Scheduling voice-over-IP users in wireless systems using carrier aggregation
A carrier aggregation and secondary carrier technology, applied in transmission systems, wireless communications, digital transmission systems, etc., and can solve the problems of inability to decode downlink data, not receiving downlink assignments, and inability to determine UE.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
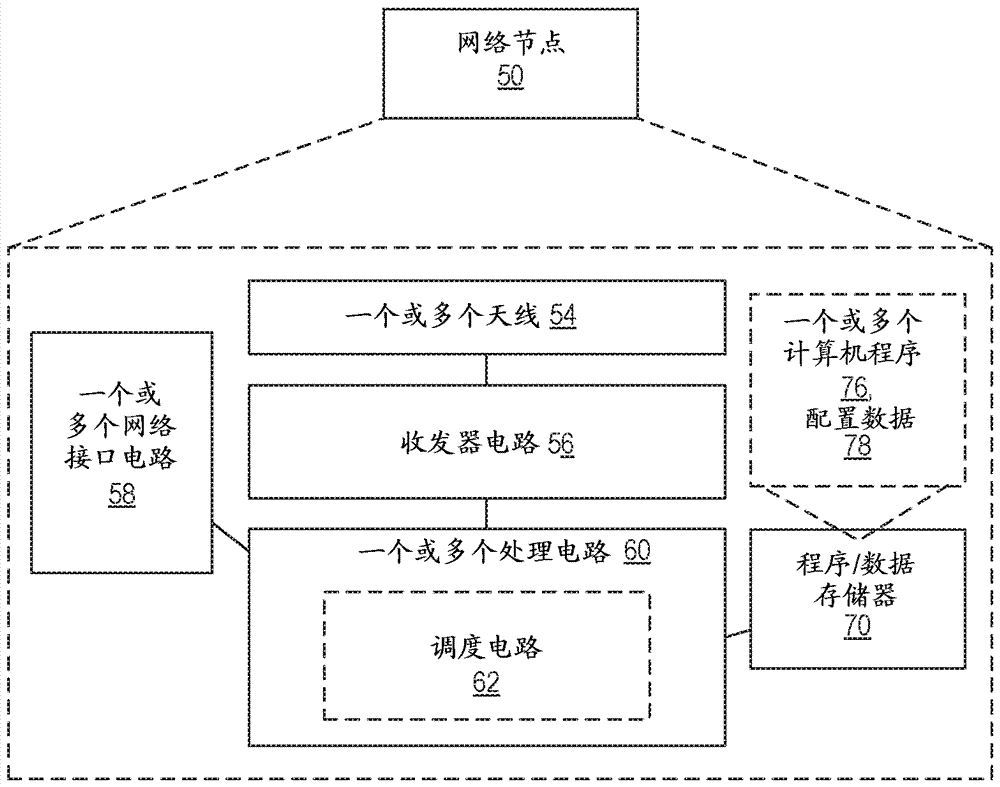
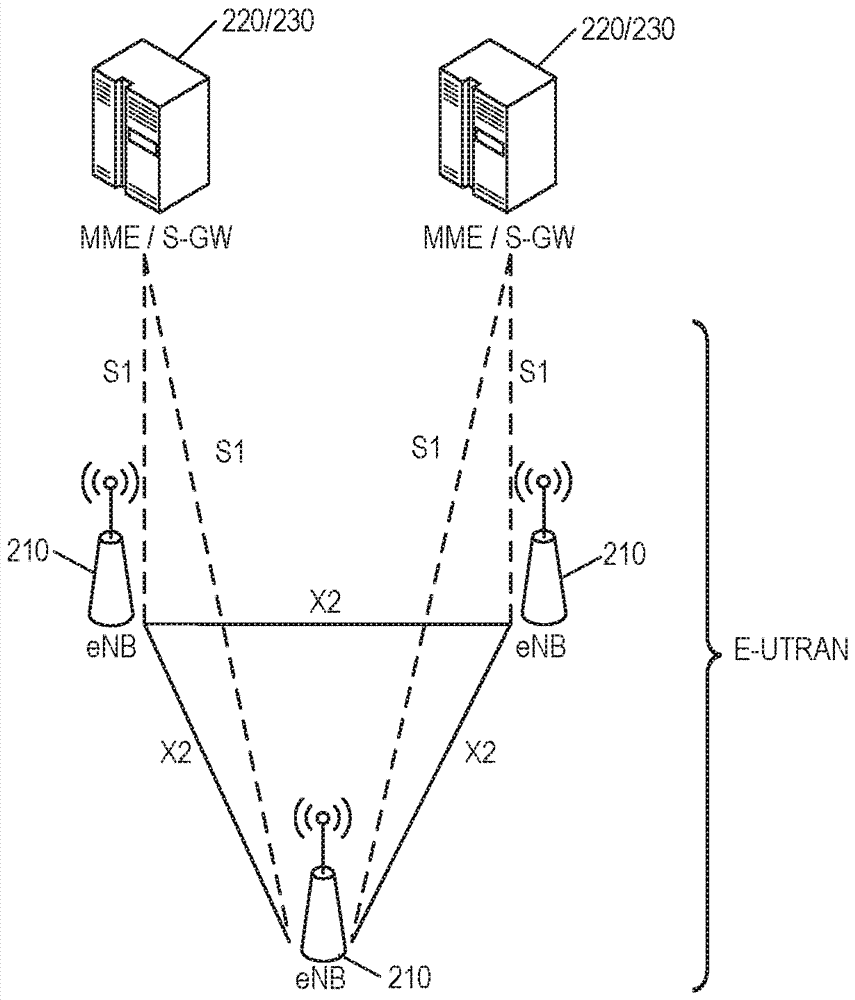
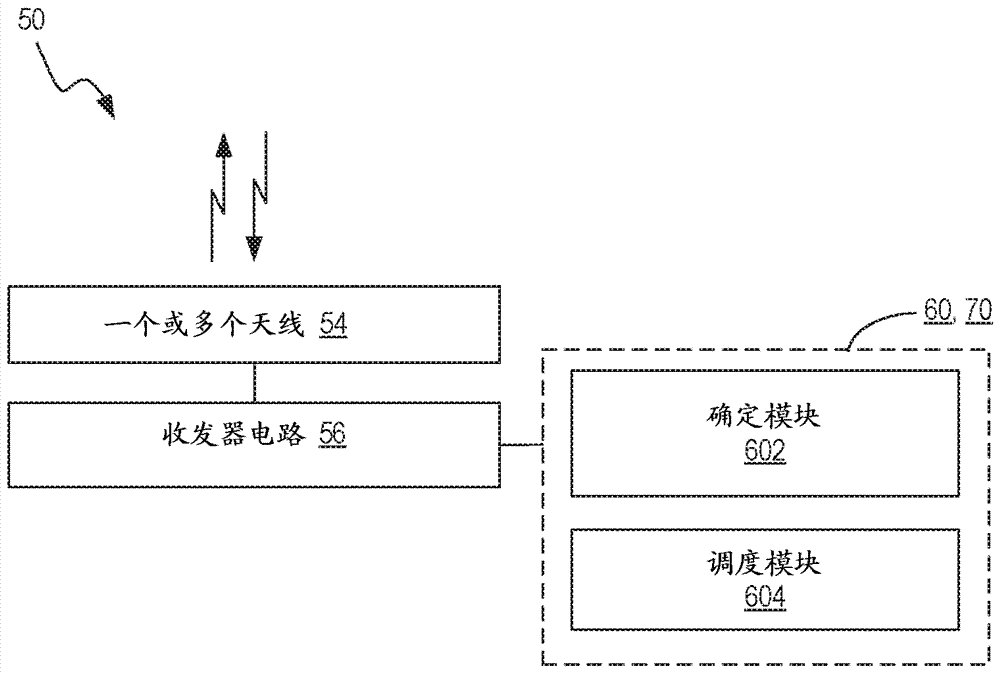
[0044] The inventive concept will be described more fully hereinafter with reference to the accompanying drawings, in which examples of embodiments of the inventive concept are shown. These inventive concepts may, however, be embodied in many different forms and should not be construed as limited to the embodiments set forth herein. Rather, these embodiments are provided so that this disclosure will be thorough and complete, and will fully convey the scope of the inventive concept to those skilled in the art. It should also be noted that these embodiments are not mutually exclusive. Components from one embodiment may be present in or used in another embodiment by default.
[0045] For purposes of illustration and explanation only, these and other embodiments of the inventive concept are described herein in the context of a radio access network communicating with mobile terminals (also referred to as terminal devices, wireless terminals or UEs) over radio communication channel...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap