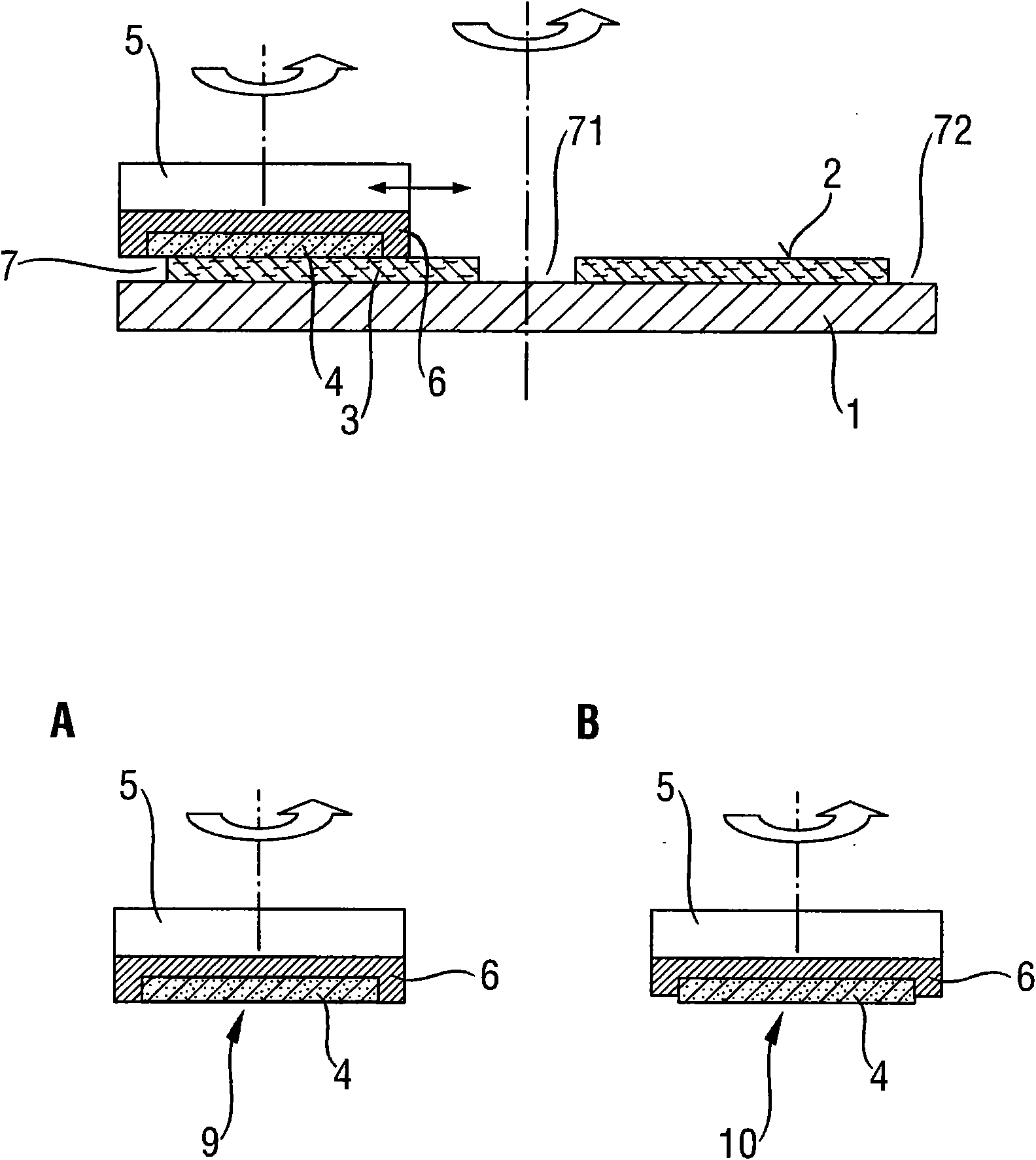
[0110] All polishing processes presented below were carried out using monolithic supports (no membrane supports, no multi-region supports) equipped with templates.
[0111] The carrier substrate itself may have a planar, convex or concave shape.
[0112] A 3-plate polisher such as AMAT Reflection from Applied Materials, Inc. was used as the polisher.
[0113] A. Polishing the backside of a semiconductor wafer with workpiece offset:
[0114] An FA polishing pad with an average abrasive grain size of 0.5 μm was used. Abrasive-free polishing compounds such as dilute K are available 2 CO 3 .
[0115] A second partial polishing step of the backside of the semiconductor wafer is optionally carried out on the same polishing pad, but with a supply of silica sol, eg Glanzox 3900, in order to adjust the roughness of the backside of the wafer in a targeted manner.
[0116] B. Polishing the front side of the semiconductor wafer in three steps:
[0117] B.1. Plate 1 equipped with a F...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com