Piezoelectric-hydraulic hybrid linear stepping motor and its working method
A stepping motor, linear technology, applied in piezoelectric effect/electrostrictive or magnetostrictive motors, generators/motors, electrical components, etc. Wide working frequency band, ensuring work stability, driving control signal and the effect of low machining accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
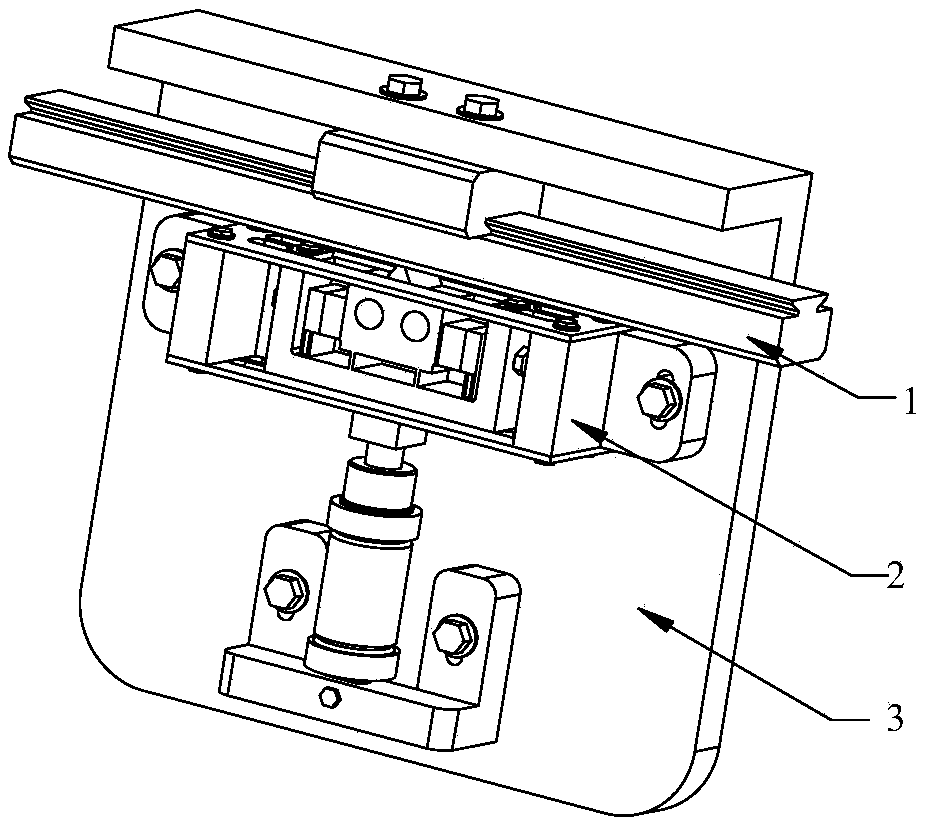
[0049] Such as figure 1 The piezoelectric-hydraulic hybrid linear stepping motor structure shown includes mover 1, stator 2 and base 3; the mover is fixed on the side plate of the base by bolts; the stator 2 is fixed on the bottom plate of the base by bolts; The initial pressure between the stator 2 and the mover 1 can be controlled by controlling the front and rear positions of the stator 2 on the base.
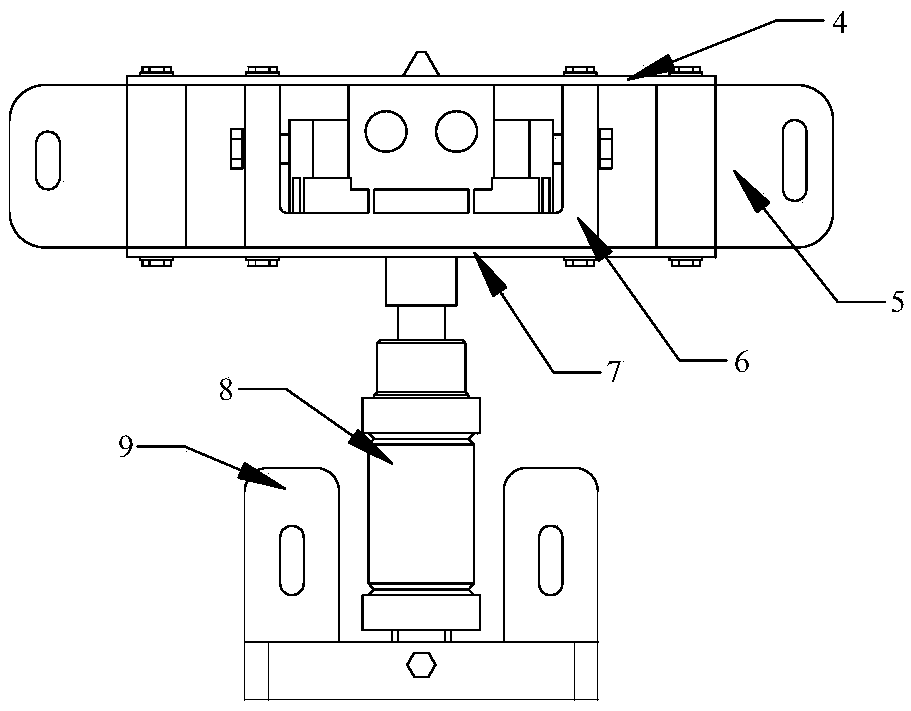
[0050] Such as figure 2 As shown, the stator structure includes a driving foot 6, a support 5, a pre-compressed leaf spring, a vibrating hydraulic cylinder 8 and a fixed block 9.
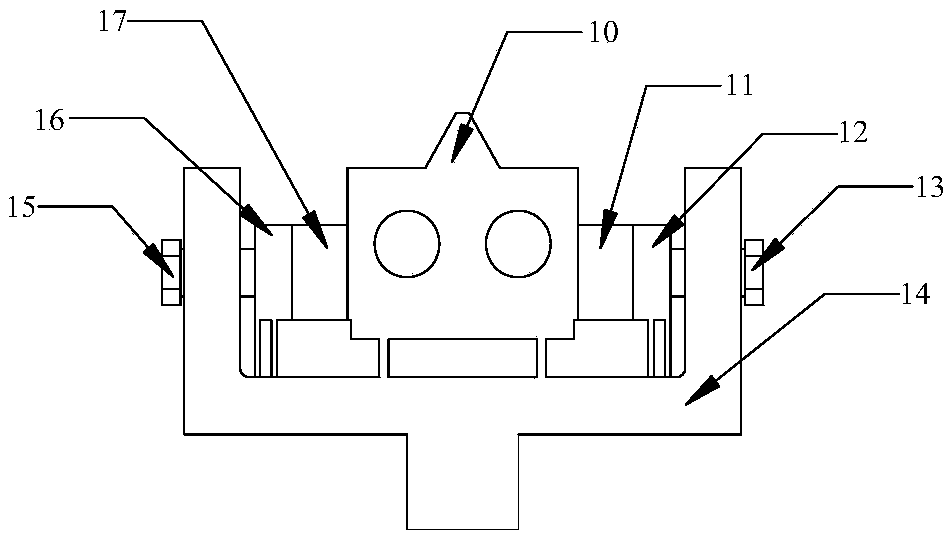
[0051] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the pre-compressed leaf spring includes a ring frame structure, a flexible hinge and a square plate; the short side of the ring frame structure and the square plate are connected by a flexible hinge; the ring frame is provided with a round hole, which can be fixedly connected with the support 5; the square plate has Through holes, the upper and lower ends of ...
Embodiment 2
[0066] The difference between Embodiment 2 and Embodiment 1 is that the second transverse piezoelectric stack 11 in Embodiment 1 is replaced by a pre-tension spring, and nothing else is changed.
[0067] The working principle of embodiment 2 is basically the same as that of embodiment 1, except that in structure, the transverse piezoelectric laminations of embodiment 1 are arranged symmetrically, and symmetrical excitation voltage is also used in the way of excitation voltage. Embodiment 2 is asymmetric in structure and excitation mode, and the asymmetric excitation voltage mode of embodiment 2 can have multiple options, and the signal waveform is as follows Figure 10 ~ Figure 13 shown.
[0068] For the symmetrical structure and excitation voltage in Embodiment 1, the differential principle can only be realized by changing the positive pressure between the stator and the mover, that is, the vibration of the vibrating hydraulic cylinder; while the asymmetrical differential pri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com