Patents
Literature
1778 results about "Transmission Time Interval" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
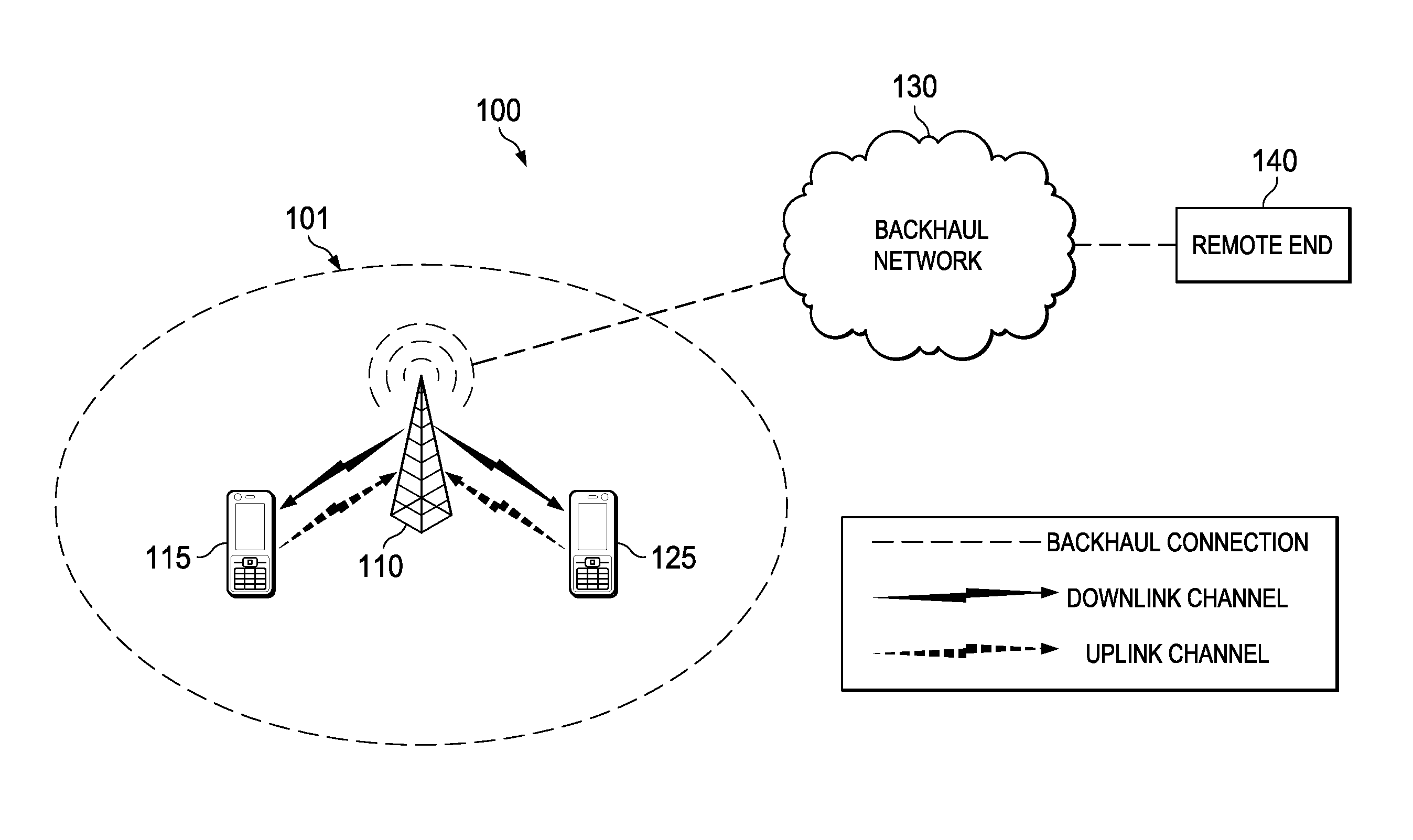
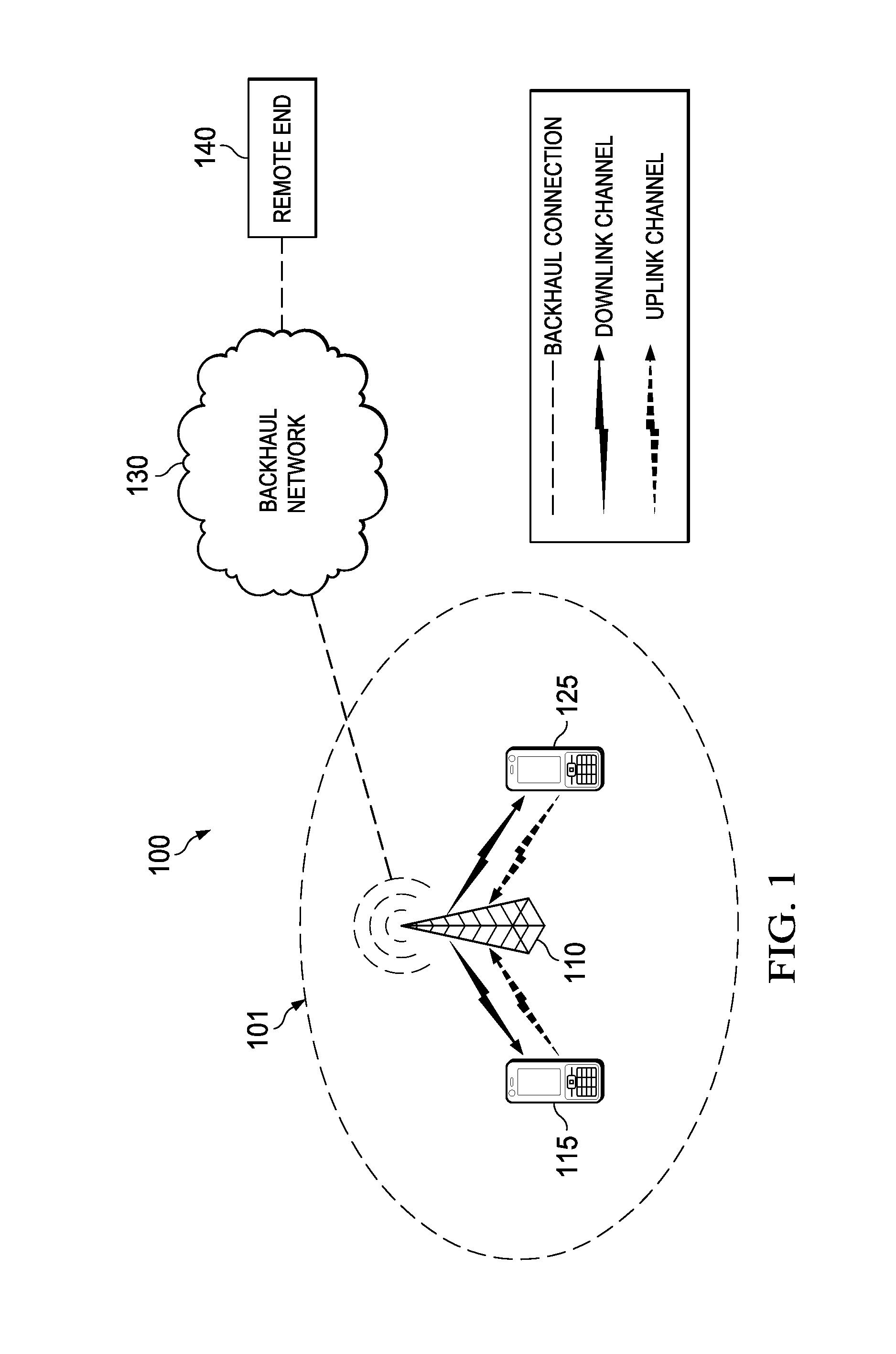
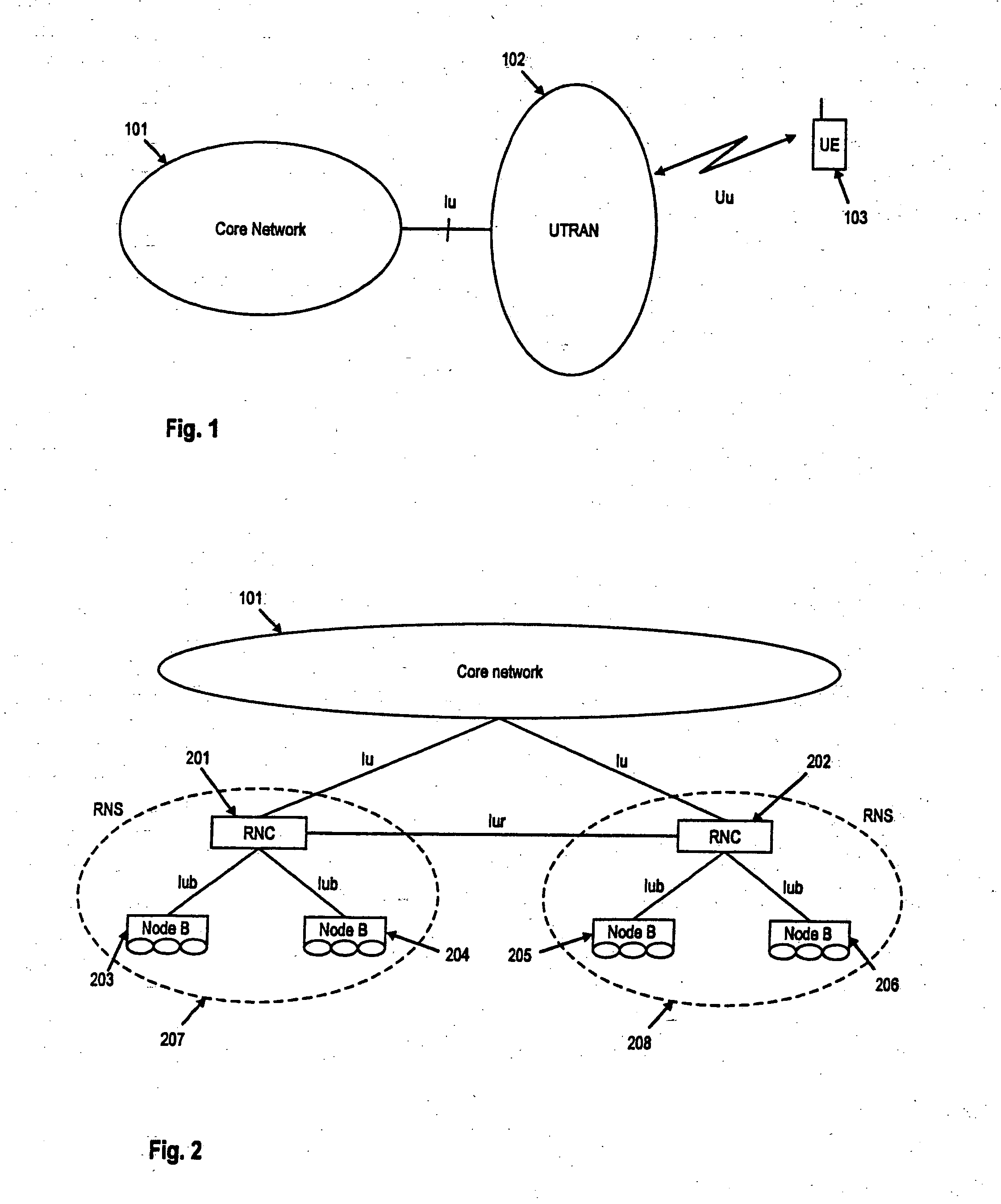
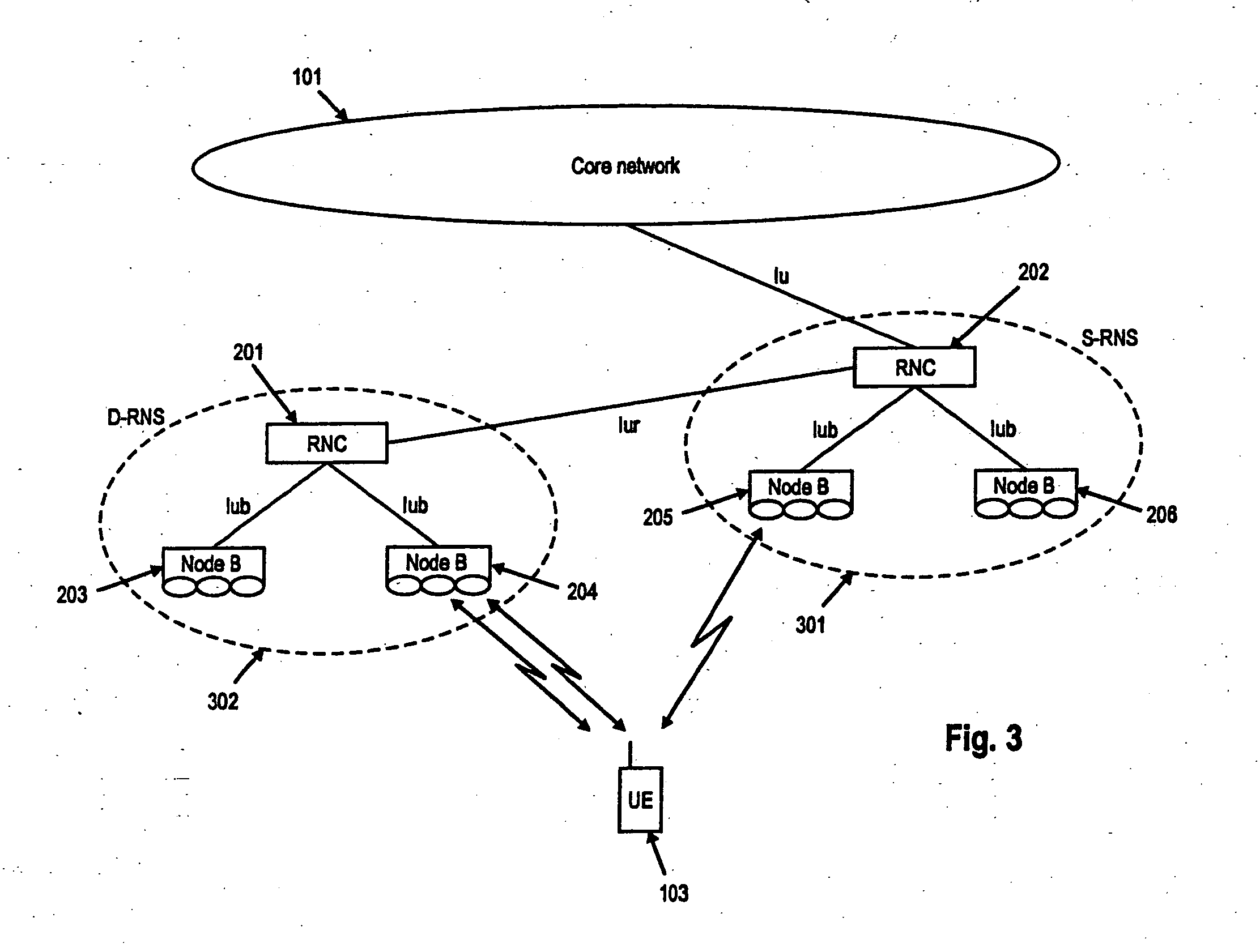
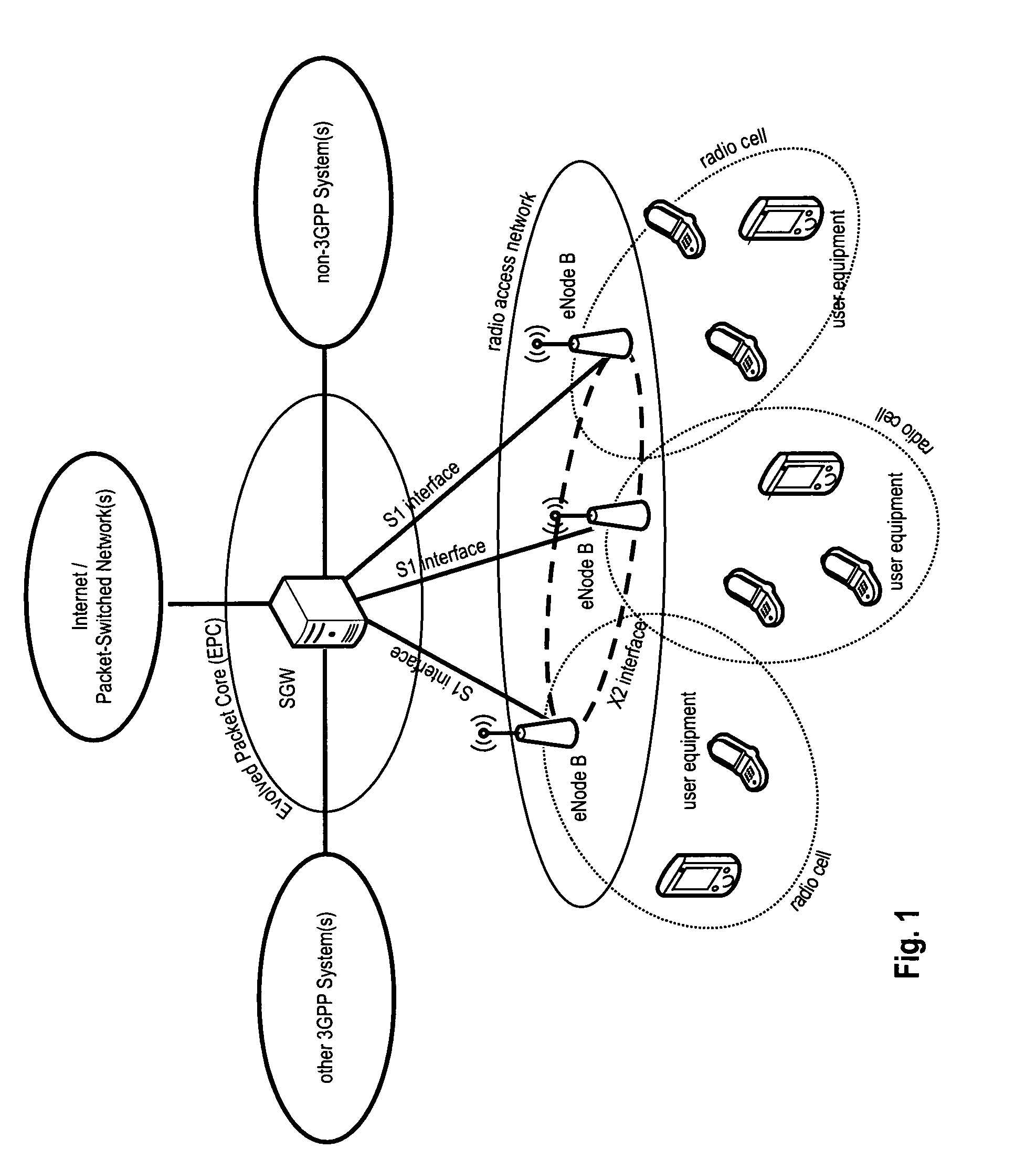
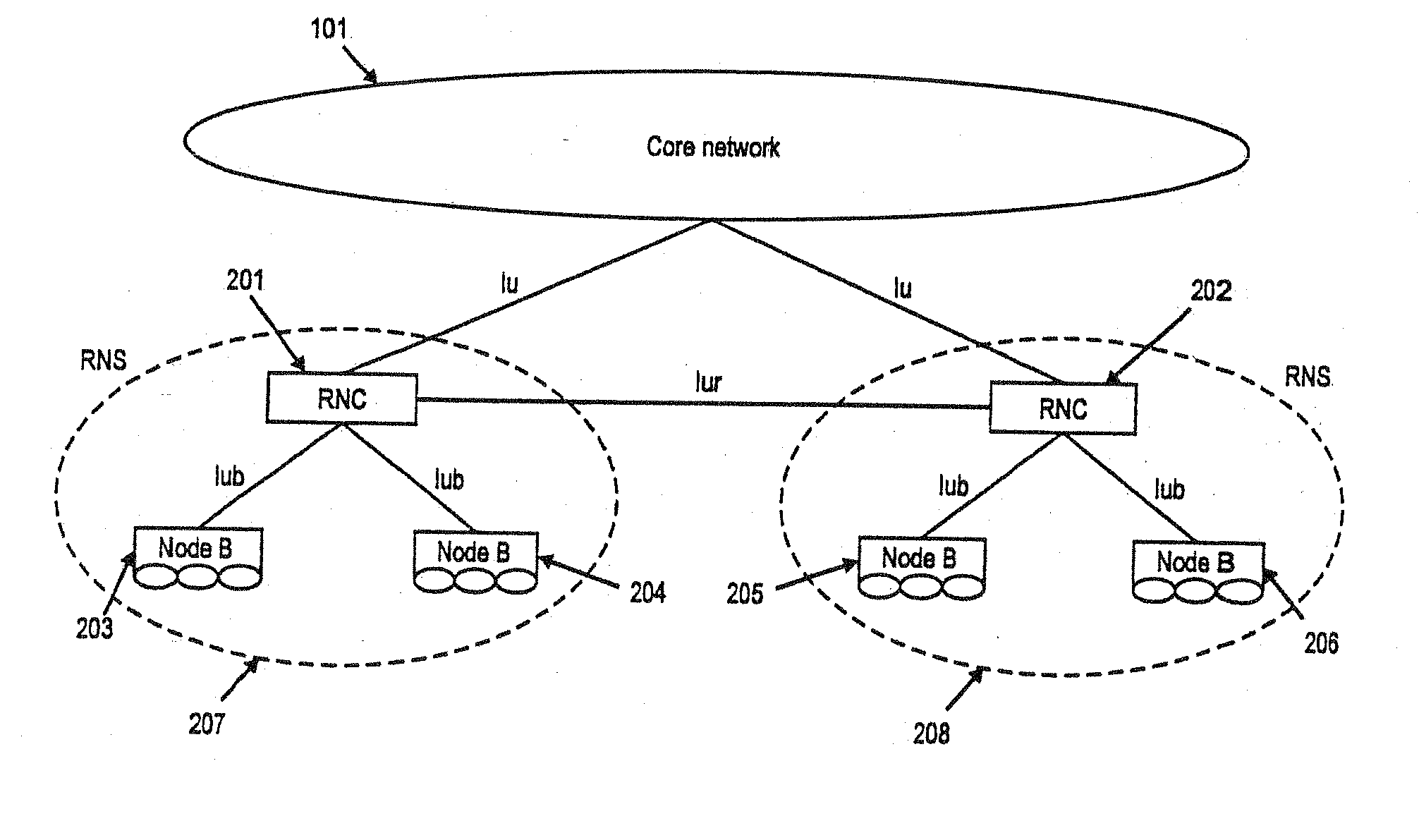
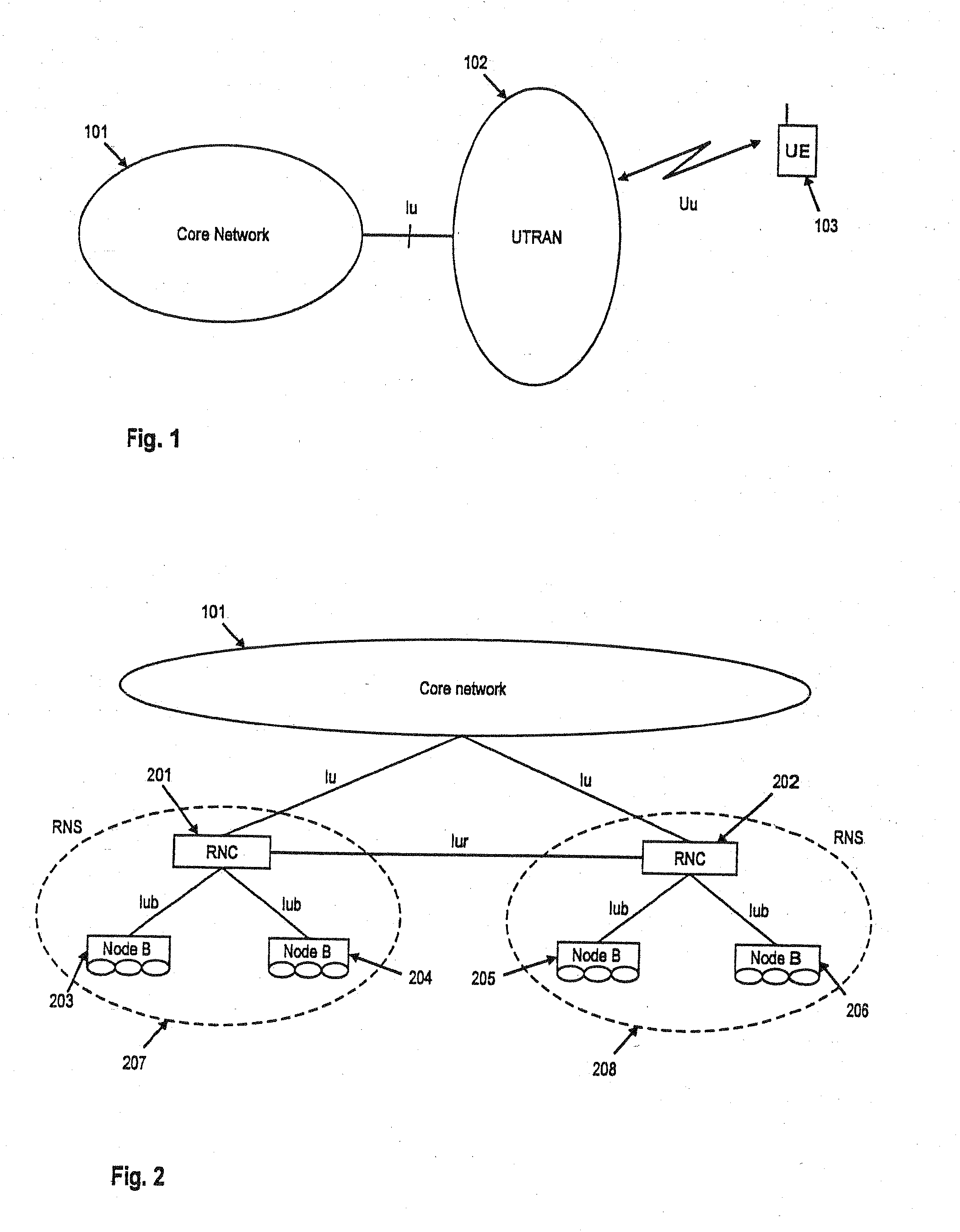
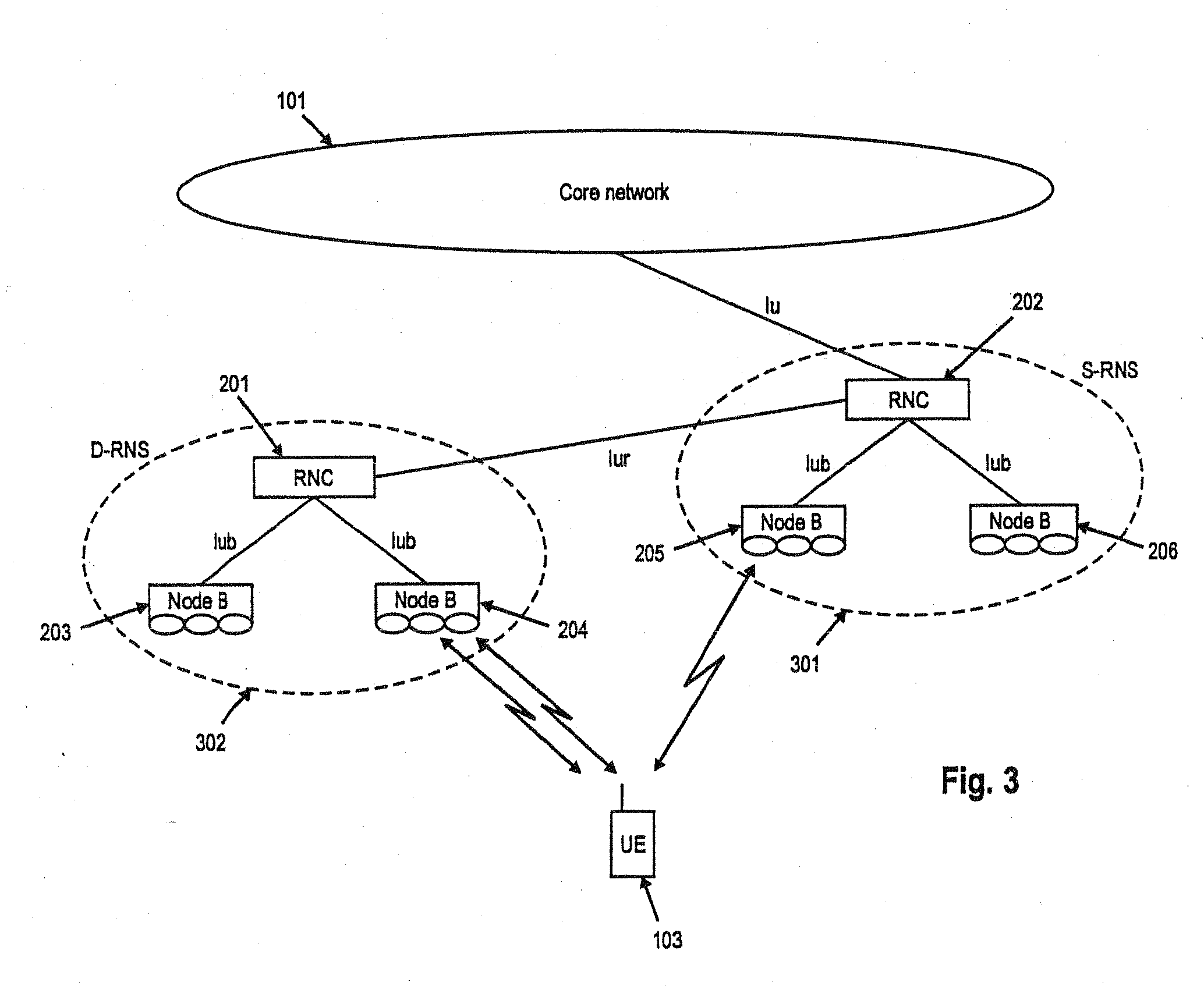
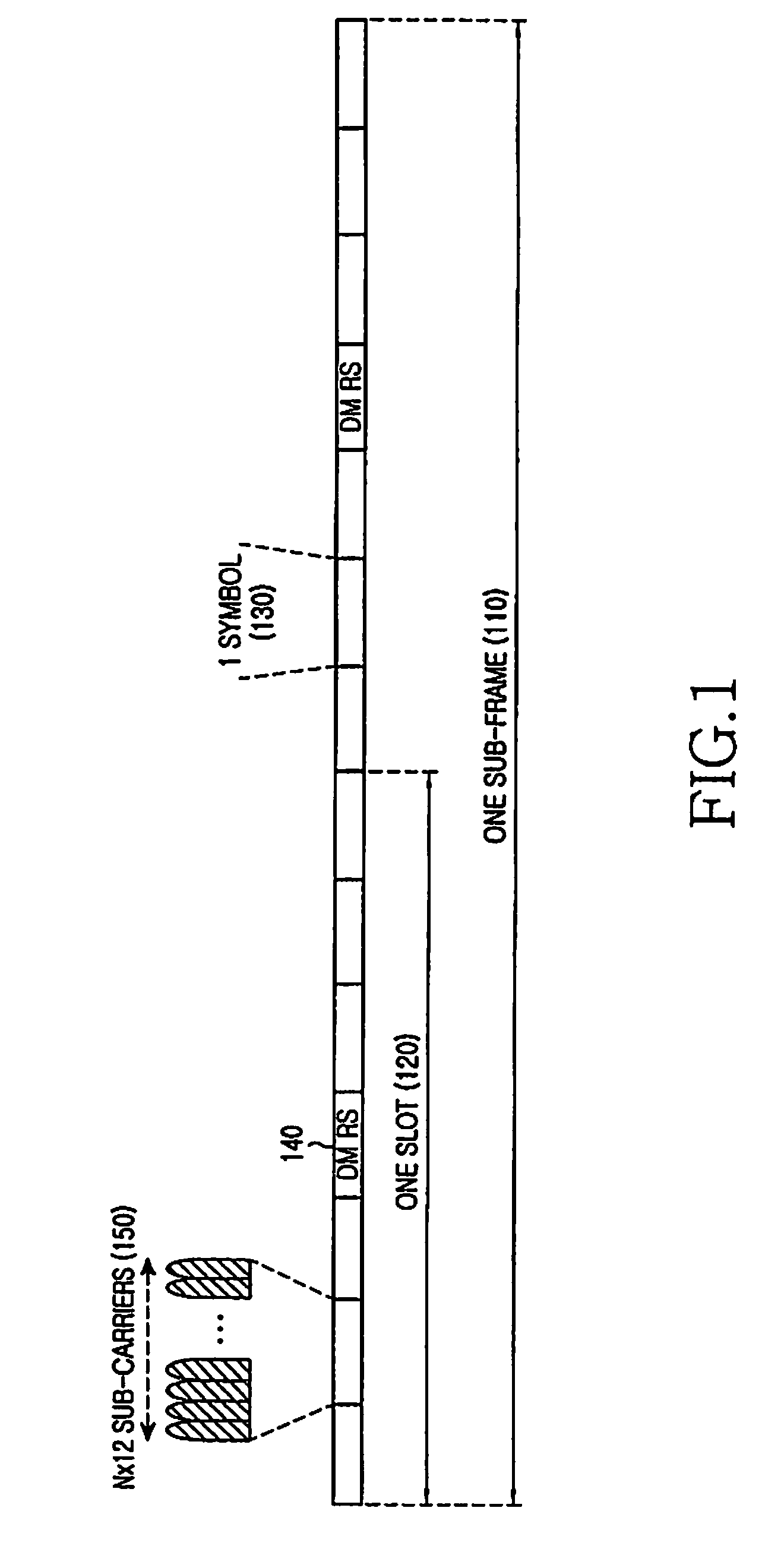
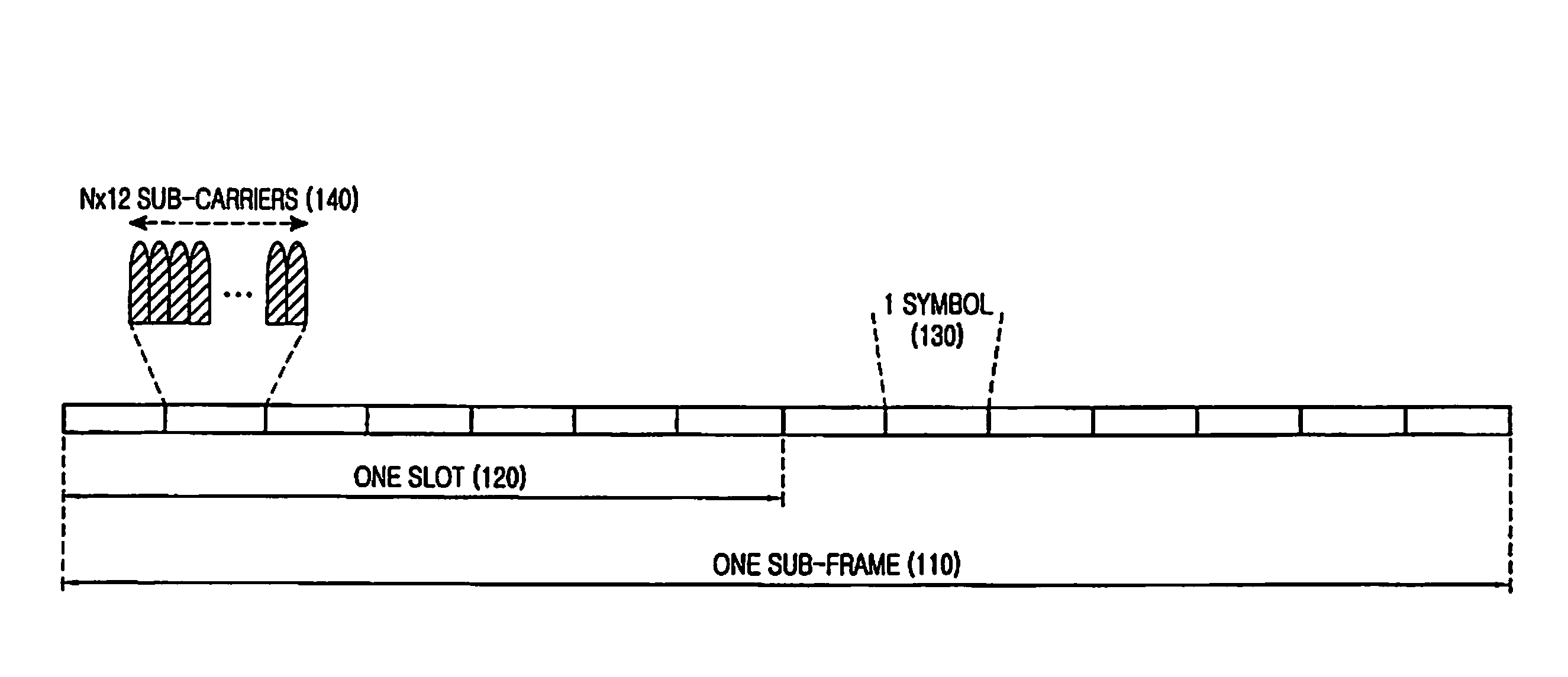
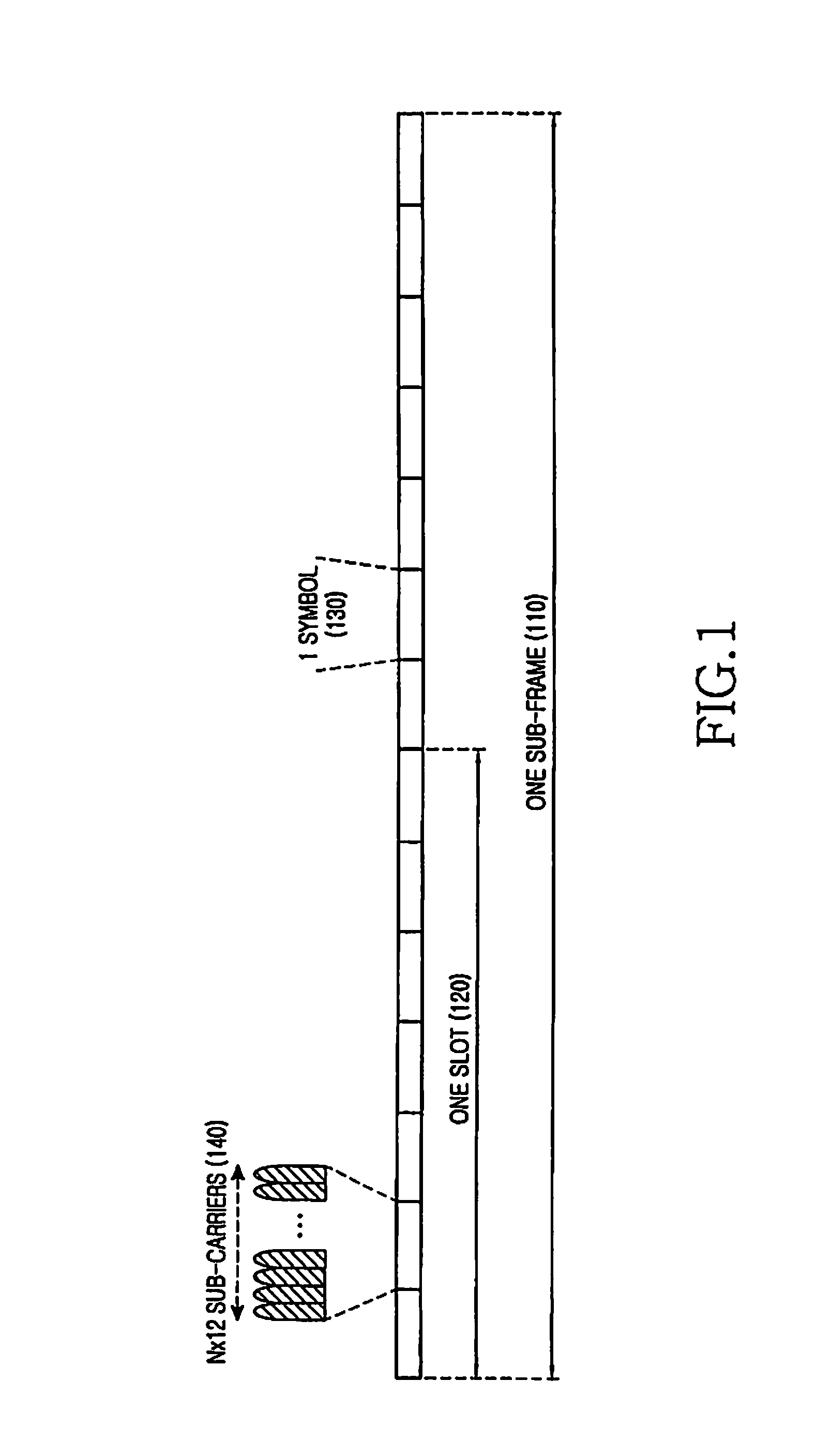
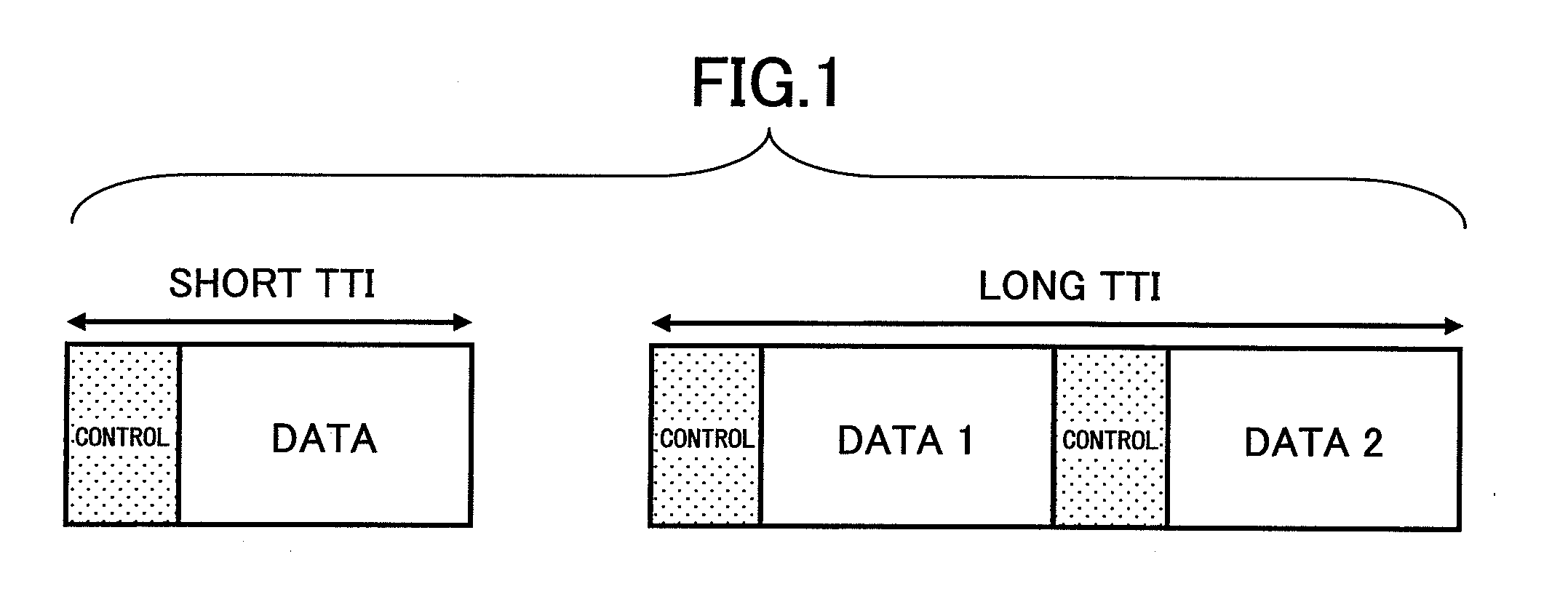
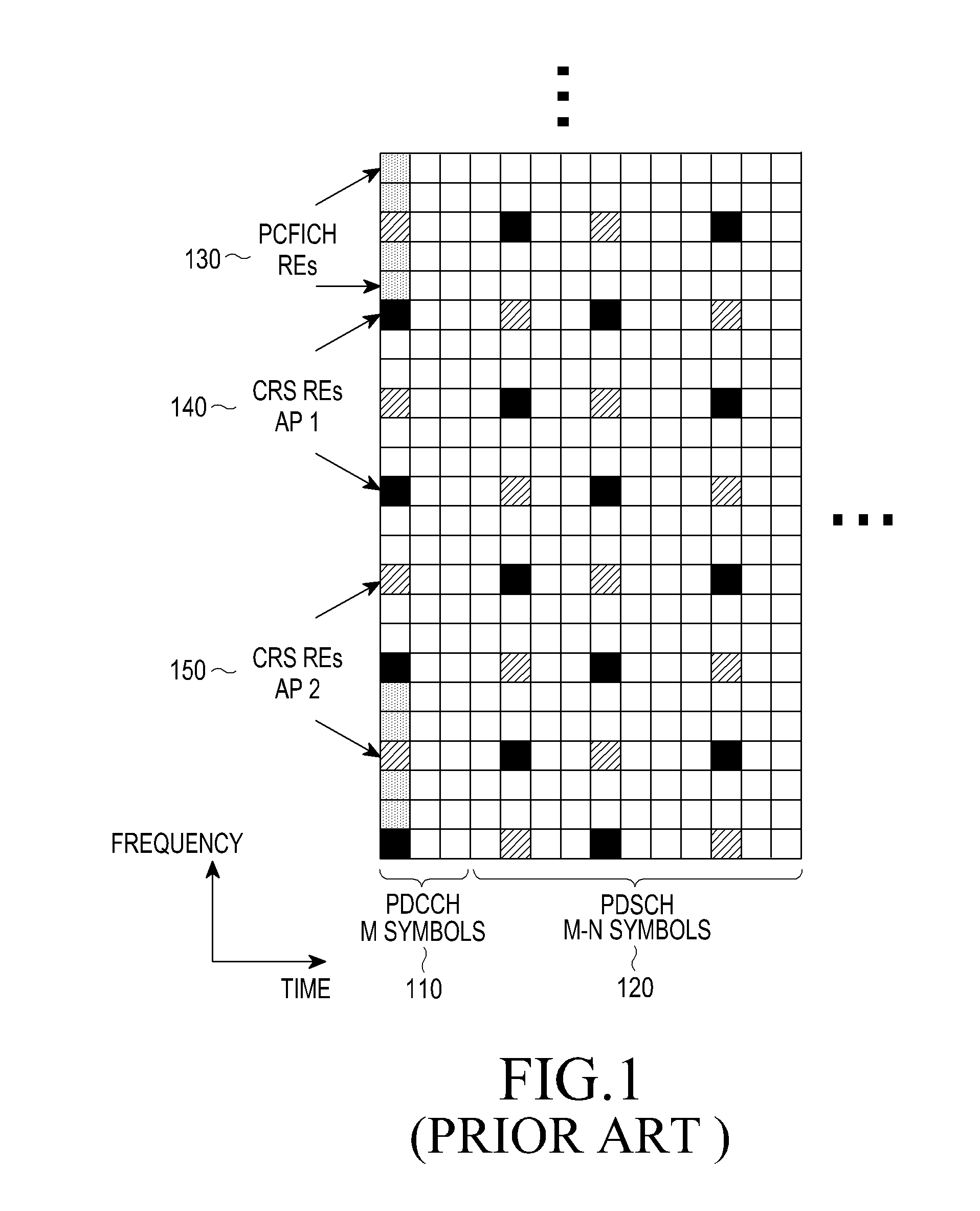
TTI, Transmission Time Interval, is a parameter in UMTS (and other digital telecommunication networks) related to encapsulation of data from higher layers into frames for transmission on the radio link layer. TTI refers to the duration of a transmission on the radio link. The TTI is related to the size of the data blocks passed from the higher network layers to the radio link layer.
System and Method for Adaptive Transmission Time Interval (TTI) Structure
ActiveUS20140071954A1Length be adaptNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexQuality of serviceStructure of Management Information
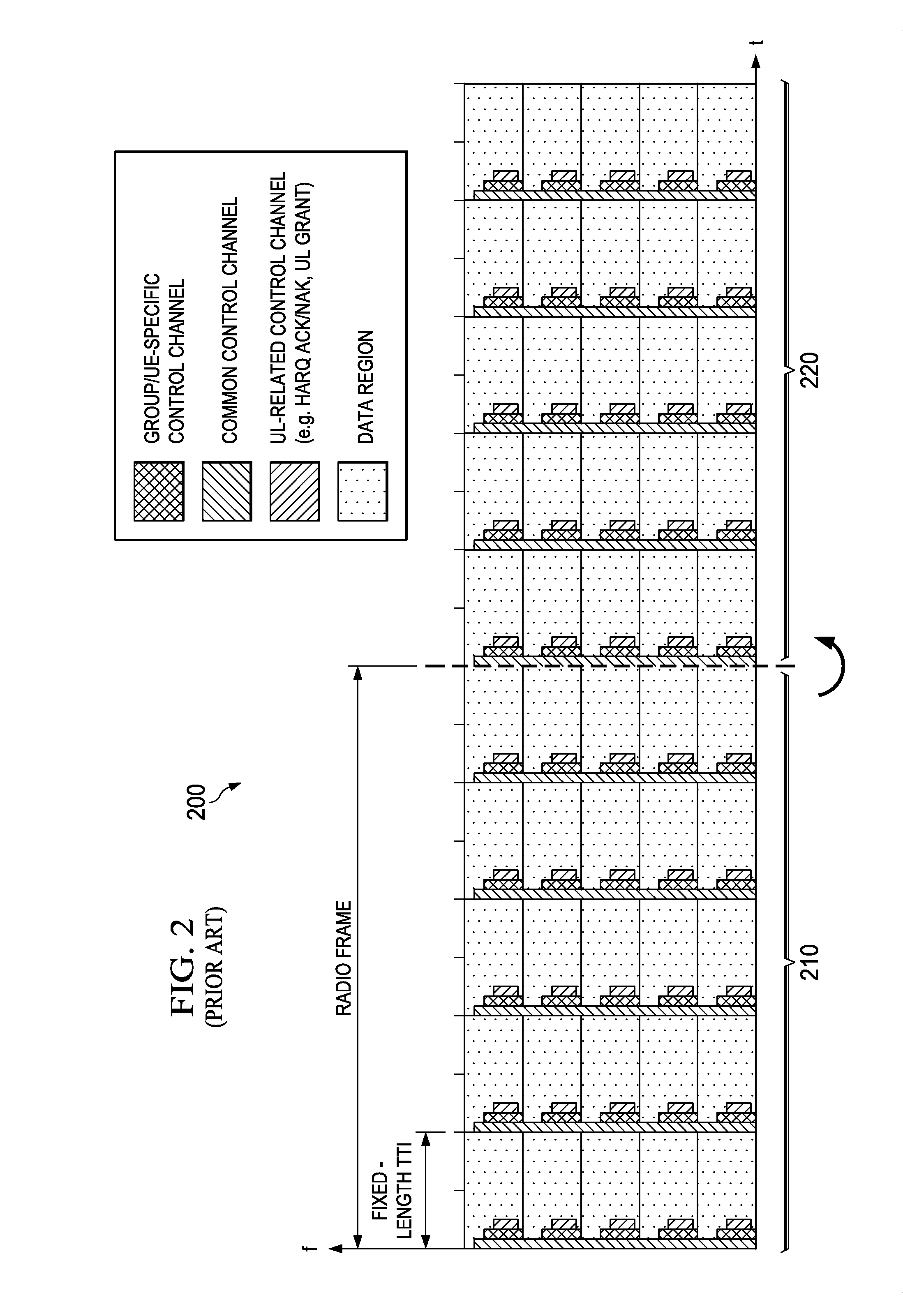
Methods and devices are provided for communicating data in a wireless channel. In one example, a method includes adapting the transmission time interval (TTI) length of transport container for transmitting data in accordance with a criteria. The criteria may include (but is not limited to) a latency requirement of the data, a buffer size associated with the data, a mobility characteristic of a device that will receive the data. The TTI lengths may be manipulated for a variety of reasons, such as for reducing overhead, satisfy quality of service (QoS) requirements, maximize network throughput, etc. In some embodiments, TTIs having different TTI lengths may be carried in a common radio frame. In other embodiments, the wireless channel may partitioned into multiple bands each of which carrying (exclusively or otherwise) TTIs having a certain TTI length.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
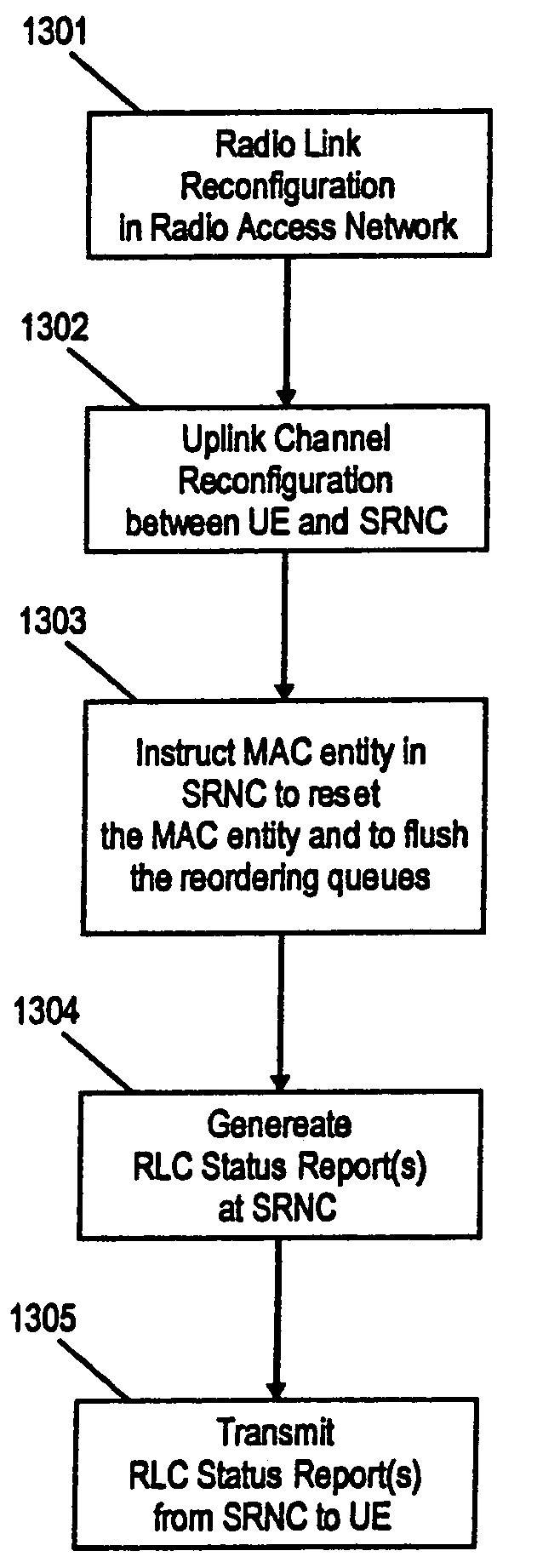
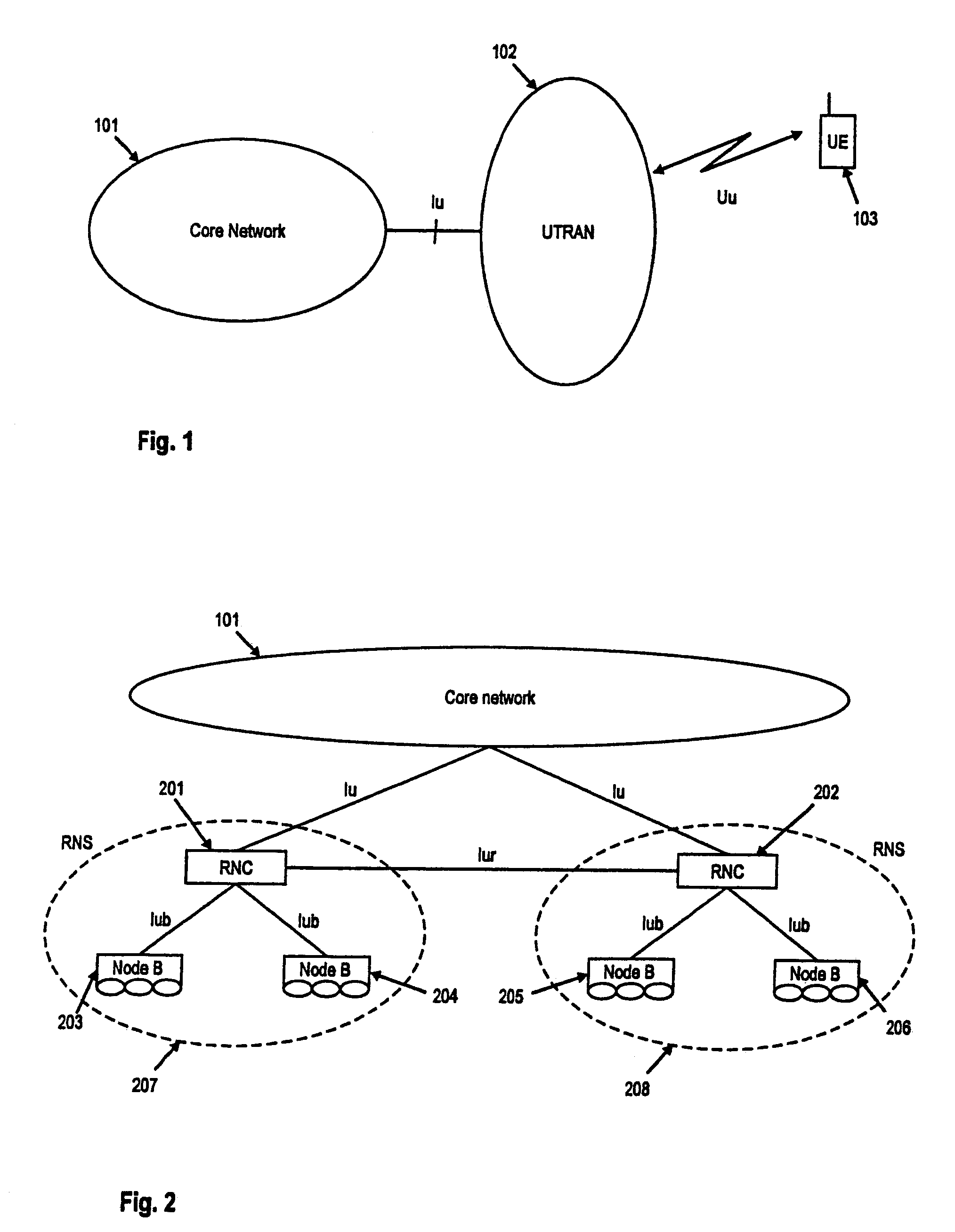
MAC layer reconfiguration in a mobile communication system
ActiveUS20070047452A1Effective controlEfficient triggerError preventionTransmission systemsRadio access networkMobile communication systems
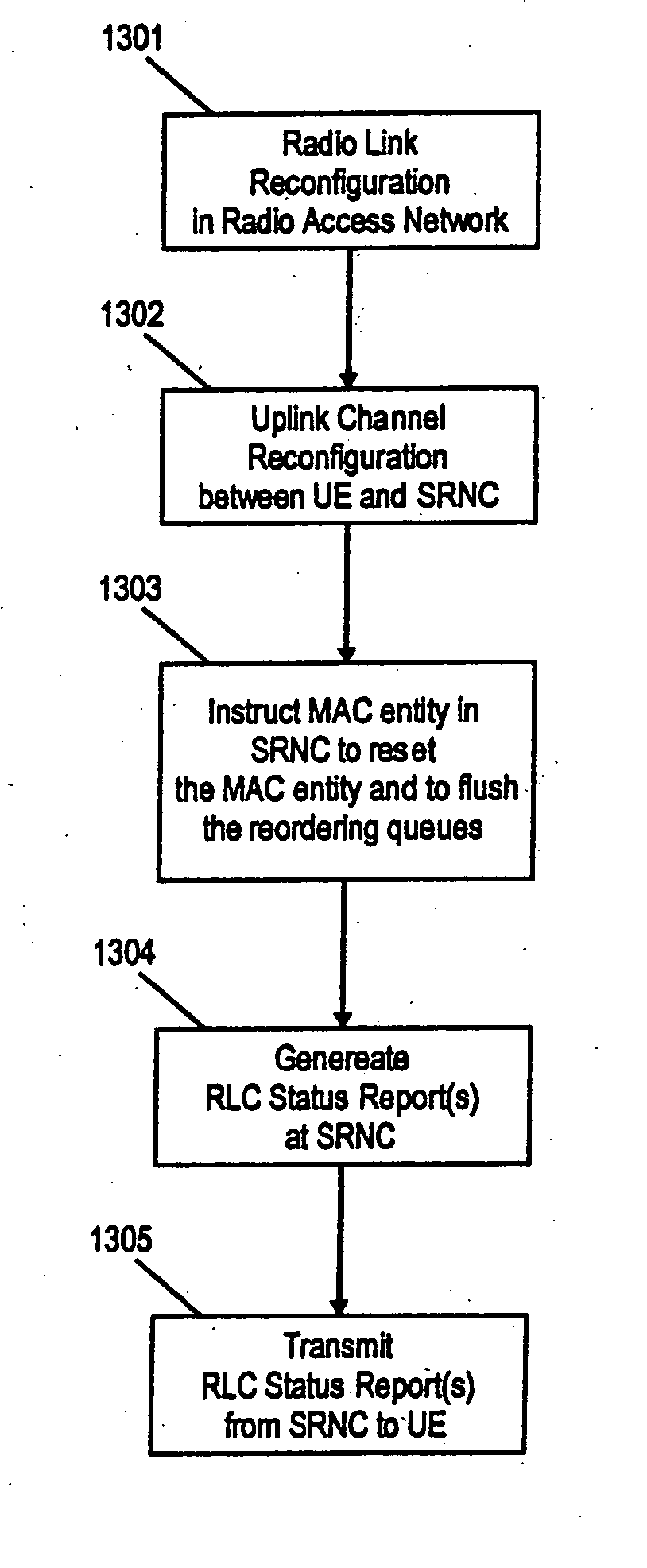
The invention relates to method and apparatus for reconfiguring a MAC entity of a MAC layer of the apparatus receiving protocol data units from a mobile terminal via on uplink upon reconfiguration of the uplink channel. Further, the invention relates to methods and mobile terminals for triggering the transmission of a status report from an RLC entity configured for an uplink channel of a network element in a radio access network, as well as a method and terminal for configuring the MAC layer of the mobile terminal. In order to enable an efficient and fast generation of RLC status reports after an uplink channel reconfiguration the invention suggests new mechanisms to trigger the transmission of status reports upon uplink reconfiguration as well a new operation and configuration of radio access network elements and UEs upon uplink channel reconfiguration, in particular a transmission time interval (TTI) reconfiguration.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
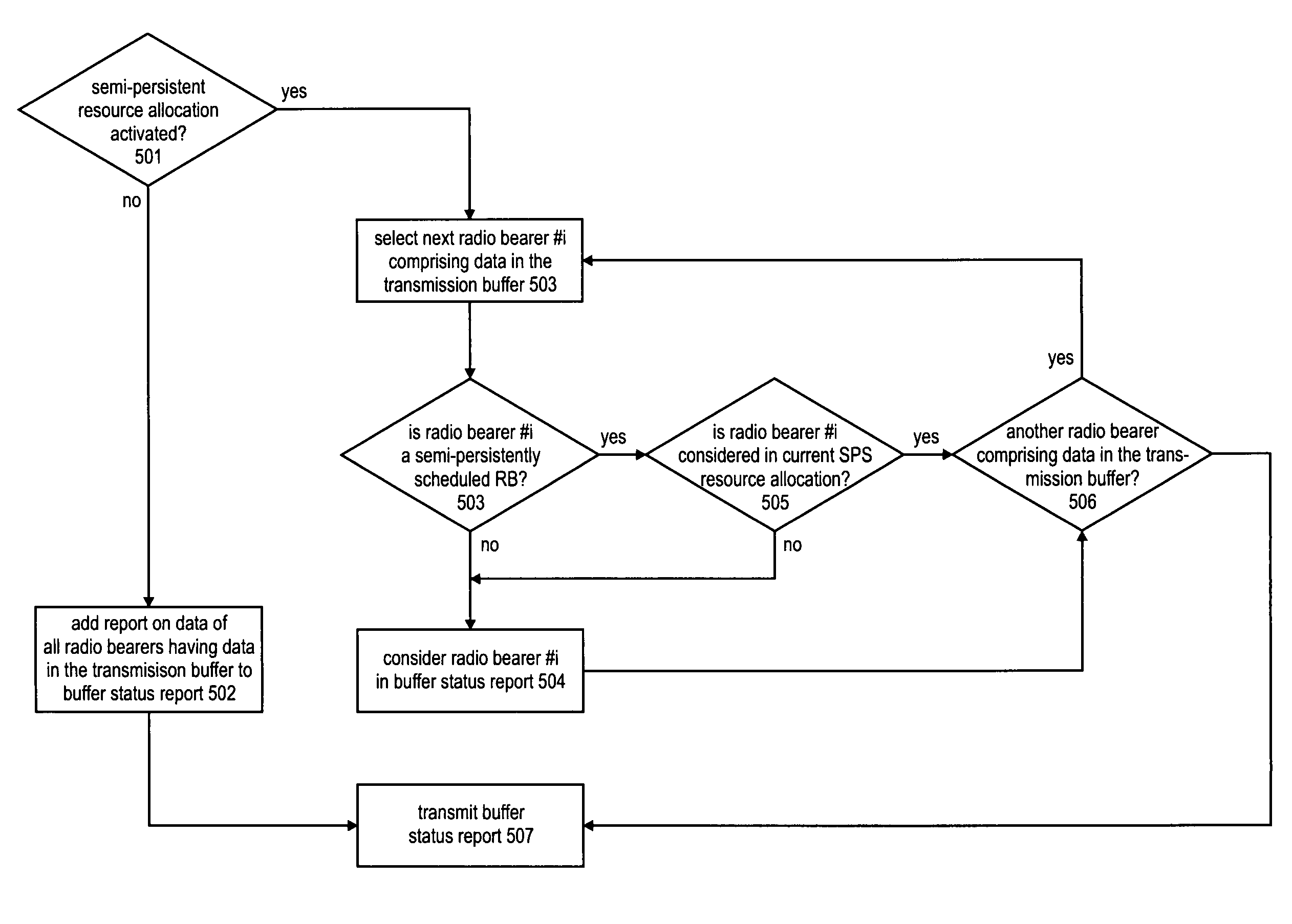
Buffer status reporting in a mobile communication system
ActiveUS20120069805A1Good effectOptimize schedulingNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission path multiple useRelevant informationMobile communication systems
The invention relates to methods for transmitting a buffer status report (BSR) in a mobile communication system, more particularly to the definition of rules for triggering, generating and transmitting buffer status reports. The invention also relates to a data transmission method utilizing new rules to decide data of which radio bearers is transmitted within a given transmission time interval. Moreover, the invention relates to scheduling method for radio resources that is taking into account additional scheduling—relevant information from the buffer status reporting and / or data transmission method. To avoid unnecessary grants from the network and to suggest an advanced handling of data transmissions the invention suggests a buffer status reporting and data transmission schemes that take into account the scheduling mode of data of radio bearers pending for transmission to decide whether to report on it in a buffer status report, respectively, whether to multiplex the data to a transport block for transmission.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
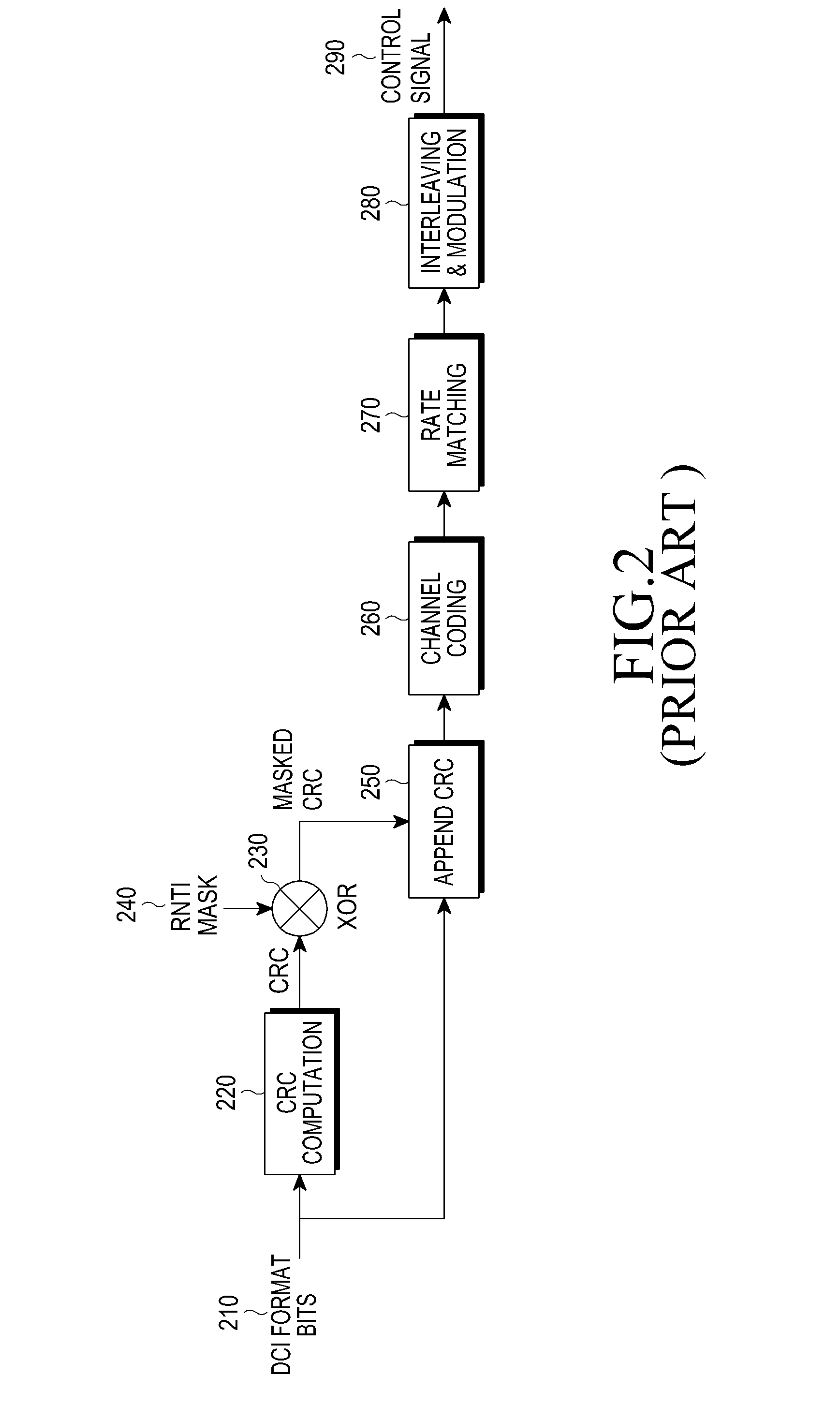
Two-stage pdcch with dci flag and dci format size indicator
ActiveUS20160128028A1Well formedError prevention/detection by using return channelReceiver specific arrangementsTelecommunicationsControl channel
Methods, systems, and devices are described for wireless communication employing two-stage control channel messaging. Systems, methods, and apparatuses for two stage two-stage physical downlink control channel (PDCCH) with a downlink control information (DCI) flag and DCI format size indicator are described. For instance, the present disclosure presents an example method of wireless communication at a wireless device, which may include receiving, at a first bandwidth and during a transmission time interval (TTI), a first control channel message. In addition, the example method may include determining, based on a flag in the first control channel message, whether a second control channel message is present in the TTI. Furthermore, the example method may include receiving, at a second bandwidth, the second control channel message where the flag indicates that the second control channel message is present for the TTI.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Mac layer reconfiguration in a mobile communication system
ActiveUS20080008152A1Error preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio access networkMobile communication systems
The invention relates to method and apparatus for reconfiguring a MAC entity of a MAC layer of the apparatus receiving protocol data units from a mobile terminal via on uplink upon reconfiguration of the uplink channel. Further, the invention relates to methods and mobile terminals for triggering the transmission of a status report from an RLC entity configured for an uplink channel of a network element in a radio access network, as well as a method and terminal for configuring the MAC layer of the mobile terminal. In order to enable an efficient and fast generation of RLC status reports after an uplink channel reconfiguration the invention suggests new mechanisms to trigger the transmission of status reports upon uplink reconfiguration as well a new operation and configuration of radio access network elements and UEs upon uplink channel reconfiguration, in particular a transmission time interval (TTI) reconfiguration.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
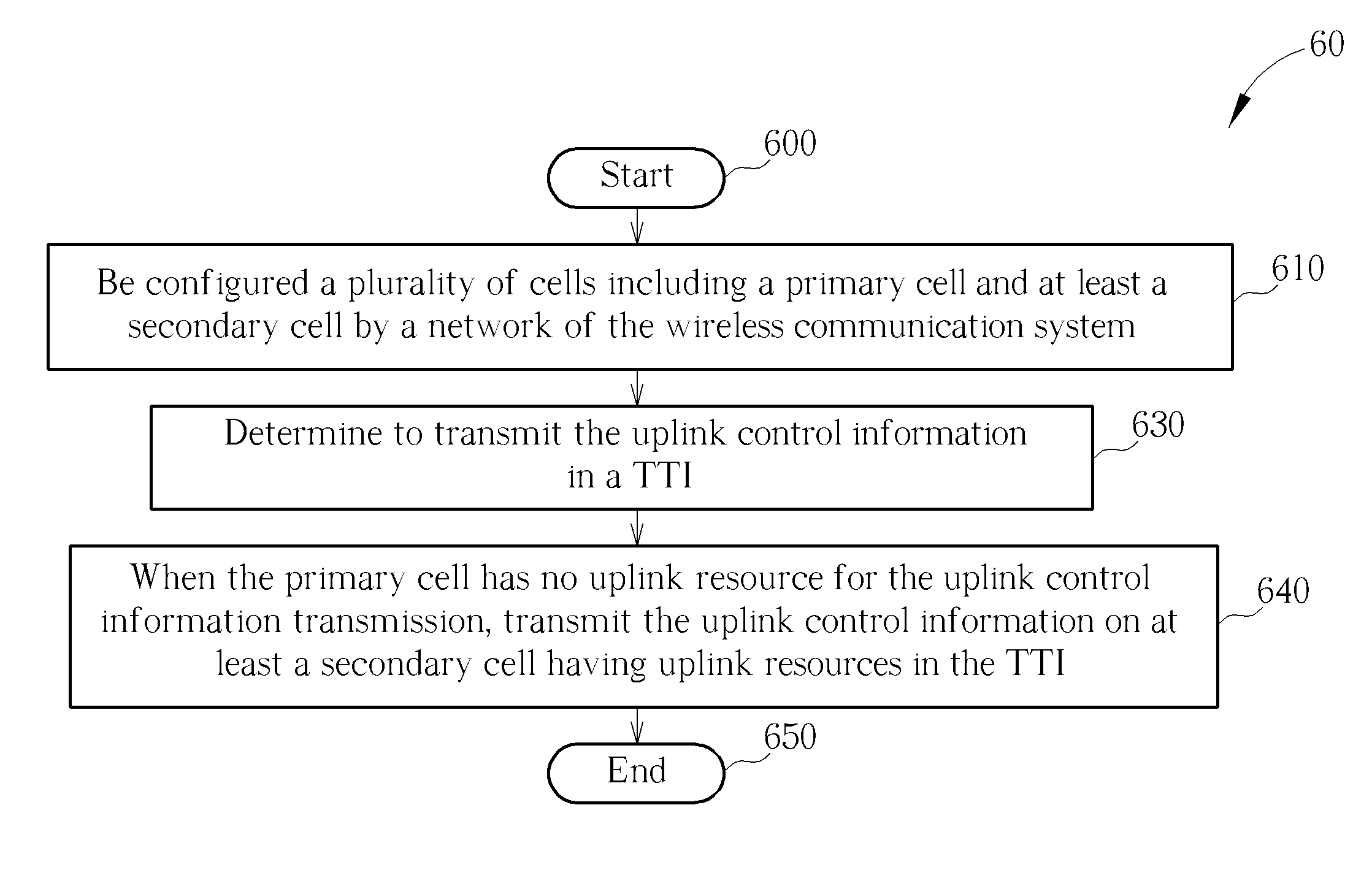
Method of Uplink Control Information Transmission
ActiveUS20130039231A1Transmission be dropError preventionTransmission path divisionInformation transmissionCommunications system
A method of uplink control information transmission for a mobile device with carrier aggregation in a wireless communication system is disclosed. The method comprises being configured a plurality of cells including a primary cell and at least a secondary cell by a network of the wireless communication system, determining to transmit the uplink control information in a transmission time interval, and when the primary cell has no uplink resource for the uplink control information transmission, transmitting the uplink control information on at least a secondary cell having uplink resources in the TTI.
Owner:ACER INC
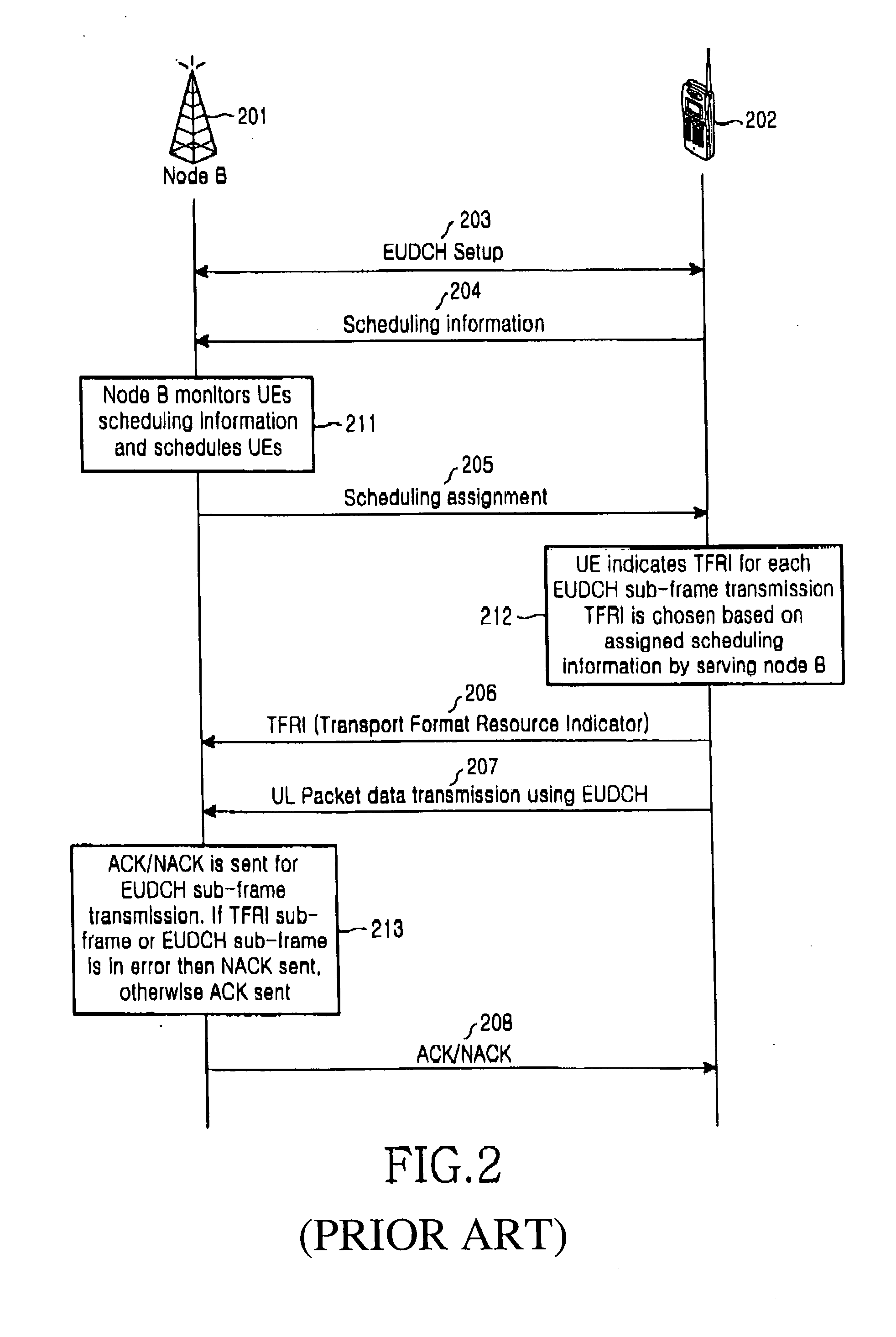
System and method for controlling a TTI in a W-CDMA communication system supporting enhanced uplink dedicated transport channel
InactiveUS20050073985A1Error preventionRadio transmission for post communicationCommunications systemMobile communication systems
A system and a method for enabling a node B to control a transmission time interval (TTI) in consideration of radio resources of a cell, a channel environment of a UE, and a buffer state of the UE, in an asynchronous wideband code division multiple access (W-CDMA) mobile communication system that supports a packet data service through an enhanced uplink dedicated transport channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multiplexing scheme in a communication system
ActiveUS20070177631A1Interference minimizationPerformance maximizationSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationSimultaneous amplitude and angle demodulationMultiplexingCommunications system
A method for multiplexing communication resources to multiple users in a communication system having no network resource planning. The method includes the steps of: generating a generic time-frequency (T-F) mapping pattern (TFPgeneric), generating a set of orthogonal T-F mapping patterns from said generic T-F mapping pattern (TFPgeneric), performing a random variable cyclic offsetting of said set of orthogonal T-F mapping patterns in each transmission time interval (TTI), and allocating the orthogonal T-F mapping patterns to the one or more users and / or traffic channels in each TTI. A transmitter for executing said multiplexing method, and a system including such transmitters, are also disclosed.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Flexible multiplexing and feedback for variable transmission time intervals
ActiveUS20160119948A1Improve latencyError prevention/detection by using return channelSignal allocationMultiplexingHybrid automatic repeat request
Methods, systems, and devices for wireless communication are described. A base station may employ a multiplexing configuration based on latency and efficiency considerations. The base station may transmit a resource grant, a signal indicating the length of a downlink (DL) transmission time interval (TTI), and a signal indicating the length of a subsequent uplink (UL) TTI to one or more user equipment (UEs). The base station may dynamically select a new multiplexing configuration by, for example, setting the length of an UL TTI to zero or assigning multiple UEs resources in the same DL TTI. Latency may also be reduced by employing block feedback, such as block hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) feedback. A UE may determine and transmit HARQ feedback for each transport block (TB) of a set of TBs, which may be based on a time duration of a downlink TTI.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Device, system and method employing unified flexible 5g air interface
ActiveUS20180007673A1Modulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionRadio access technologyTelecommunications
An eNodeB (eNB), user equipment (UE) and method of providing a flexible Radio Access Technology (FRAT) are generally described. The information (resource allocation, partition information and numerology) of at least one of a plurality of RATs used by the eNB is provided to a UE. Each RAT has a flexible subcarrier spacing and symbol duration, which are integer multiples of a base subcarrier spacing and symbol duration, and is associated with at least one of different temporal and frequency resources. The symbol and / or frame structure of each RAT are independent. A Transmission Time Interval (TTI) boundary between the RATs is common, and the RATs comprise a common reference TTI duration. The information of the RATs is provided either via a different RAT than the RAT used by the UE for communication or via a dedicated carrier in the RAT used by the UE for communication.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method for transmitting data in wireless communication system
InactiveUS20100260164A1Improve data transfer efficiencyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemRadio resource
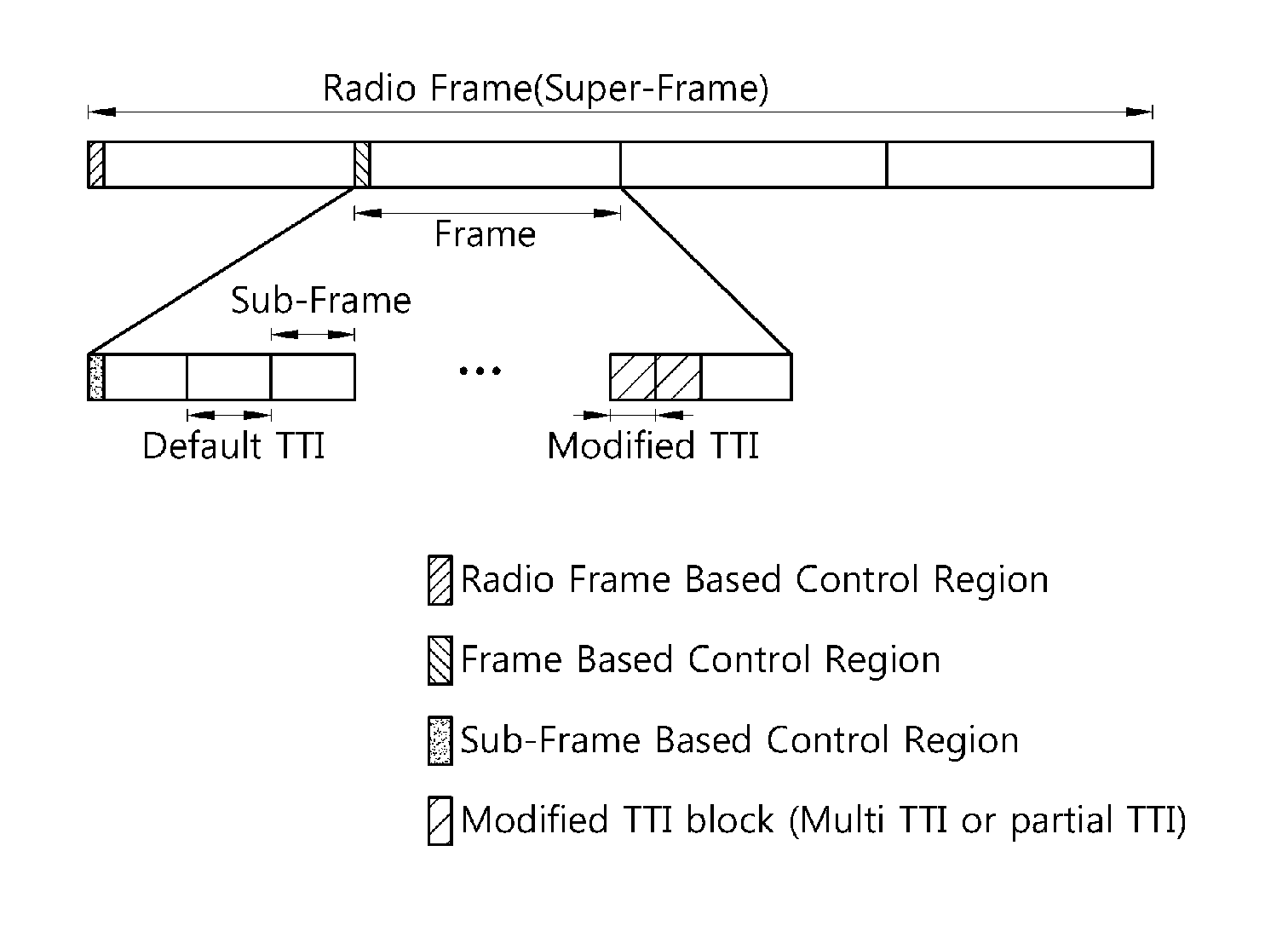
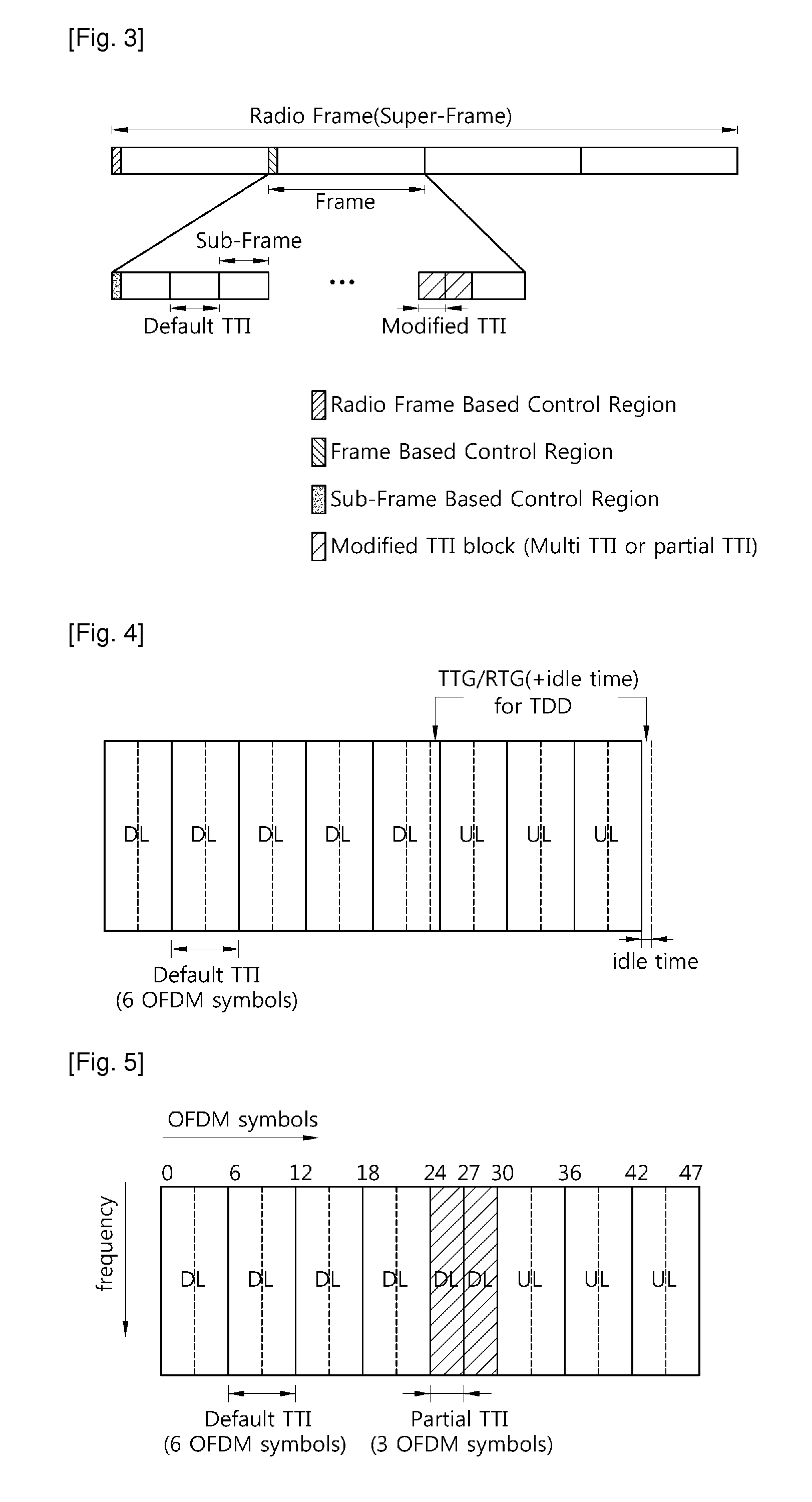
A method for transmitting data in a wireless communication system is provided. The method includes: transmitting first data through a radio resource allocated in a unit of a default transmission time interval (TTI) including at least one sub-frame in a frame including a plurality of sub-frames consisting of a plurality of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) symbols; and transmitting second data through a radio resource allocated in a unit of a modified TTI obtained by changing the number of sub-frames included in the default TTI in the frame.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
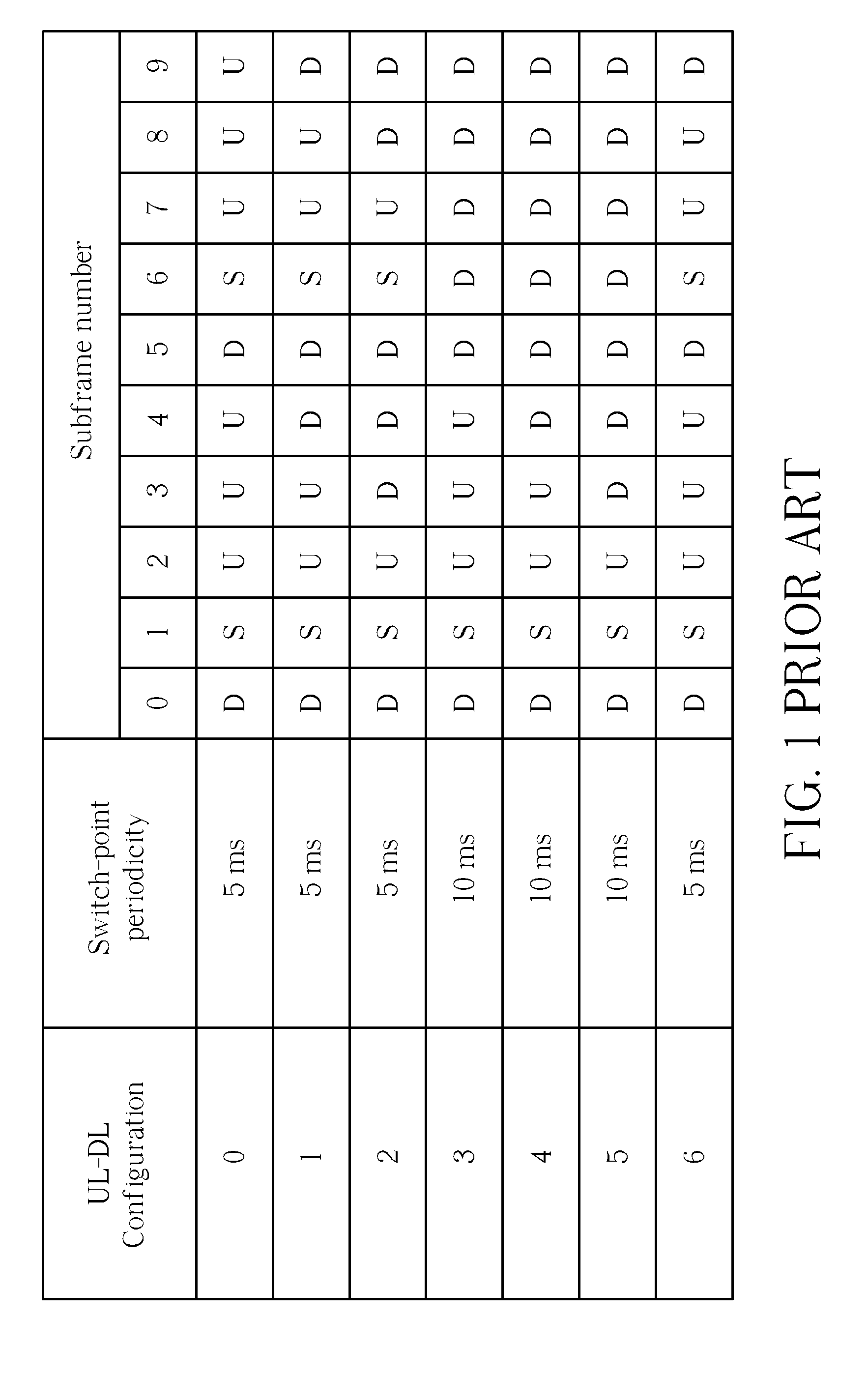
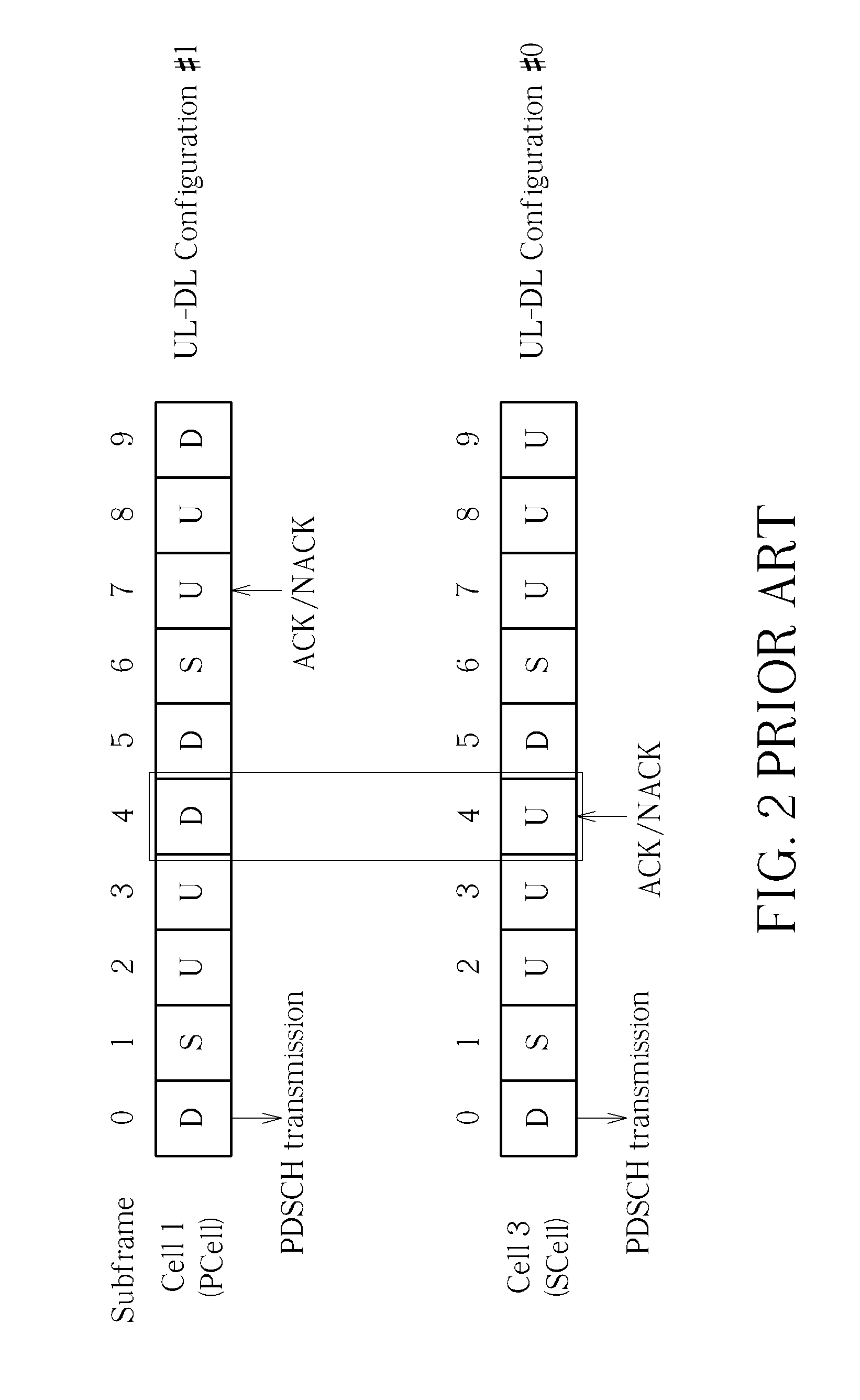
Generation of harq-ack information and power control of harq-ack signals in TDD systems with downlink of carrier aggregation
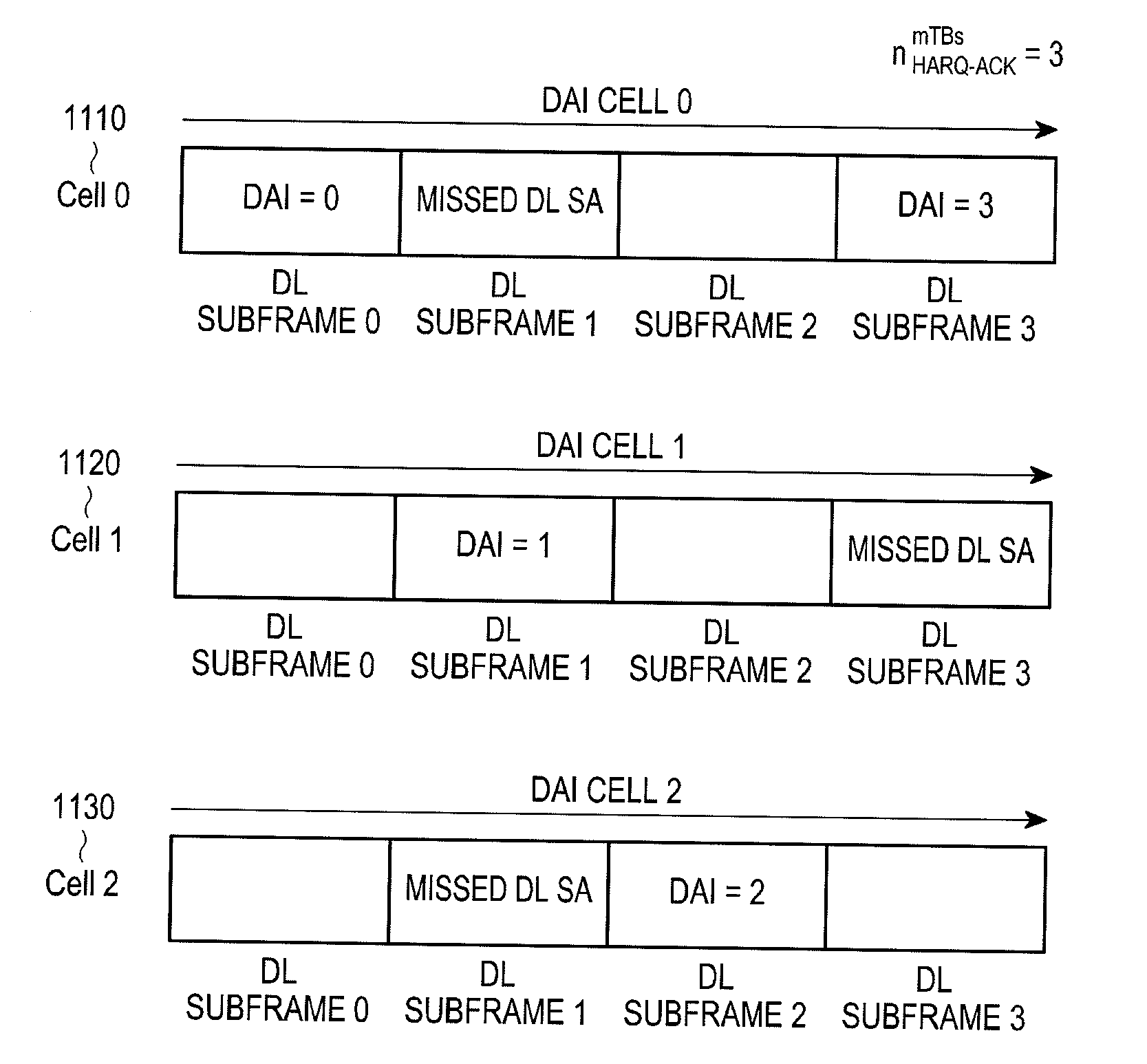
Methods and apparatus are provided for a User Equipment (UE) configured to have multiple cells in a DownLink (DL) of a Time Division Duplex (TDD) communication system so as to determine a power of an acknowledgement signal that the UE transmits in a control channel and to determine a number of acknowledgement information bits that the UE multiplexes with data information bits in a data channel. A transmission power of the control signal is determined based on DL Assignment Index (DAI) Information Elements (IEs) in DL Scheduling Assignments (SAs) that the UE detects through multiple transmission time intervals and through the multiple configured DL cells. The number of acknowledgement information bits in the data channel is determined based on a DAI IE of an UpLink (UL) SA associated with the transmission of the data channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Processing unexpected transmission interruptions in a wireless communications system
InactiveUS6904016B2Avoid dangerError preventionTransmission systemsCommunications systemRadio Link Control
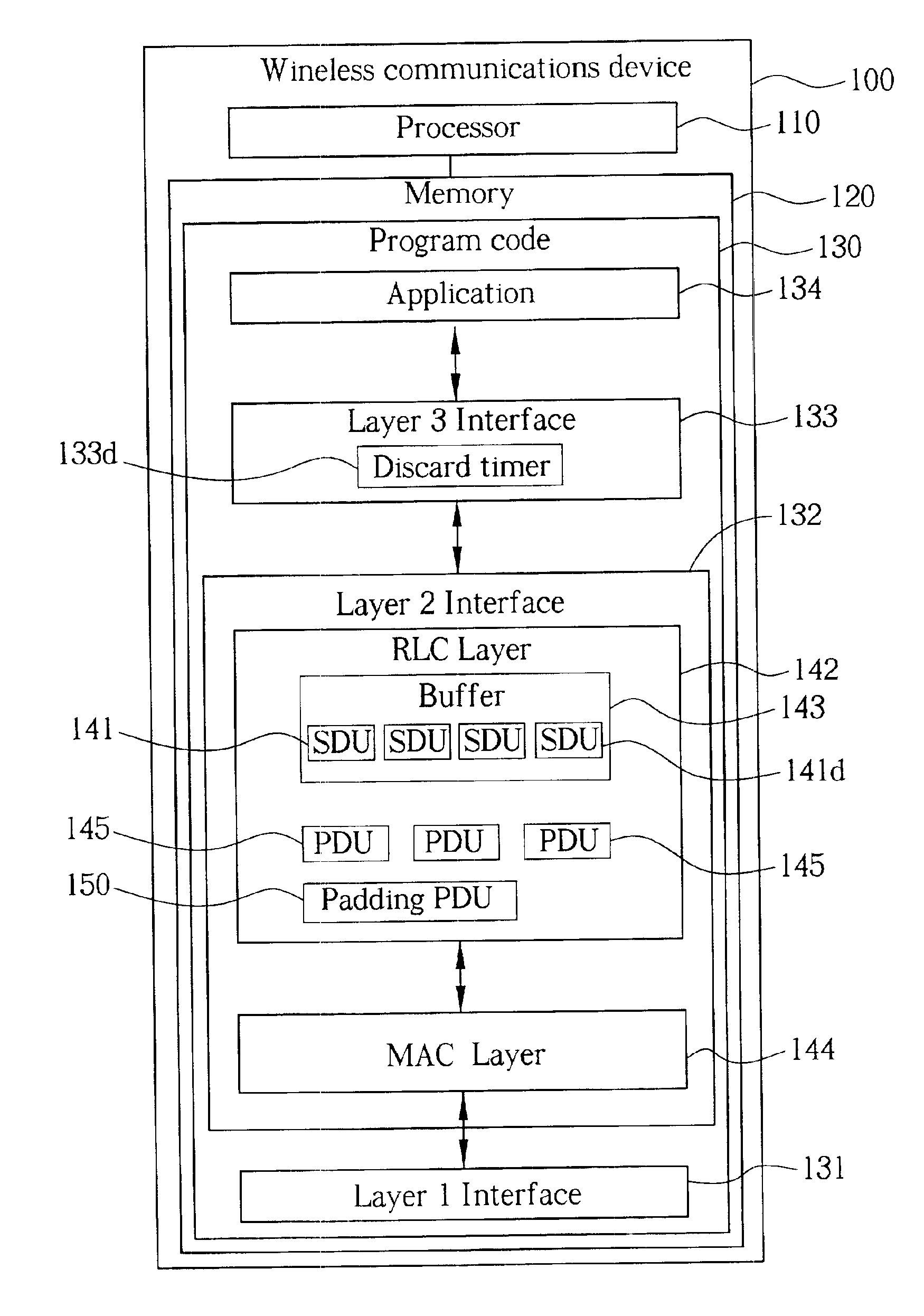
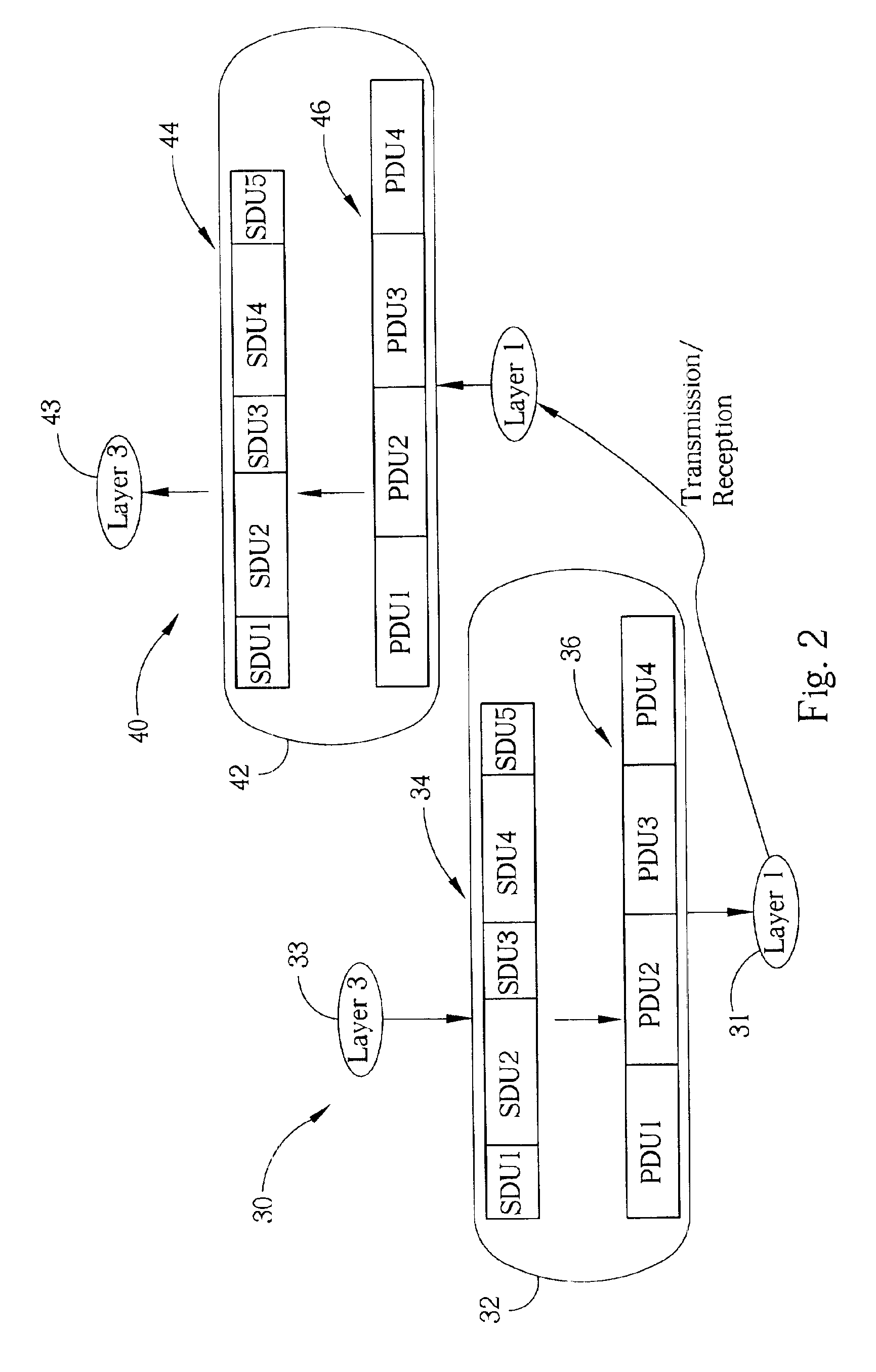
A radio link control (RLC) layer provides RLC entity information to a medium access control (MAC) layer. The RLC entity information indicates that the RLC layer has service data unit (SDU) data to be transmitted. After providing the RLC entity information, the RLC layer receives an unexpected data interruption that requires the RLC layer to discard or interrupt transmitting the SDU data. After the unexpected data interruption, the MAC layer requests at least a protocol data unit (PDU) from the RLC layer in response to the RLC entity information. The RLC layer then submits to the MAC layer at least one padding PDU in response to the MAC request. The padding PDU is submitted in place of the discarded SDU data. Alternatively, the affected SDU data is not discarded until the next transmission time interval (TTI).
Owner:L2 MOBILE TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for scheduling uplink data transmission using UE-ID in a mobile communication system supporting uplink packet data service
ActiveUS20060114877A1Minimize signaling overheadEffectively transmitting a scheduling grantTransmission systemsNetwork traffic/resource managementData rateMobile communication systems
A method and apparatus for controlling an uplink data rate, without increasing downlink signaling overhead, in a mobile communication system that supports an uplink packet data service. A Node B transmits an Absolute grants (AG) using one of first and second IDs to a User Equipment (UE). Upon receipt of an AG with the first UE-ID, the UE transmits uplink data within an allowed maximum data rate indicated by the AG and receives a Relative Rrant (RG) in the next Transmission Time Interval (TTI). Upon receipt of an AG with the second UE-ID, the UE does not receive an RG.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Ack/nack transmission on pucch in lte-atdd with nxpdcch structure
InactiveUS20110141878A1Maximum transmissionImprove reliabilityFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsBundle methodTime domain
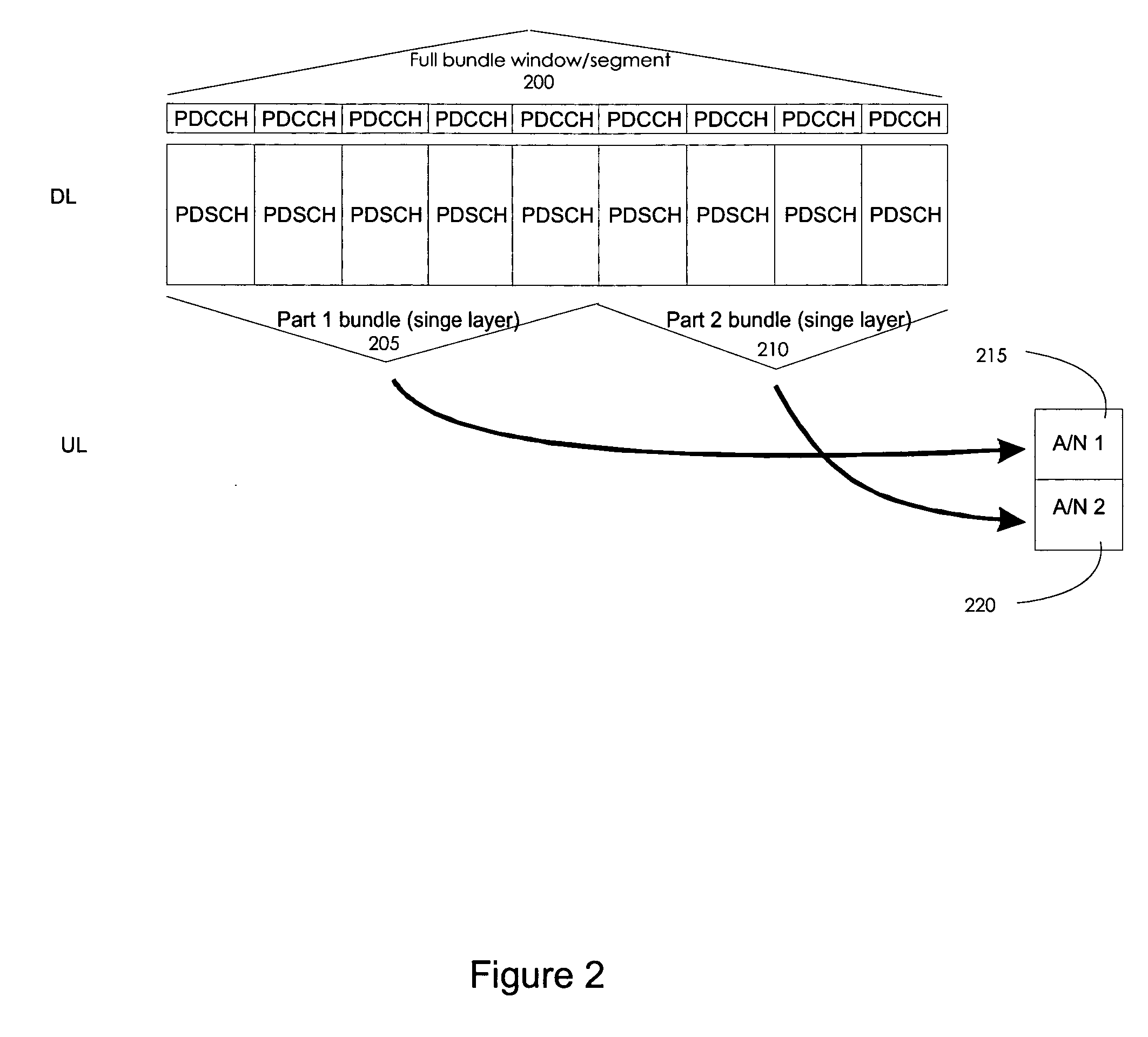
Systems and methods are provided for enabling different “bundling” methods for downlink transmissions and provide different interpretations of the acknowledgement / negative-acknowledgement bit. A user equipment is configured so that it commonly acknowledges all downlink transmission time intervals within a bundle so that if one packet is determined to be erroneous, all packets in that bundle will be retransmitted. Additionally, the systems and methods are implemented by allowing an interpretation to be applied to the uplink acknowledgement / negative-acknowledgement field such that the user equipment is able to divide bundled downlink packets into smaller windows in Long Term Evolution (LTE) Release 8 time division duplex (TDD) mode. In LTE Advanced (LTE-A) TDD mode, various embodiments provide bundling within the time domain, within the frequency domain, and within a hybrid time-frequency domain. Furthermore, enhanced channel selection methods are also provided in support of the above-mentioned bundling methods in accordance with various embodiments.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Method of performing random access procedure in wireless communication system
InactiveUS20100002590A1Reduce power consumptionError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemRadio networks
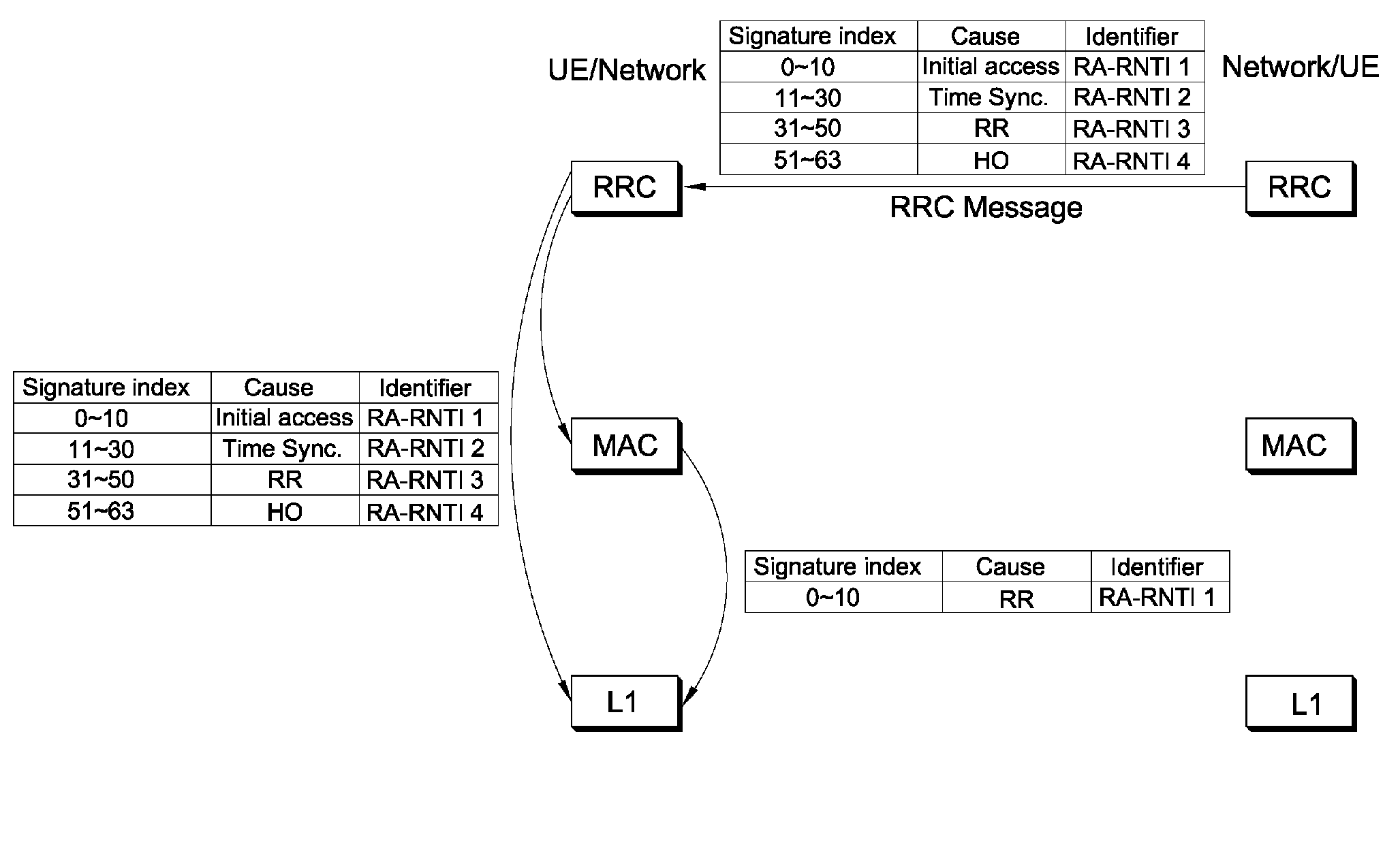
A method of performing a random access procedure in a wireless communication system is provided. The method includes transmitting a random access preamble, and monitoring a downlink control channel in a transmission time interval (TTI) window for a random access response, the TTI window comprising a plurality of TTIs, wherein a TTI is an interval to search a random access-radio network temporary identity (RA-RNTI) transmitted on the downlink control channel and monitoring the downlink control channel for the random access response is stopped when the random access response including an random access preamble identifier corresponding to the transmitted random access preamble is received.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method and Apparatus for Transmitting CSI on the PUSCH in an LTE System
ActiveUS20110032895A1Low amount of overhead signalingReduce controlAssess restrictionSignal allocationTelecommunicationsRadio resource
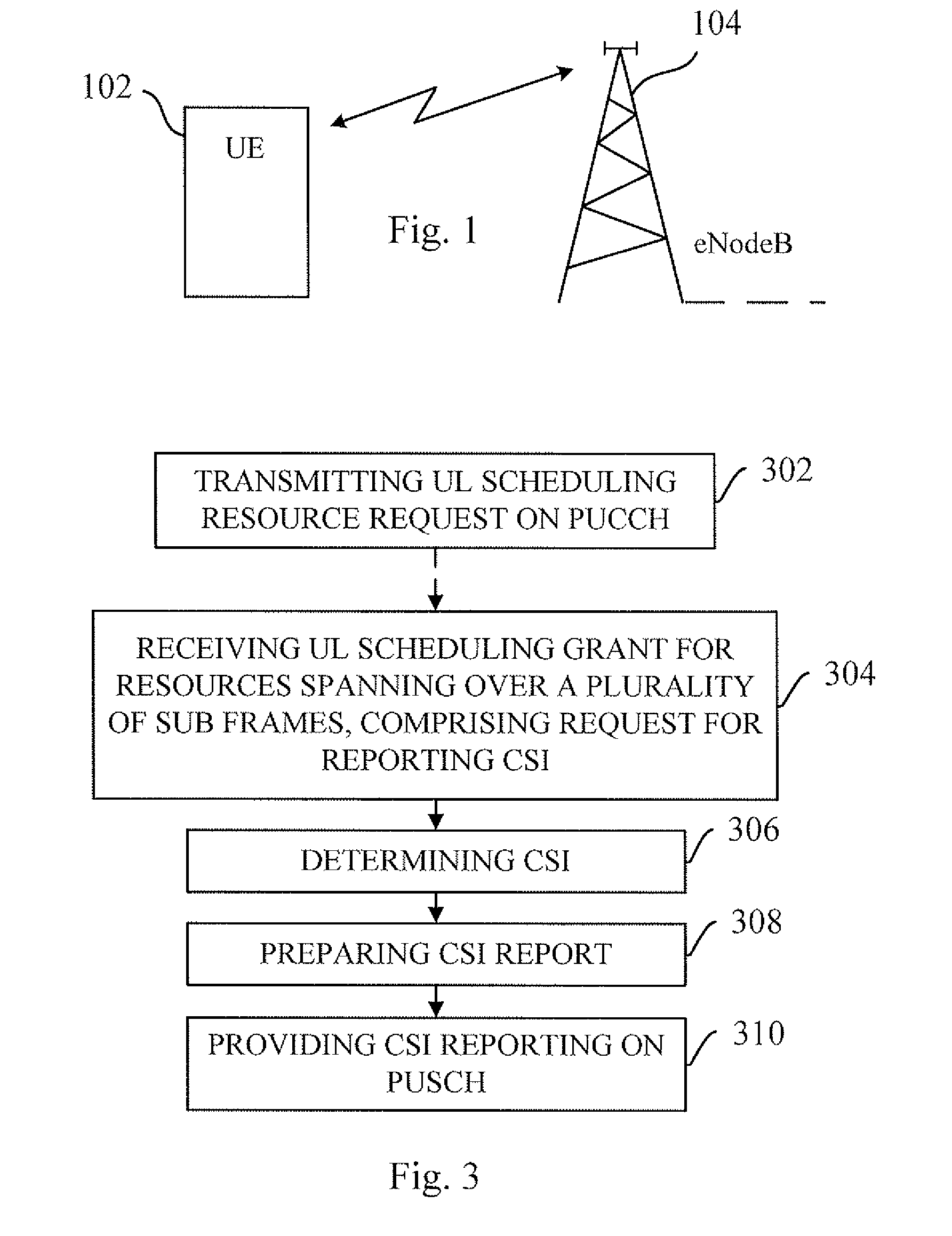
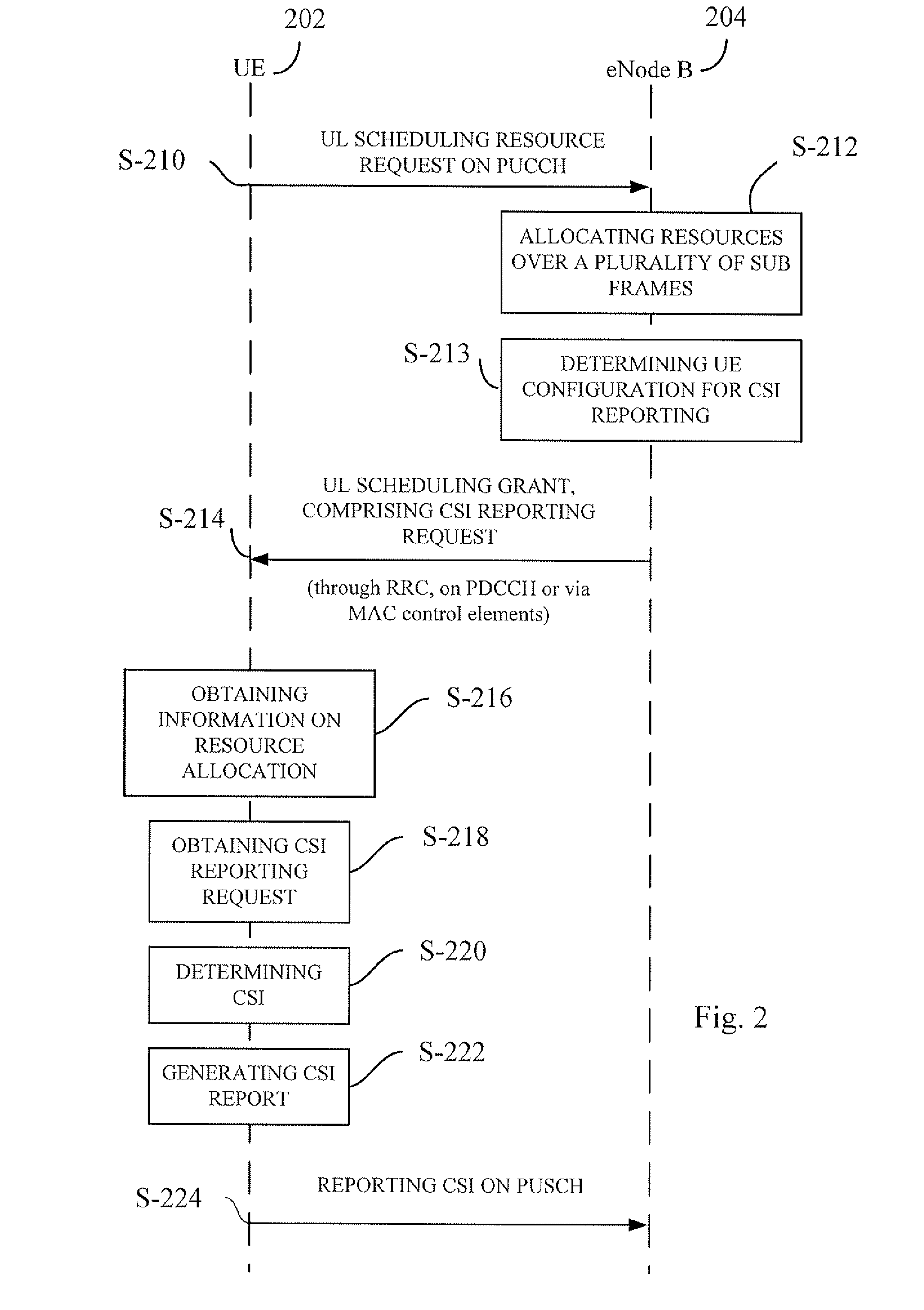
The present invention relates to allowing configuring CSI reporting (step S-224, 310) on radio resources that are allocated over a plurality of sub frames on Physical Uplink Shared Channel (PUSCH). Allocation of said radio resources (steps S-202, 404) can be performed by semi-persistent allocation or by using Transmission Time Interval (TTI) bundling. By using either semi-persistent scheduling or TTI-bundling as decided by an eNB (104, 204, 600) the UE (102, 202, 500) can be configured to report CSI (step S-224, 310) for a plurality of UL transmissions. By allocating radio resources by using semi-persistent scheduling, the signaling overhead, which can be substantial for dynamic scheduling of radio resources, decreases. By using TTI-bundling the coverage of the CSI-reports increases.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving different signal types in communication systems
ActiveUS20090034505A1Without consuming additional bandwidth resourcesWithout consuming additional bandwidth resourceModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionCommunications systemSounding reference signal
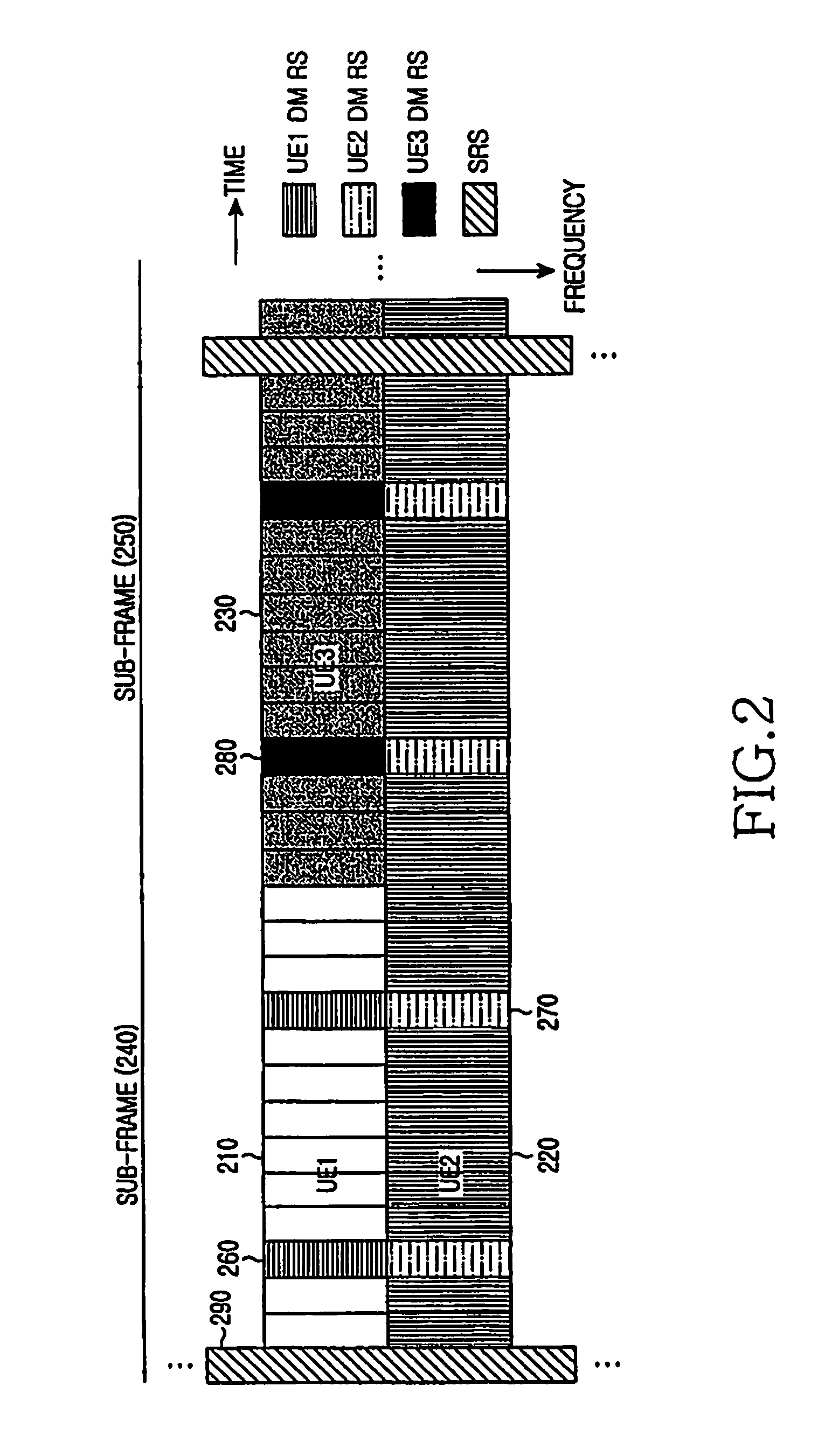
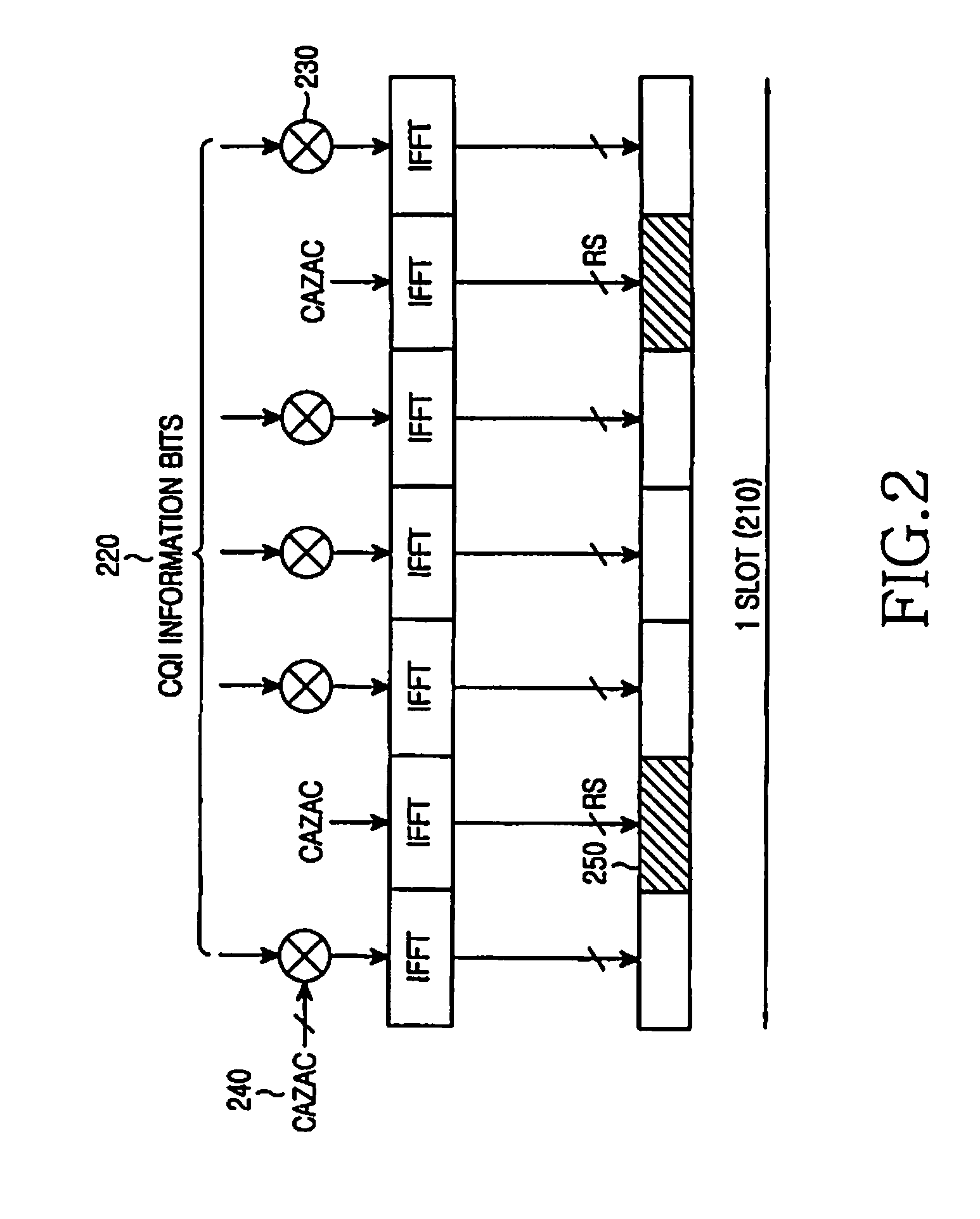
