Double-cable composite damping cable
A composite damping and damper technology, applied in the field of damping cables, can solve the problems of reducing structural swing suppression, reducing cable axial stiffness, and small cable spacing, etc., to achieve reduced additional force, significant cable force changes, and longitudinal The effect of low stiffness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0015] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
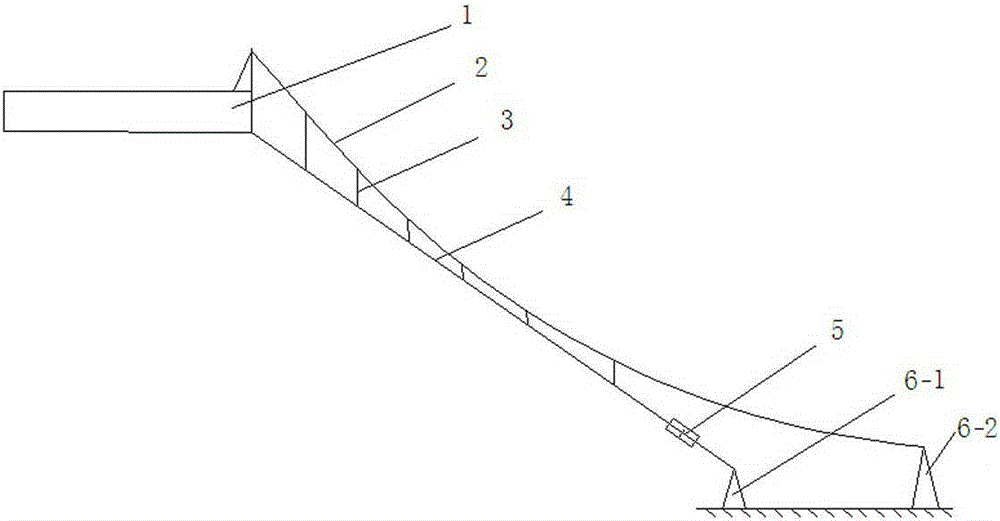
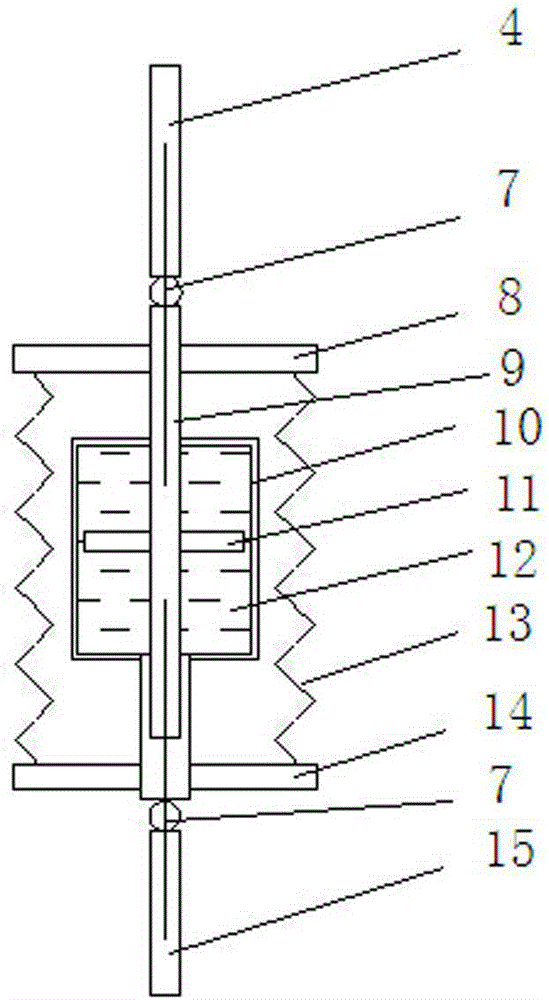
[0016] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention includes an auxiliary cable 2, a boom 3, a main cable 4, a viscous damper 5, a first support 6-1 and a second support 6-2, and the first support 6-1, The second support 6-2 is all installed on the ground, one end of the main cable 4 is connected with the bridge girder 1, the other end is connected with one end of the viscous damper 5, and the other end of the viscous damper 5 is connected with the first The support 6-1 is connected, the auxiliary cable 2 is located above the main cable 4, the main cable 4 and the auxiliary cable 2 are located in the same plane, the main cable 4 is straight, and the auxiliary cable 2 is in the middle The two ends of the auxiliary cable 2 are respectively connected to the main girder 1 of the bridge and the second support 6-2, between the main cable 4 and the auxili...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com