A transmission method and terminal for uplink control signaling
A transmission method and a technology of control signaling, which is applied in the transmission of base stations and uplink control signaling, and in the field of terminals, which can solve the problems of system throughput performance degradation and the inability to judge whether UE has correctly received one or correct reception, so as to achieve guaranteed performance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
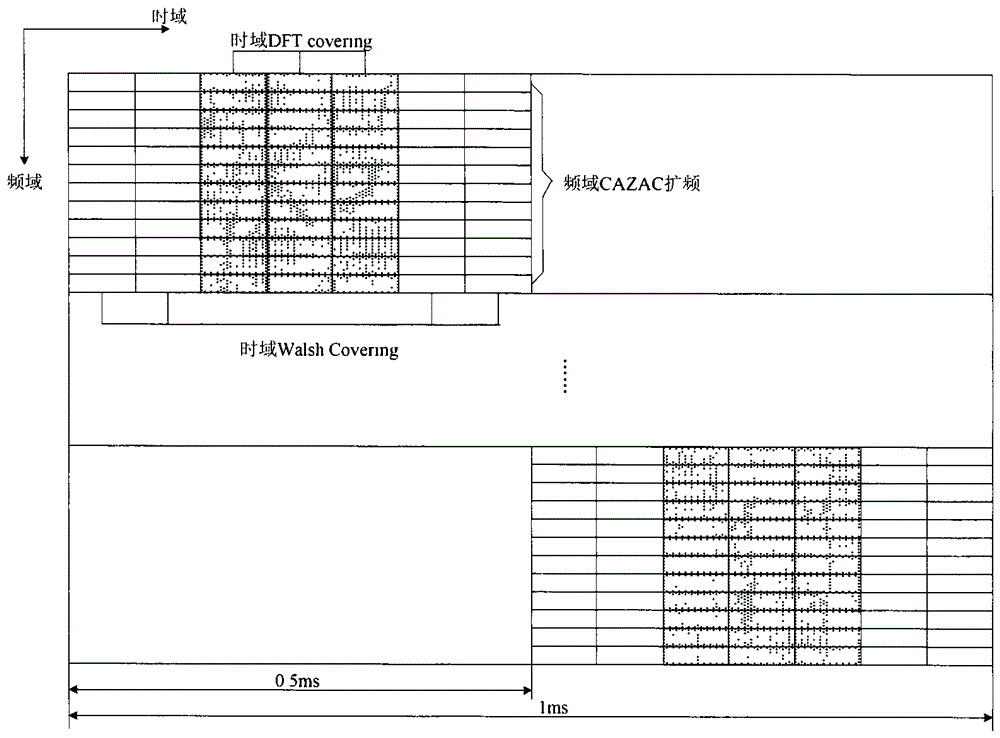
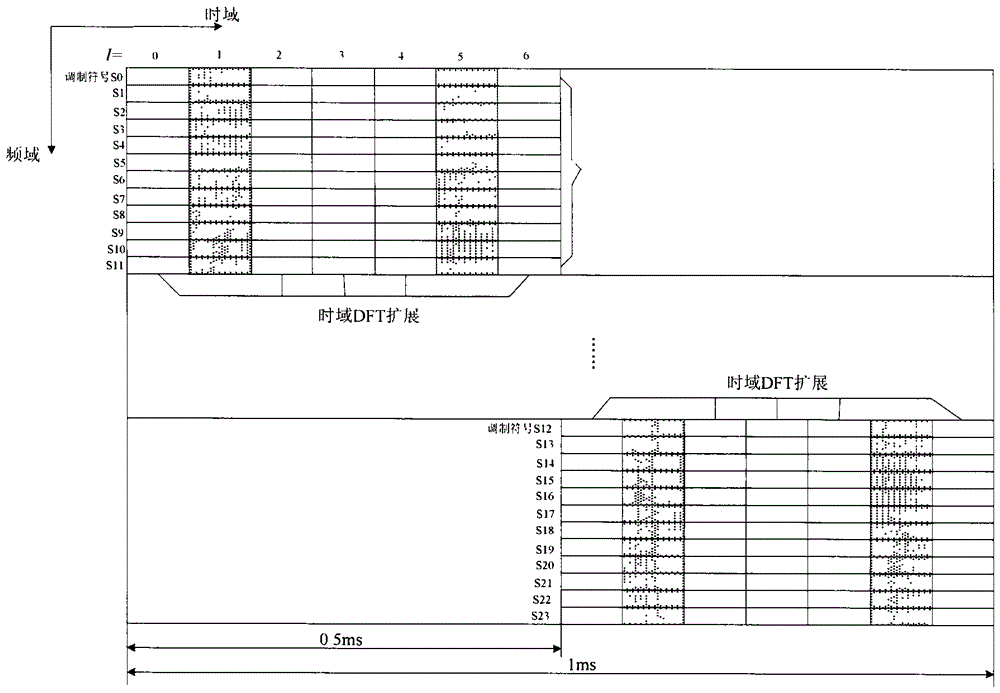
[0052] In a time division duplex (TDD) system, the mode in which the terminal feeds back the ACK / NACK response message is the channel selection mode, and the number of serving cells configured by the terminal is 2. When the ACK / NACK response message and the scheduling request SR are incorrect, only the ACK / NACK response message and SR corresponding to the primary cell are fed back, wherein the ACK / NACK response message corresponding to the primary cell is mapped to 2 according to the binding mode of the channel selection mode bits, M=2;
[0053] The specific binding methods are shown in Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4; HARQ-ACK(0), HARQ-ACK(1), HARQ-ACK(2), HARQ-ACK(3) represent N physical downlink shared channels The correct / wrong ACK / NACK response message of PDSCH is the response message after space binding; DTX indicates that there is no corresponding response message, and any indicates ACK(A) / NACK(N) / DTX(D);
[0054] Table 2 Mapping relationship when the number of downlink sub...
