Heuristics to quantify data quality
A data and quality technology, applied in data processing applications, based on specific mathematical models, dynamic trees, etc., can solve problems such as difficult analysis, errors, and unrealistic data
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0012] overview
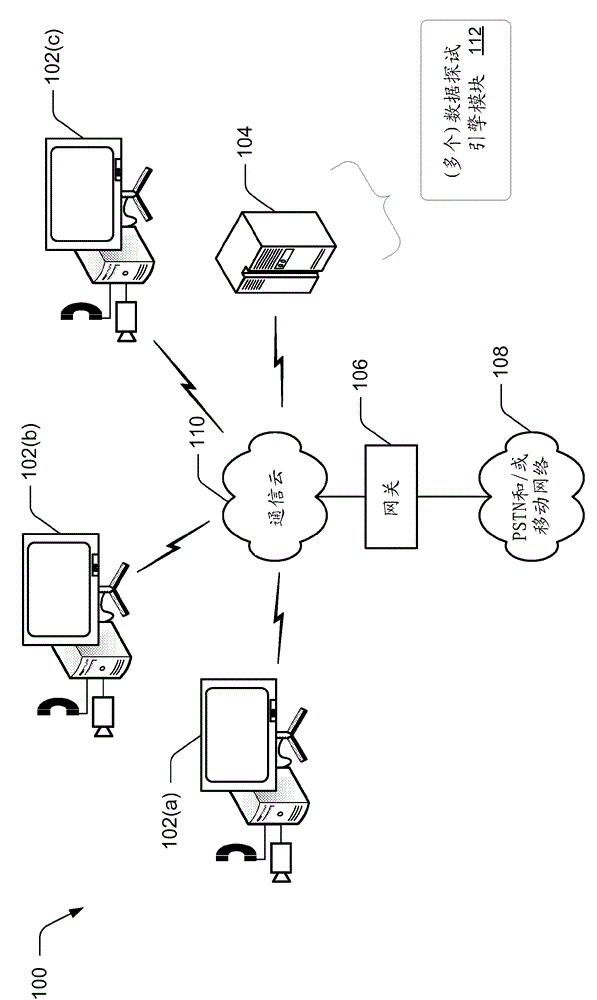
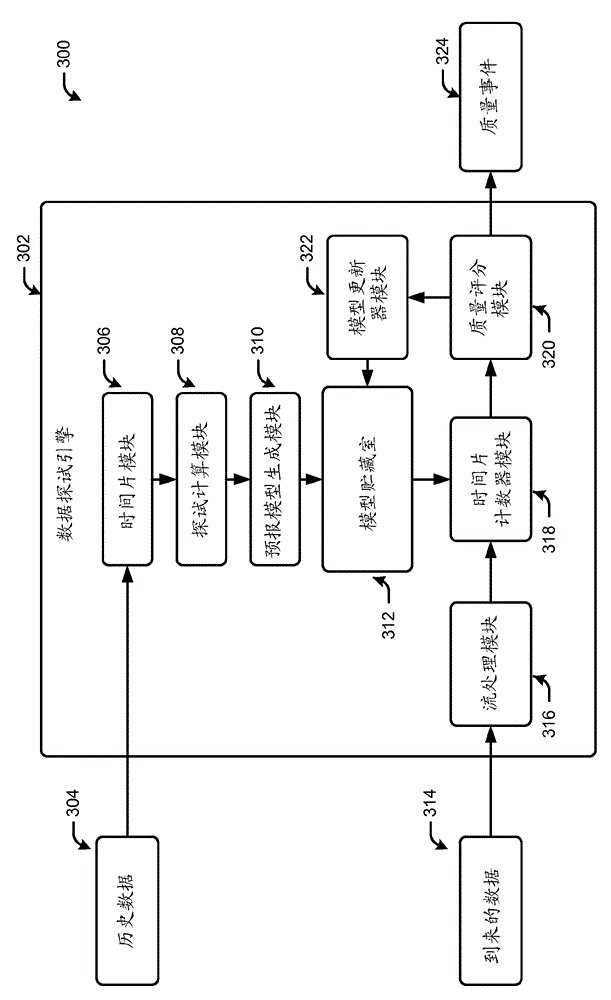
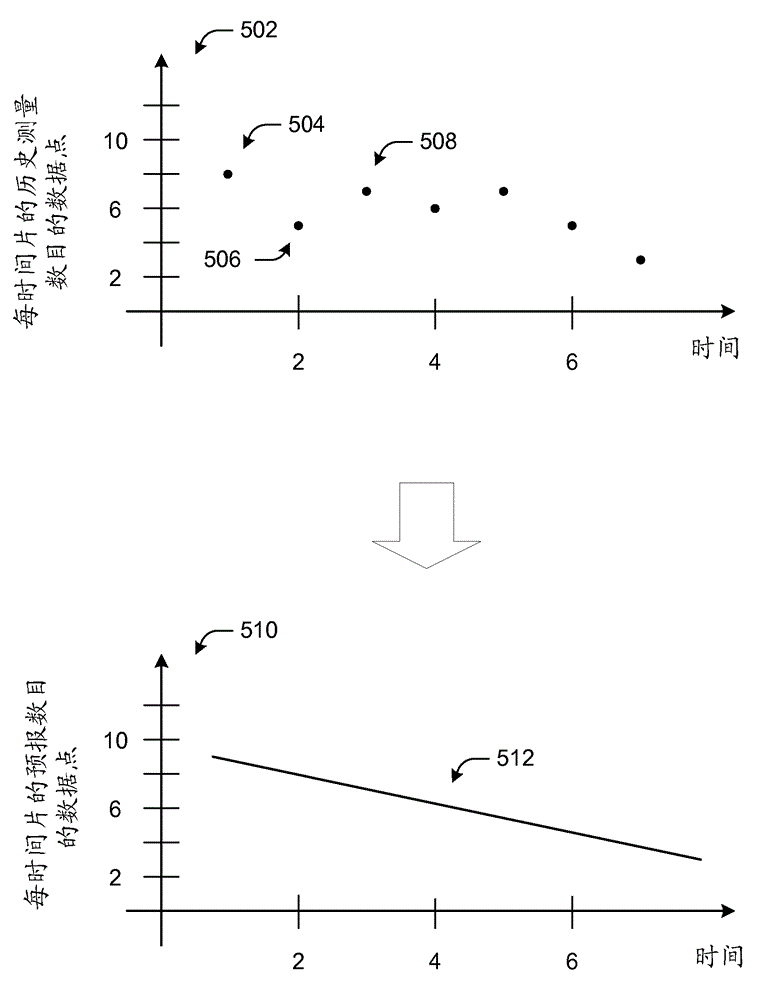
[0013] Various embodiments generate at least one heuristic for a set of historical data. For example, data associated with past performance of systems and / or products may be collected and / or stored in a repository. In some cases, a historical data set may be partitioned into segments, and heuristic(s) may be generated for each segment. The size of each segment may be variable and / or fixed in length relative to each other. Alternatively or additionally, the size of the segments may be based at least in part on characteristics and / or attributes associated with the analyzed historical data. In response to generating the heuristic(s) from historical data, some embodiments generate one or more forecasts based at least in part on the heuristic(s). For example, a forecast may be generated from the heuristic(s) to plan and / or anticipate future behavior(s) of the system and / or product. Some embodiments store the forecast(s) in a repository for future use, as dis...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap