Internal force path geometrical morphology based low-carbon material-saving bearing structure design method
A technology of load-bearing structure and internal force path, which is applied in computing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as cumbersome and complex algorithms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
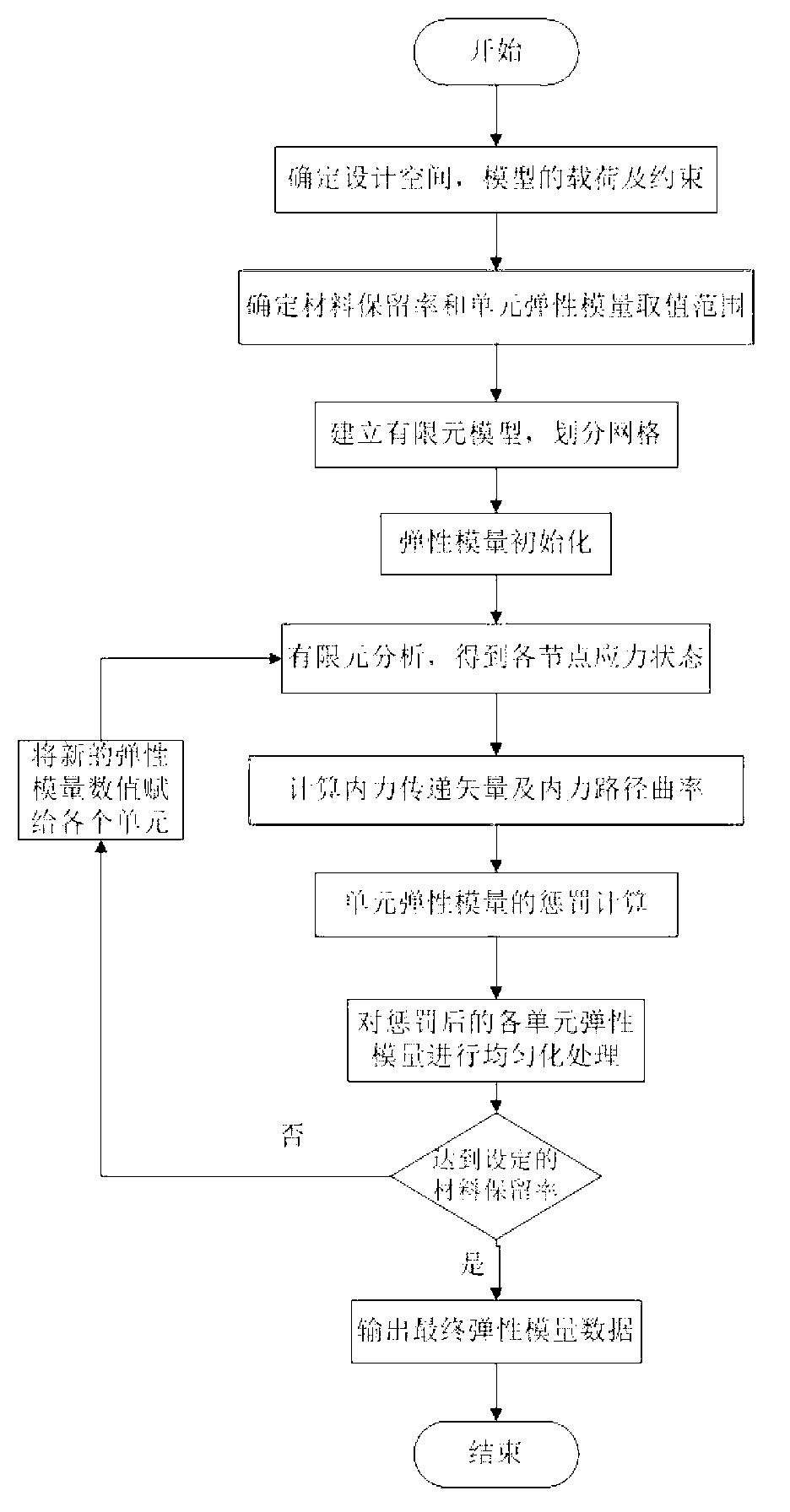
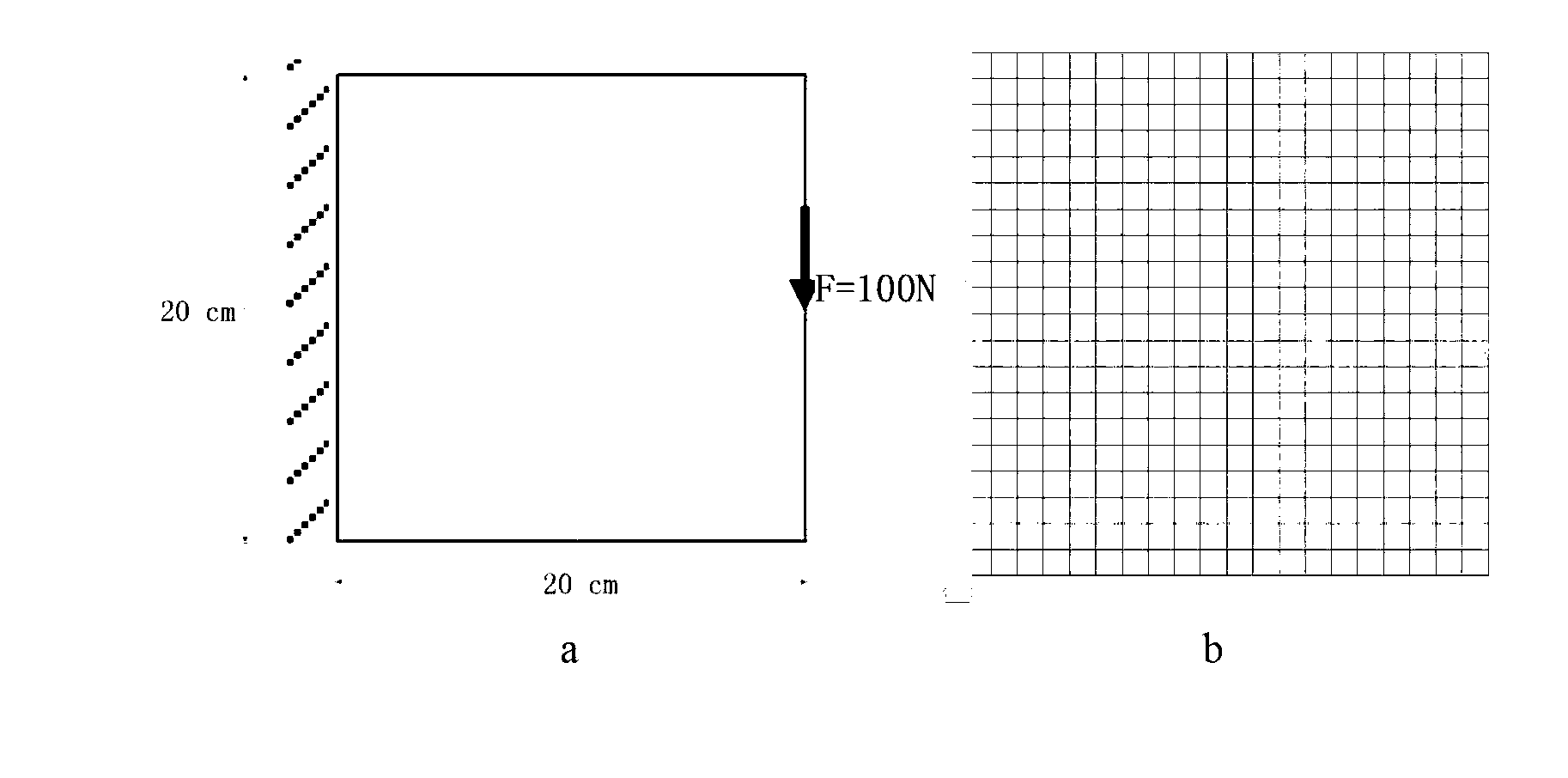
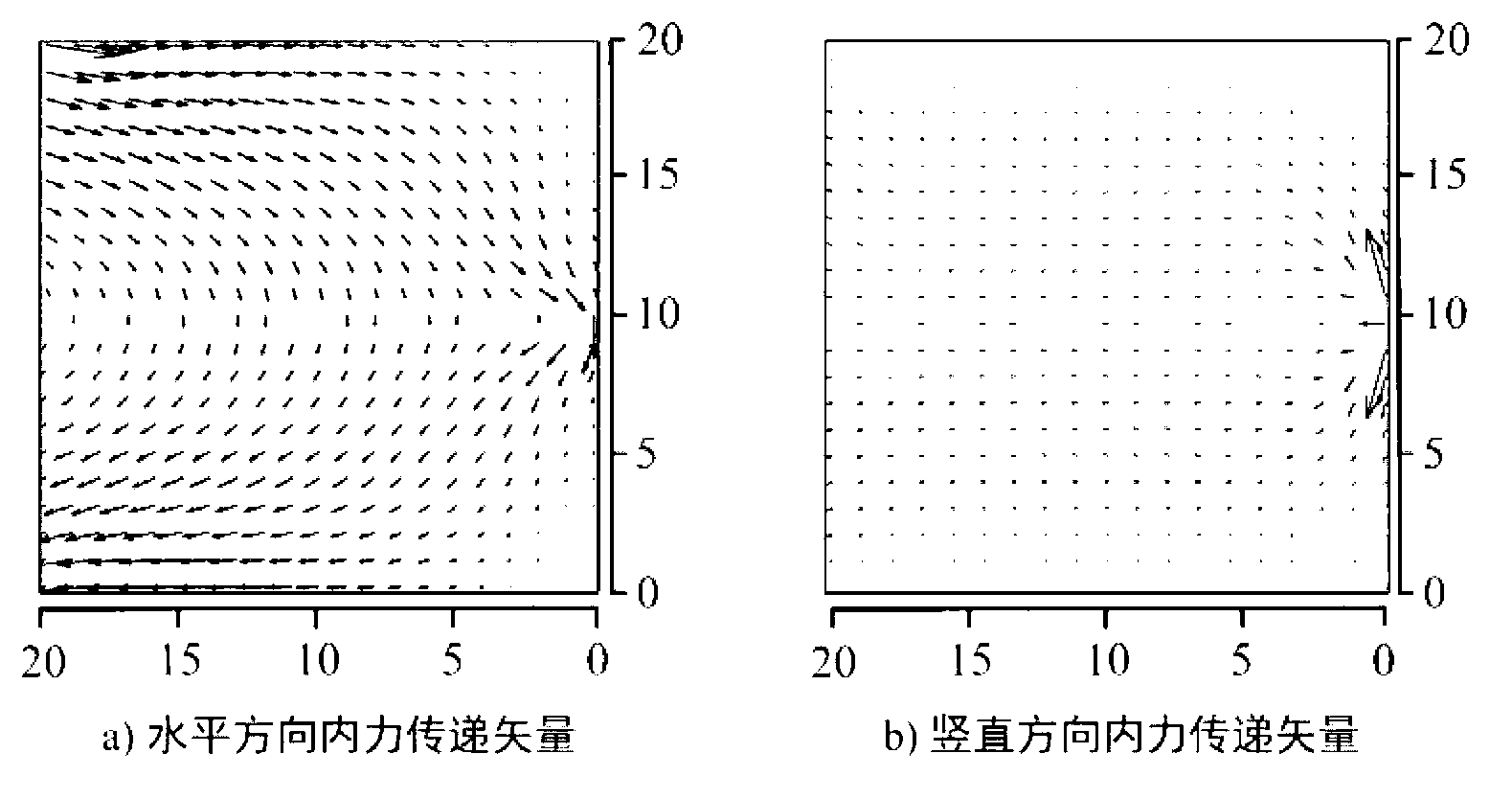
[0047] Taking a square plate fixed at one end and loaded by a concentrated force at the midpoint of the other end as an example, the specific implementation steps of this method are introduced (such as figure 2 ).
[0048] 1) Define the value range of the elastic modulus of the material in the finite element model, that is, the maximum value E max and minimum E min ; and the optimal ratio, that is, the ratio β of the material that needs to be retained. In this example, the maximum value E of the elastic modulus of the material is set max Set to 5e5Pa. Set the minimum E min is close to 0, but it must be large enough so that it will not be ignored in finite element analysis, take E min =1Pa. In addition, the areas that are subjected to concentrated loads and are constrained are considered structural features and must be preserved, so the elastic modulus of the first layer elements near these areas is defined as the maximum value E max And changes are not allowed.
[004...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com