System and method for runtime determination of camera miscalibration
A calibration error and camera technology, applied in the field of vision systems, can solve the problems of 3D vision system deterioration, the risk of false rejection/false acceptance of camera calibration, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] A. Systematic review and calibration
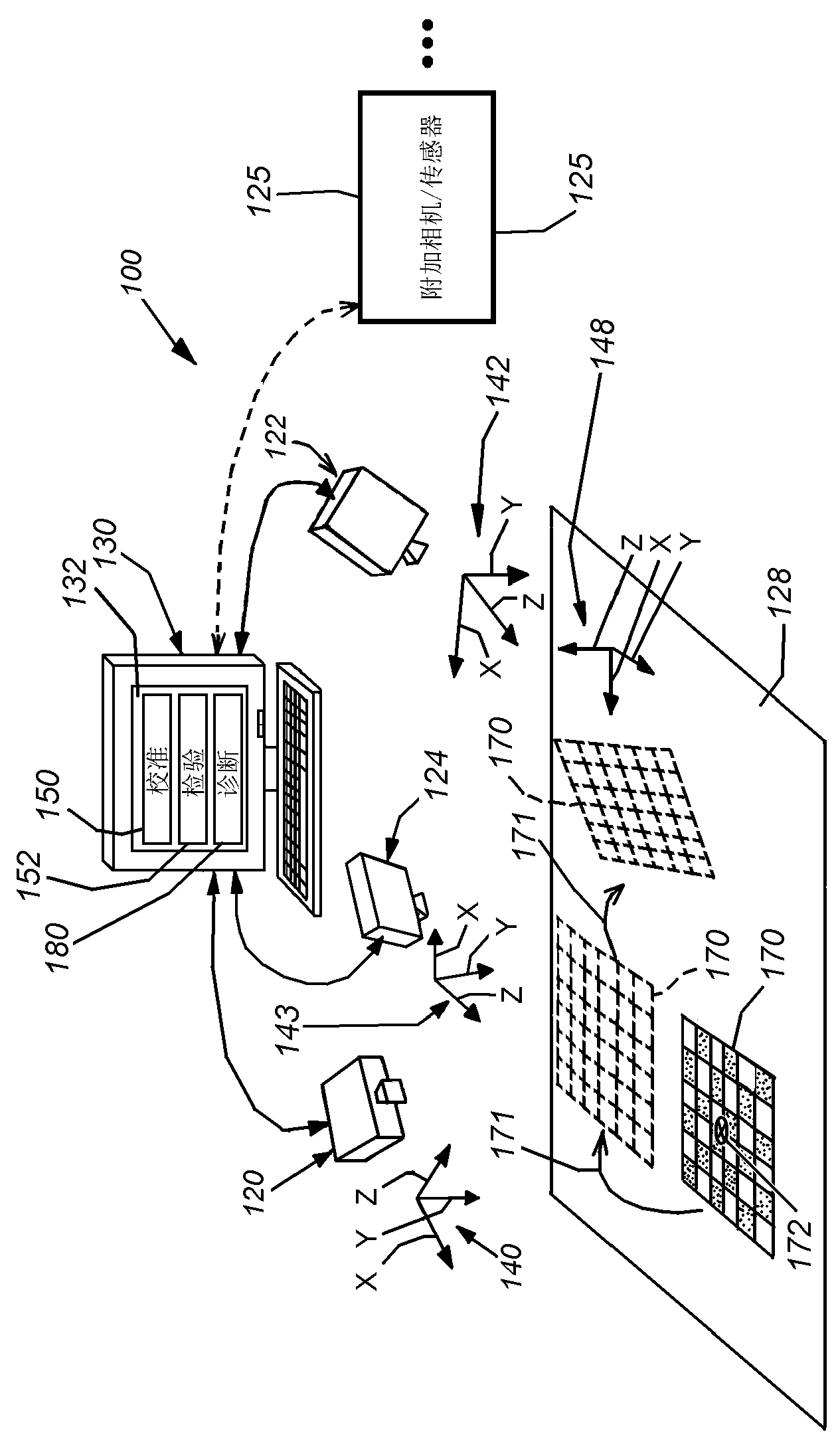
[0022] figure 1 A typical mechanism for a vision system 100 is described to determine the two-dimensional (2D) or three-dimensional (3D) calibration or pose of a viewed scene, which may include one or more A runtime object that controls or assists other operations to inspect, align, and actuate. The system can be calibrated (and the calibration can be followed by self-diagnostics) according to an illustrative embodiment of the present invention.
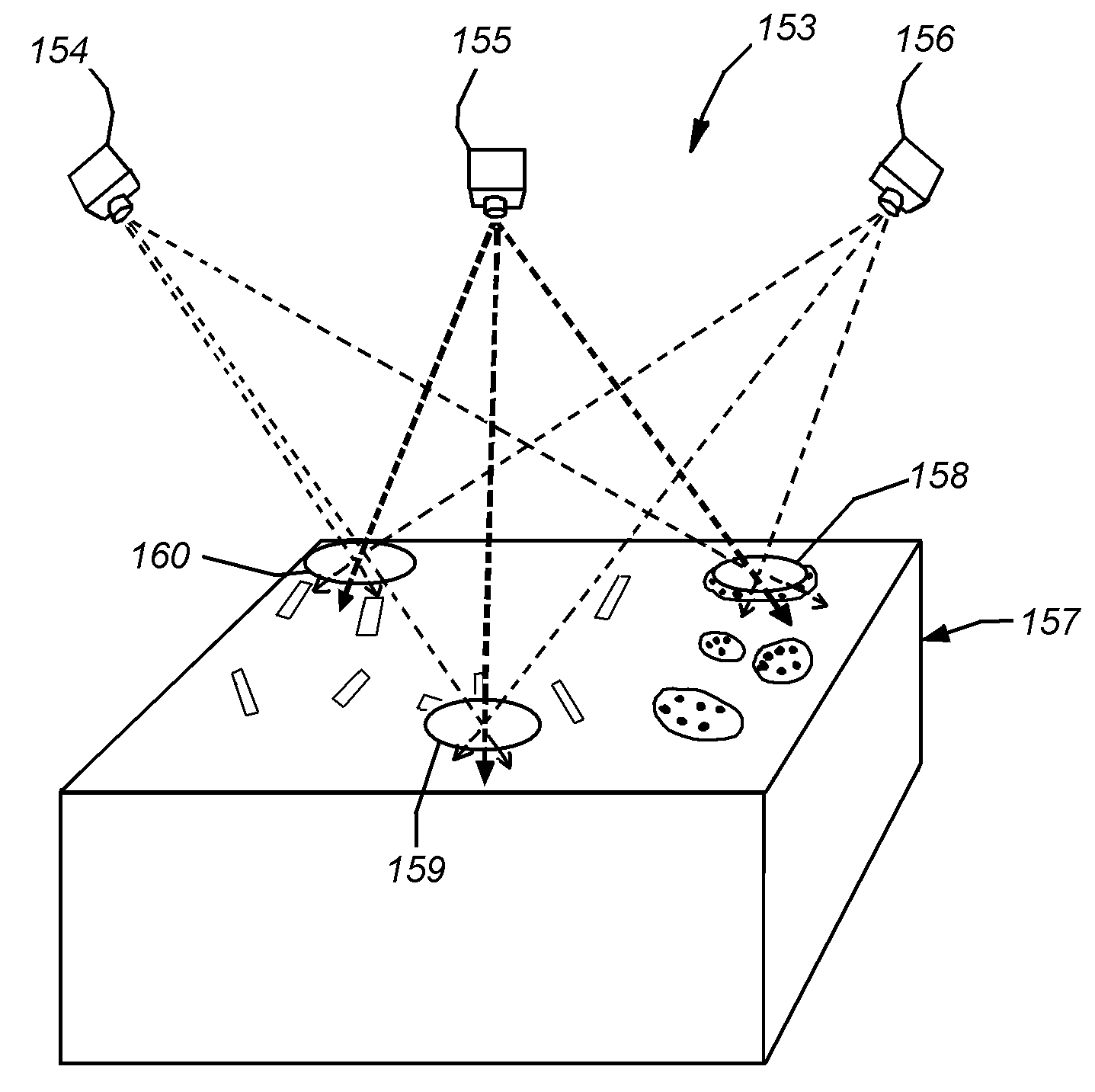
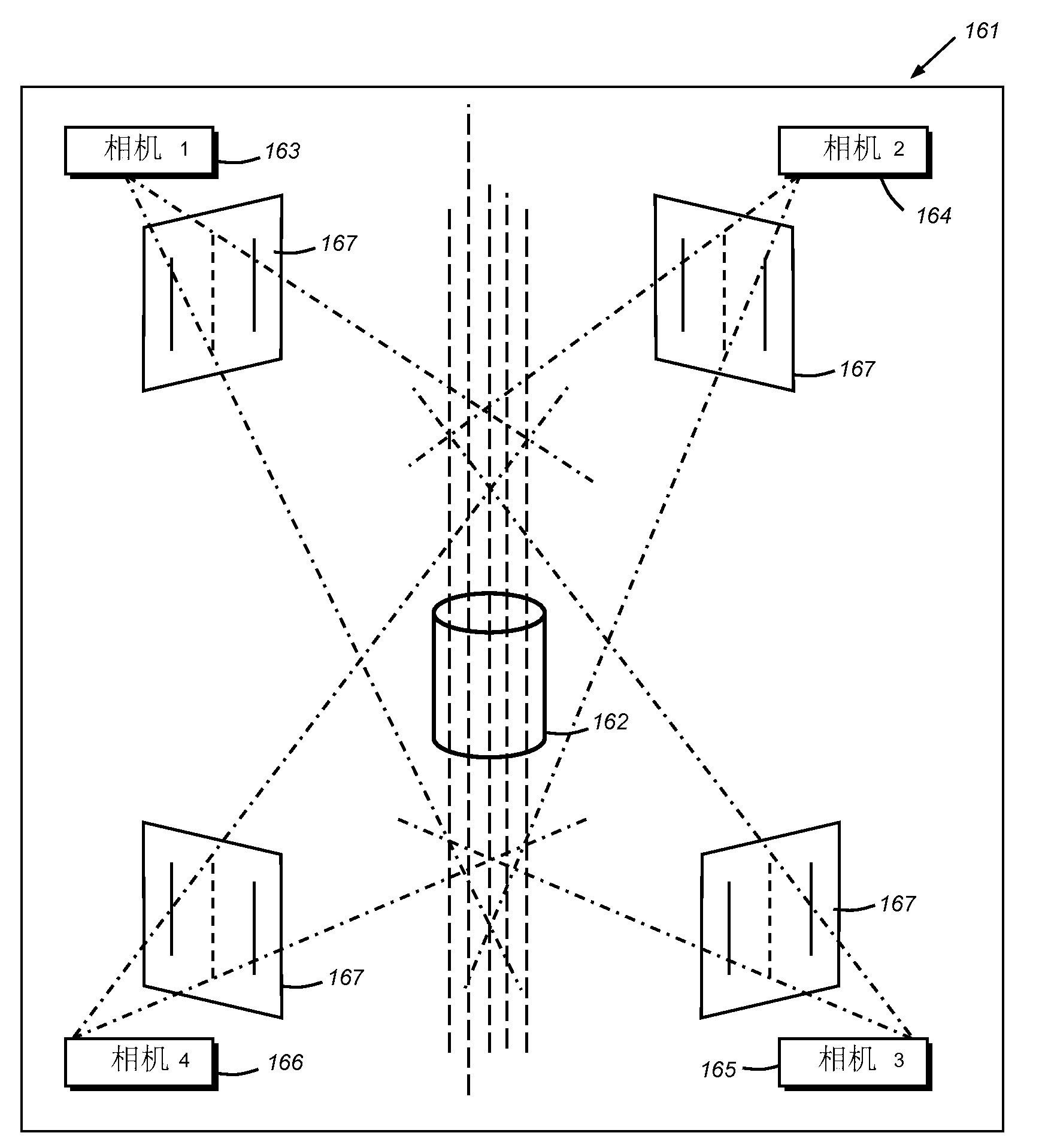
[0023]In general, system 100 may be any vision system mechanism that includes at least three cameras having a scene 128 containing an object within its field of view. The camera(s) or sensor(s) 120, 122, 124 may each comprise a 2D camera as shown, or alternatively, a 3D sensor. When provided, 3D sensor sensors may be adapted to produce a depth image of a scene using optical triangulation within a stereo camera between two discrete cameras (binocular viewing) separated by a known bas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com