Embodiment 2
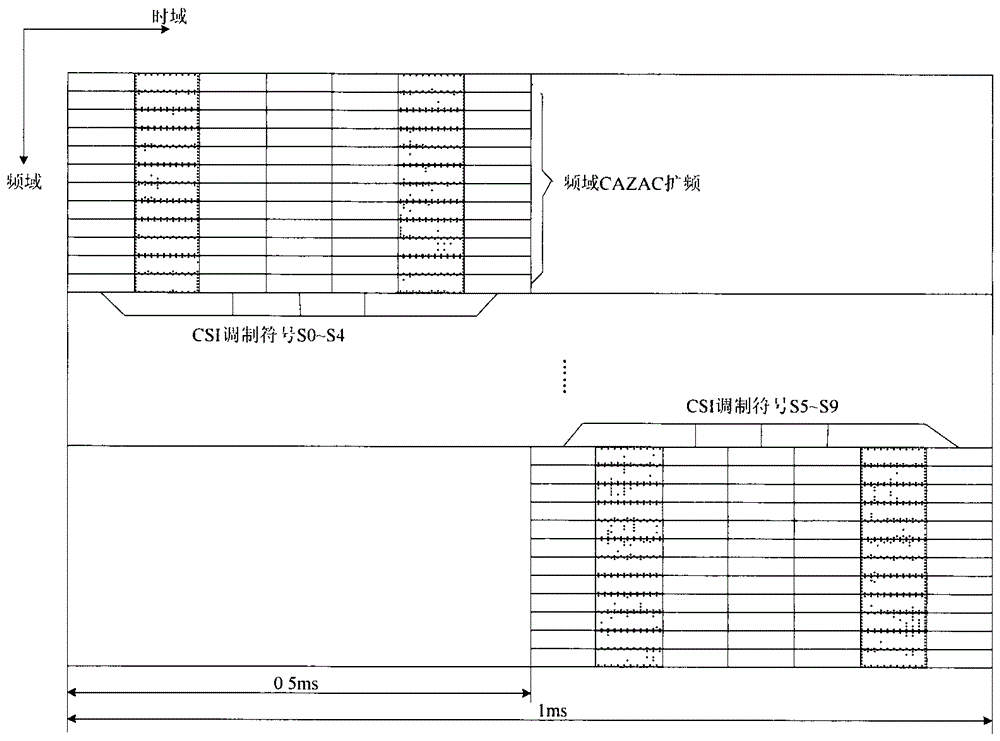
[0069] In a time division duplex (TDD) system, the mode in which the terminal feeds back ACK / NACK response messages is the channel selection mode, and the number of serving cells configured by the terminal is 2. When the correct / When the ACK / NACK response message and the channel state information CSI are wrong, the ACK / NACK response message is mapped to 4 bits according to the binding method of the channel selection mode, and each serving cell corresponds to 2 bits, and the mapped 4-bit information is transmitted and CSI information, where M=4;
[0070] Assume that the number of bits that can be transmitted by the physical uplink control channel for transmitting CSI is X, and X can be 11 or 13;
[0071] When the cyclic prefix is a standard cyclic prefix, the 2-bit information corresponding to the primary cell is sent on the second reference signal of each time slot in the physical uplink control channel format 2b after QPSK modulation, and the 2-bit information correspondin...
Embodiment 3
[0075] In a time division duplex (TDD) system, the mode in which the terminal feeds back ACK / NACK response messages is the channel selection mode, and the number of serving cells configured by the terminal is 2. When the correct / When the ACK / NACK response message and the channel state information CSI are wrong, the ACK / NACK response message is mapped to 4 bits according to the binding method of the channel selection mode, and each serving cell corresponds to 2 bits, and the mapped 4-bit information is transmitted and CSI information, where M=4;
[0076] Assume that the number of bits that can be transmitted by the physical uplink control channel for transmitting CSI is X, and X can be 11 or 13;
[0077] When the cyclic prefix is a standard cyclic prefix, the 2-bit information corresponding to the primary cell is mapped to the last two bit positions of the X bits, and the 2-bit information corresponding to the secondary cell is mapped to the fourth last bit of the X bits bi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com