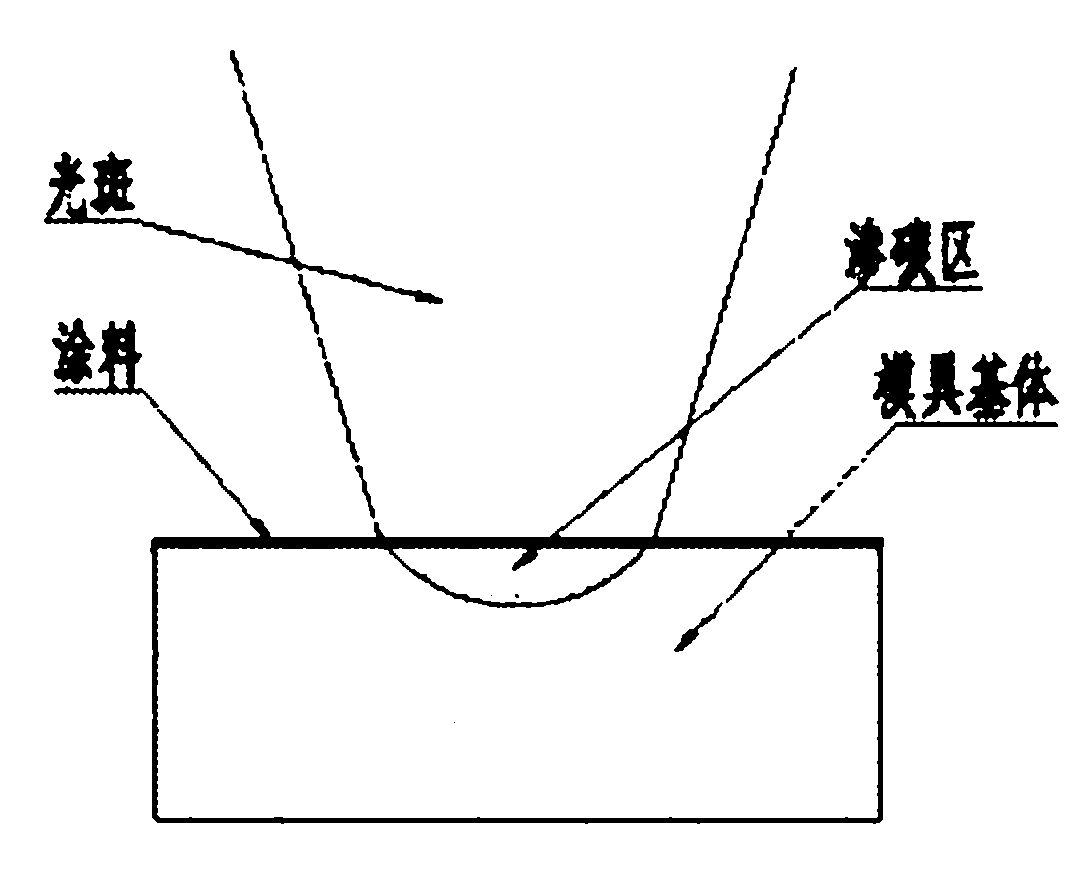
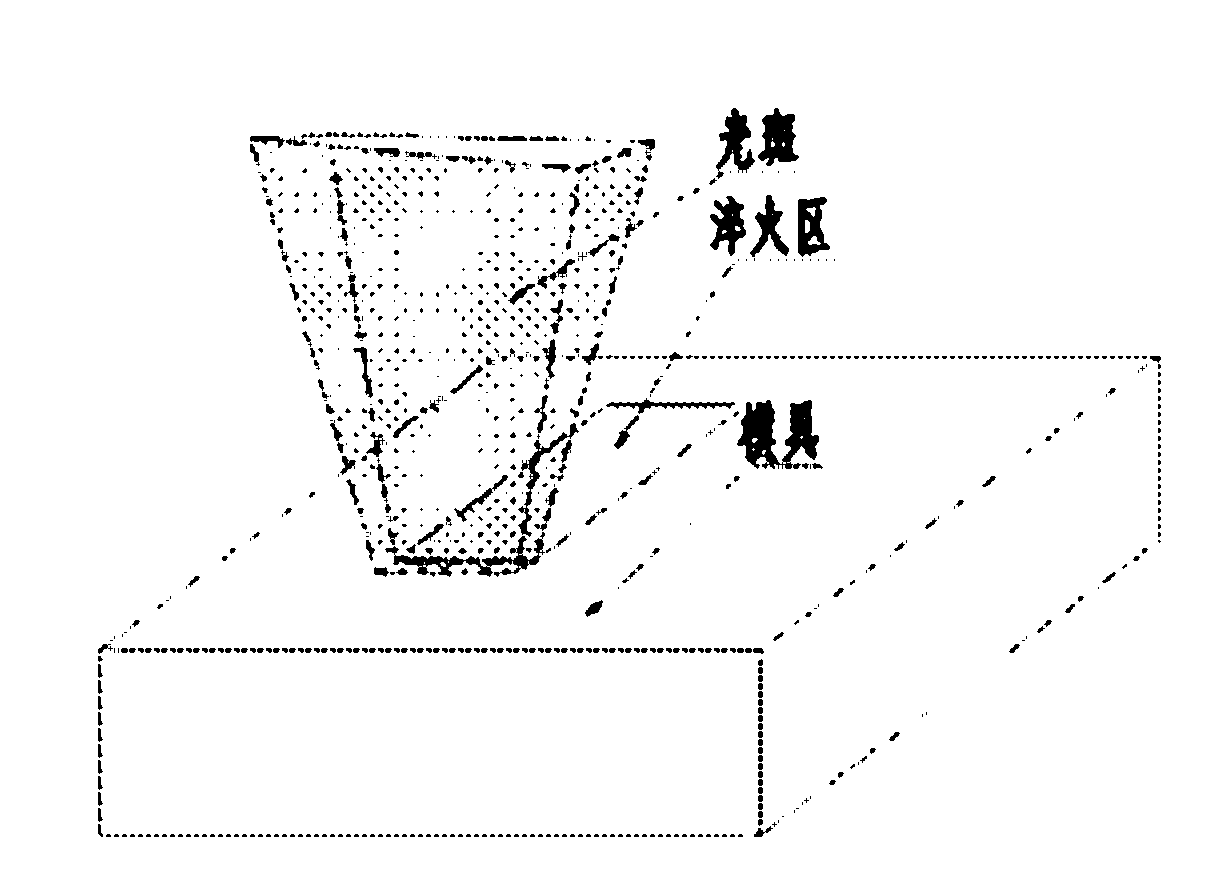
Method for treating mold surface by using laser hardening
A mold surface and laser quenching technology, which is applied in the field of mold surface surface quenching, can solve problems such as surface decarburization, large molds that cannot be strengthened, and low-carbon content materials that cannot be strengthened.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Step 1: Spray the water-based carbon-containing paint evenly on the cleaned mold surface with a spray thickness of 0.1-0.2mm. The water-based carbon-containing coating is composed of the following components according to the mass percentage: C and carbide: 5%, light-absorbing coating: 10%, binder: 85%, and the light-absorbing coating is composed of the following components according to the mass percentage: W : 20%, Cr: 20%, Mo: 5%, Co: 10%, and the balance is manganese. C and carbides are composed of carbon black and carbides, carbides account for 15% of C and carbides, carbides are mixed with tungsten carbide and silicon carbide at a mass ratio of 2:3, and the binder is composed of 1:0.05 alcohol mixed with paint flakes;
[0039] Set the laser power to 0.5KW, the scanning speed to 100mm / min, and the laser bandwidth to 2mm, and perform laser infiltration treatment;
[0040] Step 2: Set the laser power to 1KW, the scanning speed to 300mm / min, and the laser bandwidth to...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Step 1: Spray the water-based carbon-containing paint evenly on the cleaned mold surface with a spray thickness of 0.1-0.2 mm. The water-based carbon-containing coating is composed of the following components according to the mass percentage: C and carbide: 25%, light-absorbing coating: 20%, binder: 55%, and the light-absorbing coating is composed of the following components according to the mass percentage: W : 30%, Cr: 30%, Mo: 10%, Co: 20%, and the balance is boron. C and carbides are composed of carbon black and carbides, carbides account for 30% of C and carbides, carbides are mixed with tungsten carbide and silicon carbide at a mass ratio of 2:3, and the binder is composed of 1:0.05 alcohol mixed with paint flakes;
[0043] Set the laser power to 4KW, the scanning speed to 500mm / min, and the laser bandwidth to 40mm for laser infiltration treatment;
[0044] Step 2: Set the laser power to 5KW, the scanning speed to 2000mm / min, and the laser bandwidth to 40mm. Perfo...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Step 1: Spray the water-based carbon-containing paint evenly on the cleaned mold surface with a spray thickness of 0.1-0.2 mm. The water-based carbon-containing coating is composed of the following components according to the mass percentage: C and carbide: 15%, light-absorbing coating: 15%, binder: 70%, and the light-absorbing coating is composed of the following components according to the mass percentage: W : 25%, Cr: 25%, Mo: 8%, Co: 15%, and the balance is boron. C and carbides are composed of carbon black and carbides, carbides account for 20% of C and carbides, carbides are mixed with tungsten carbide and silicon carbide at a mass ratio of 2:3, and the binder is composed of 1:0.05 alcohol mixed with paint flakes;
[0047] Set the laser power to 2KW, the scanning speed to 300mm / min, and the laser bandwidth to 10mm, and perform laser infiltration treatment;
[0048] Step 2: Set the laser power to 3KW, the scanning speed to 1000mm / min, and the laser bandwidth to 1...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap