Antigen-binding protein specific for serum amyloid P component
A serum starch, specific technology, used in peptide/protein components, drug combinations, immunoglobulins, etc., can solve the problem of not removing SAP
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0276] Example 1 - Sequencing of hybridoma variable domains: SAP-E and SAP-K
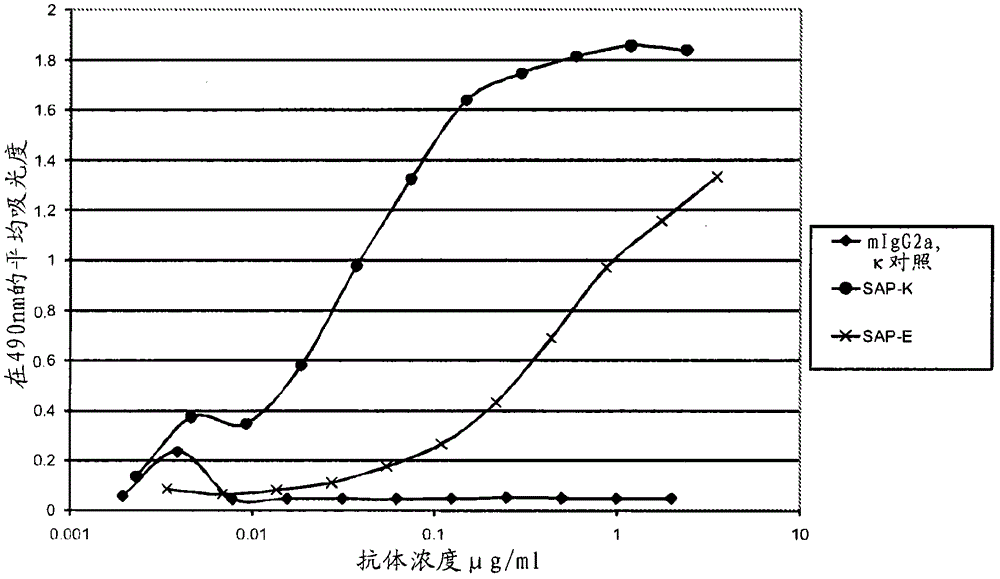
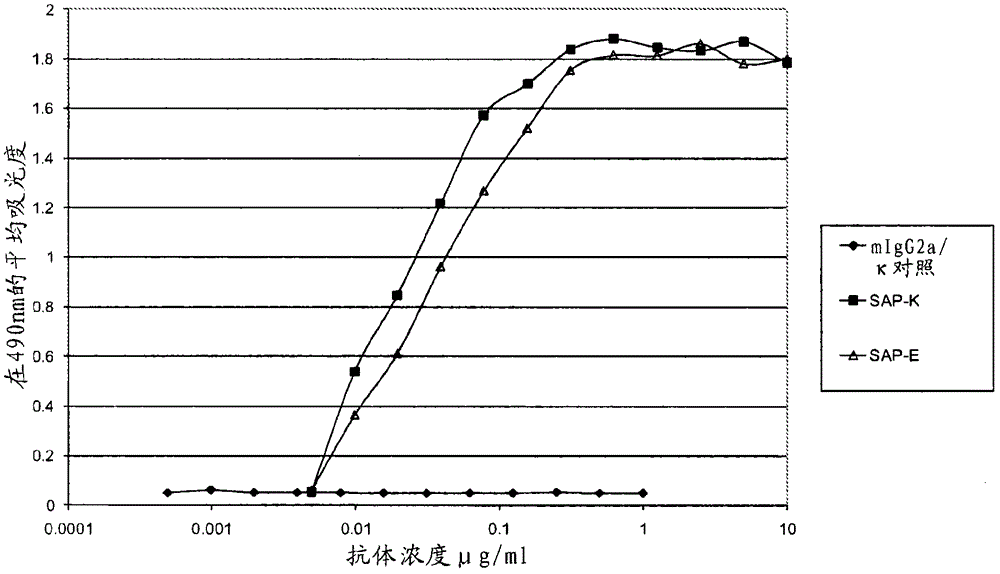
[0277] SAP-E and SAP-K are derived from 2 panels of anti-SAP monoclonal antibodies, each of which has been individually tested for in vitro binding to SAP. Within their group, SAP-E and SAP-K showed the strongest binding to SAP and they were compared with each other in different experiments.
[0278] The first panel of antibodies comprised antibodies from 7 hybridomas and was named SAP-A to SAP-G, using purified human SAP (SEQ ID NO: 43 shown below) (details of the method for purifying human SAP , see Hawkins et al. (1991) Clin. Exp. Immunol. 84, 308-316) and fusion protocols are produced in a single routine immunization. Two of these antibodies (SAP-E and SAP-B) were of the IgG2a isotype, whereas the others were of the IgGl isotype (see Example 13, Table 11).
[0279] The second panel of antibodies comprised six different IgG2a monoclonal antibodies (SAP-H to SAP-M) derived from immunization by...
Embodiment 2
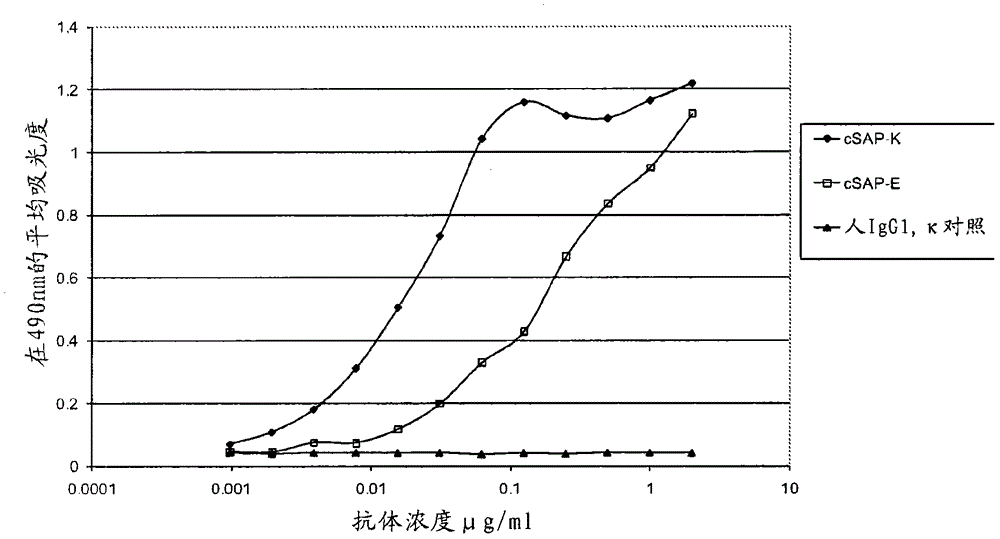
[0328] Example 2: Construction of Chimeric Antibody
[0329] Chimeric antibodies were constructed by PCR cloning of SAP-E and SAP-K, comprising parental murine variable domains grafted onto human IgGl / κ wild-type constant regions. Based on the consensus sequence, primers for the amplification of the murine variable domains were designed incorporating the restriction sites required to facilitate cloning into mammalian expression vectors. The VH amino acid sequence in SAP-E was changed from that shown in SEQ ID NO: 7 by introducing restriction sites in FR4 (framework region 4 (V-region sequence behind CDR3 and in front of the first constant domain)) TTLTVSS was changed to TLVTVSS, and the VH amino acid sequence in SAP-K was changed from TTVTVSS shown in SEQ ID NO: 17 to TLVTVSS. In the SAP-K variable light chain, an internal EcoRI site exists in CDRL1, and mutagenic primers were designed to remove this unwanted internal EcoRI site by changing one base pair (which does not cha...
Embodiment 3
[0347] Embodiment 3: humanization strategy
[0348] Humanized antibodies are prepared by grafting CDRH1, CDRH2, CDRH3, CDRL1, CDRL2, and CDRL3 from murine antibodies onto appropriate human framework sequences.
[0349] SAP-E humanization strategy
[0350] SAP-E heavy chain humanization
[0351] For the SAP-E mouse variable heavy chain sequence, the human germline acceptor framework (IGHV1-69, SEQ ID NO:25) was chosen, which is identical to the mouse SAP-E variable heavy chain sequence (SEQ ID NO:7) and the JH1 minigene (Kabat: AEYFQHWGQGTLVTVSS (SEQ ID NO: 26)) with 60% identity (including CDRs). The first 6 residues of the JH1 minigene residues fell within the CDR3 region and were replaced by importing CDRs from the donor antibody.
[0352] Based on sequence alignment and possible impact on antibody function, five humanized variants were prepared. Construct H0 is a linear graft of murine CDRs (defined using Kabat) into the human acceptor framework selected above. C...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com