A method and apparatus for multiplexing a reference signal from a User Equipment (UE), not having any other signal transmission in the respective Transmission Time Interval (TTI), with a reference signal from another UE also having data transmission in the respective TTI, or with the control signal and reference signal from another UE transmitted in the respective TTI. The multiplexed reference signal from the UE not having any other signal transmission in the respective TTI can serve as a sounding reference signal to enable the serving base station to apply link adaptation to a subsequent signal transmitted by the UE or it can serve as a reference signal conveying state information, such as resource request or service request.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET INT LTD
Apparatus and method for transmitting of channel quality indicator and acknowledgement signals in sc-fdma communication systems
ActiveUS20090022135A1Robust system operationLoss of operationError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsMultiplexingCommunications system
A method and apparatus for multiplexing positive or negative acknowledgement signals (ACK or NACK, respectively) and channel quality indication (CQI) signals from a user equipment (UE) to a serving base station (Node B) during a CQI transmission time interval (TTI) in a single-carrier frequency division multiple access (SC-FDMA) communication system. The UE does not have simultaneous data transmission. The multiplexing of acknowledgement signals is implicitly achieved by the UE applying different orthogonal covers on the reference signal (RS) symbols transmitted in the CQI TTI, depending on whether the UE sends ACK or NACK. At the Node B receiver, the detection of ACK or NACK is based on the accumulated RS energy, after removing each of the possible orthogonal covers applied at the UE transmitter. For robust system performance, absence of ACK / NACK and NACK are mapped onto the same orthogonal cover.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Radio base station, user device, and method used in mobile communication system
ActiveUS20090245190A1Prevent orReduce complicationsData switching by path configurationWireless commuication servicesResource blockControl channel
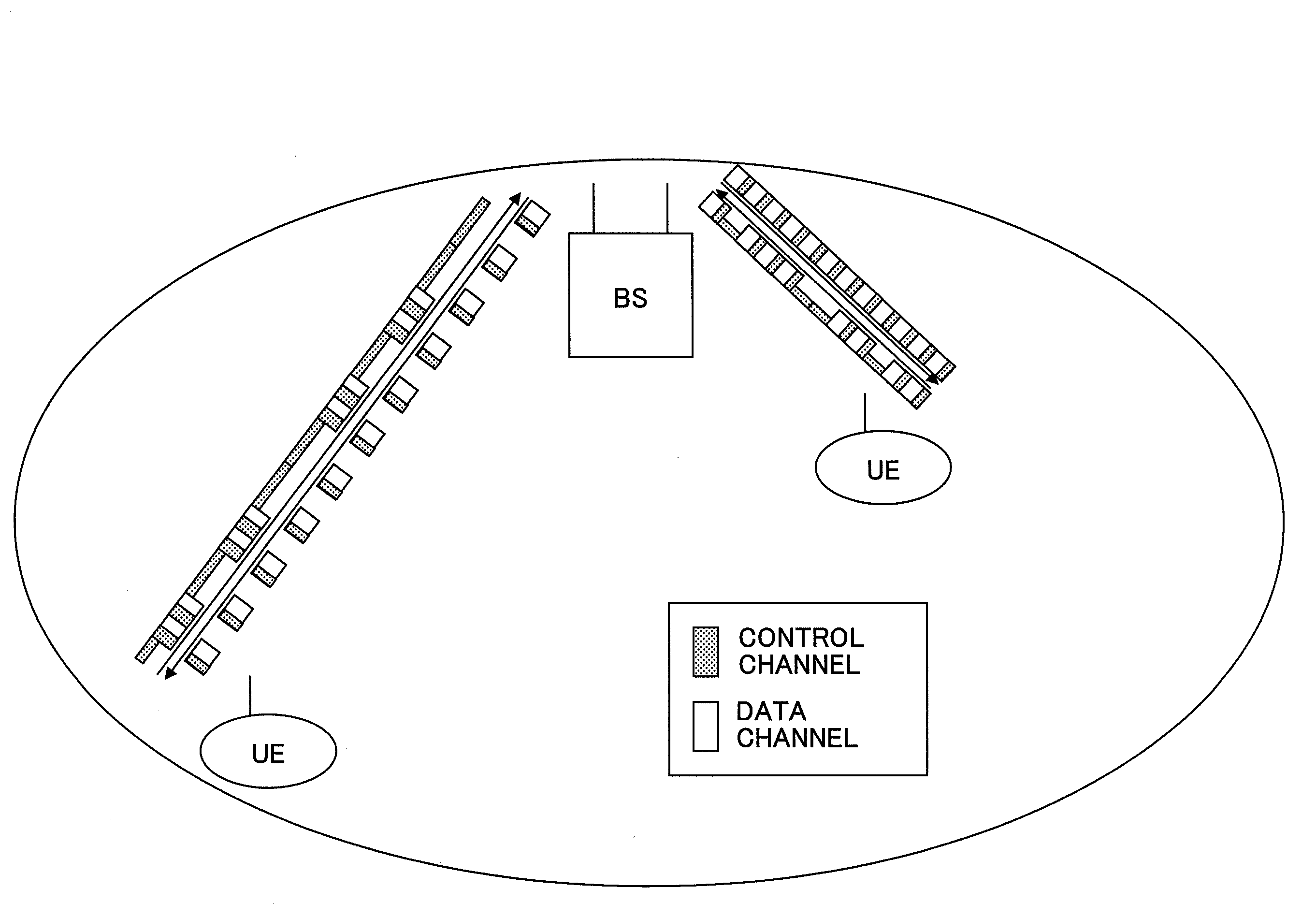
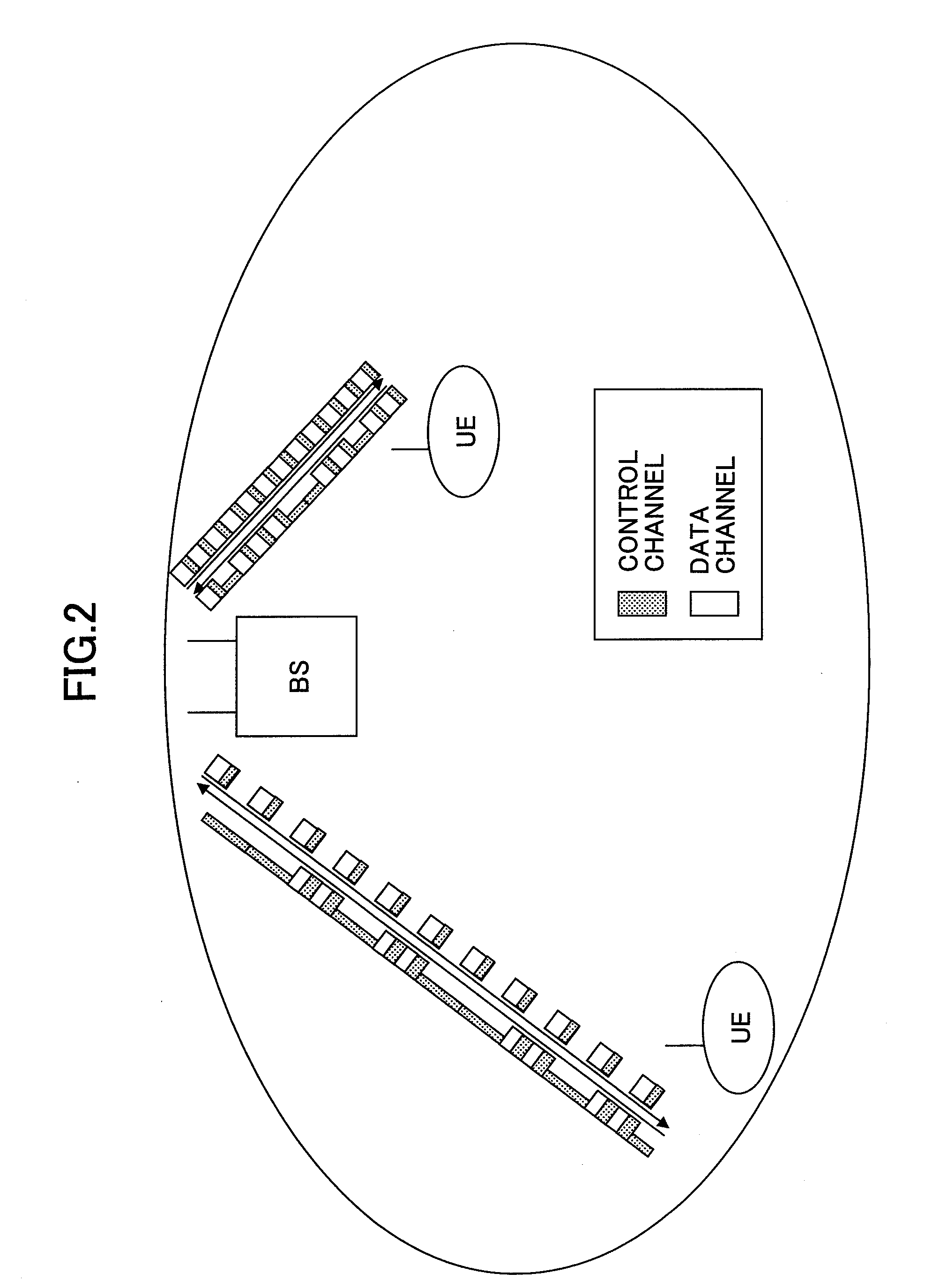
A radio base station used in a mobile communication system is disclosed. The radio base station includes a scheduler configured to allocate one or more resource blocks, which are defined by a predetermined bandwidth and a predetermined transmission time interval, to a user device; and a reporting unit configured to report scheduling information indicating radio resource allocation to the user device. The scheduler is configured to generate the scheduling information such that downlink data channels and downlink control channels are transmitted using the transmission time interval as a transmission unit and uplink control channels are transmitted using an integral multiple of the transmission time interval as a transmission unit.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
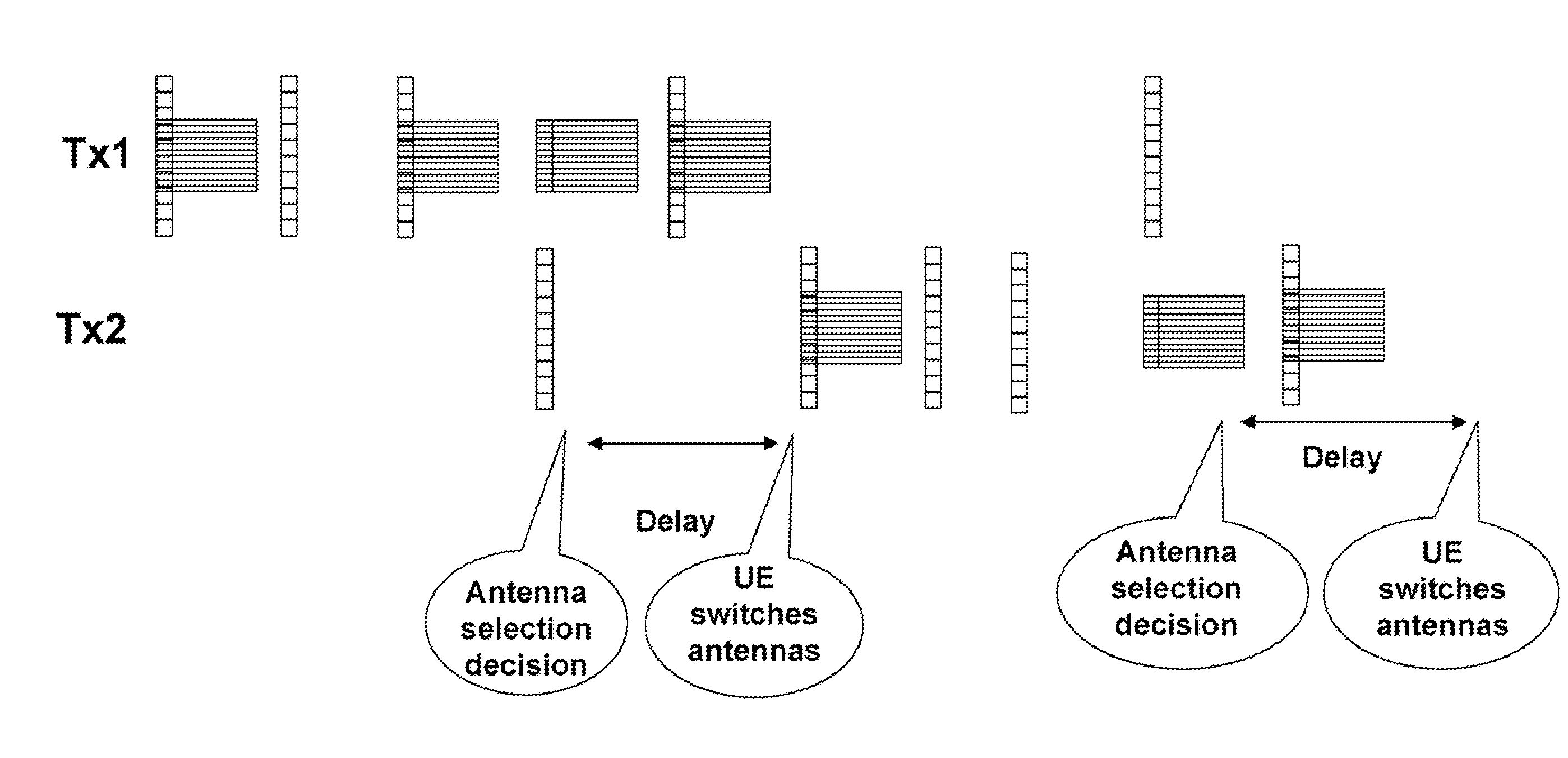
Method and System for Generating Antenna Selection Signals in Wireless Networks
ActiveUS20080232325A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionCommunications systemWireless network
A method and system generating signal to select a subset of antennas from a set of antennas to transmit user data in a wireless communication system. User data are transmitted during a first transmission time intervals (TTI) using a first subset of antennas. Pilot tones are transmitted during a second TTI using a second subset of antennas. Corresponding channels are estimated for the first subset of antennas and the second subset of antennas from the user data and the pilot tones. Then, based on the estimating, an optimal subset of antenna is selected from the first subset of antennas and the second subset of antennas to transmit the user data during a sequent TTI, and in which the selecting is performed adaptively.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
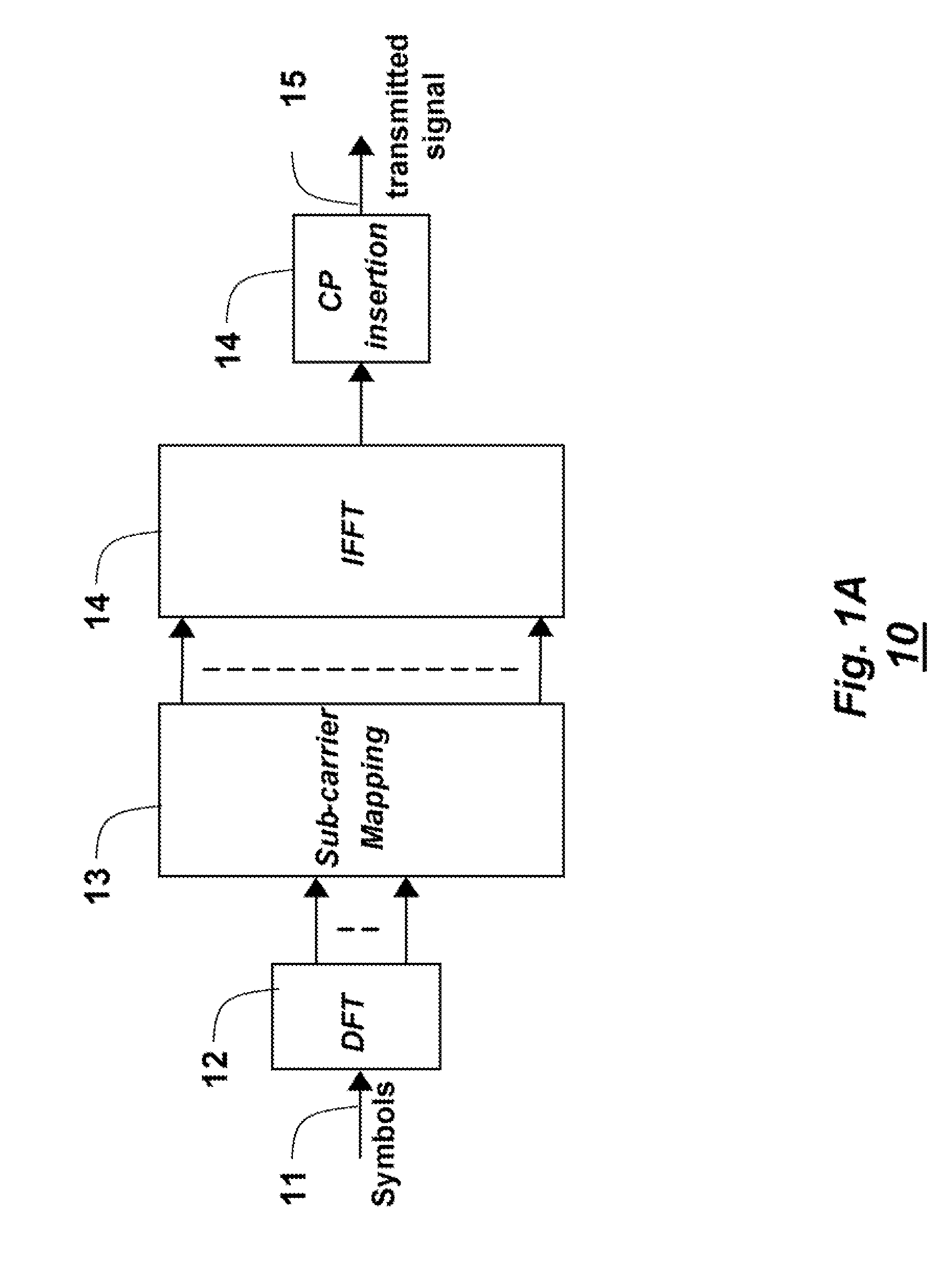
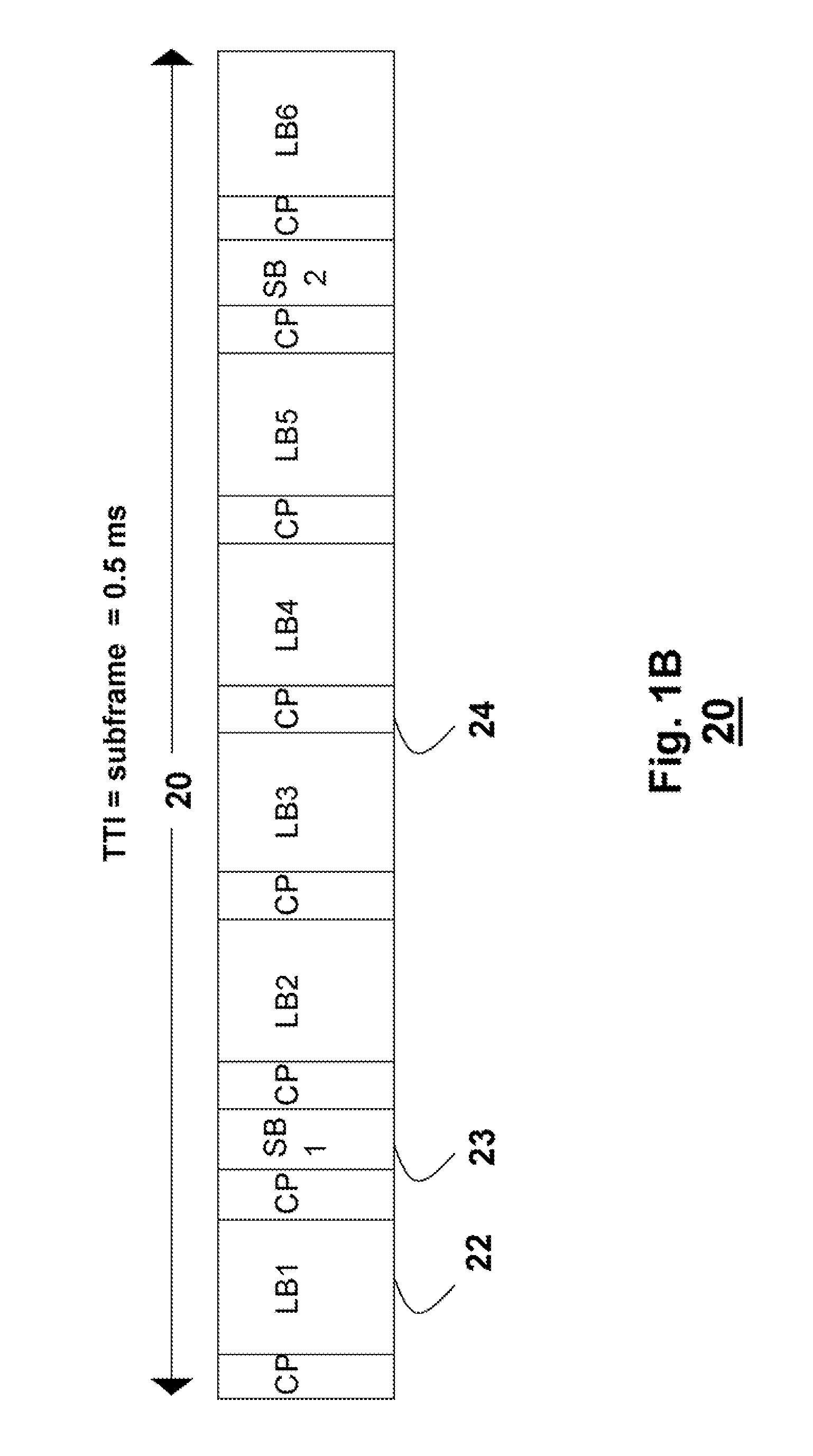
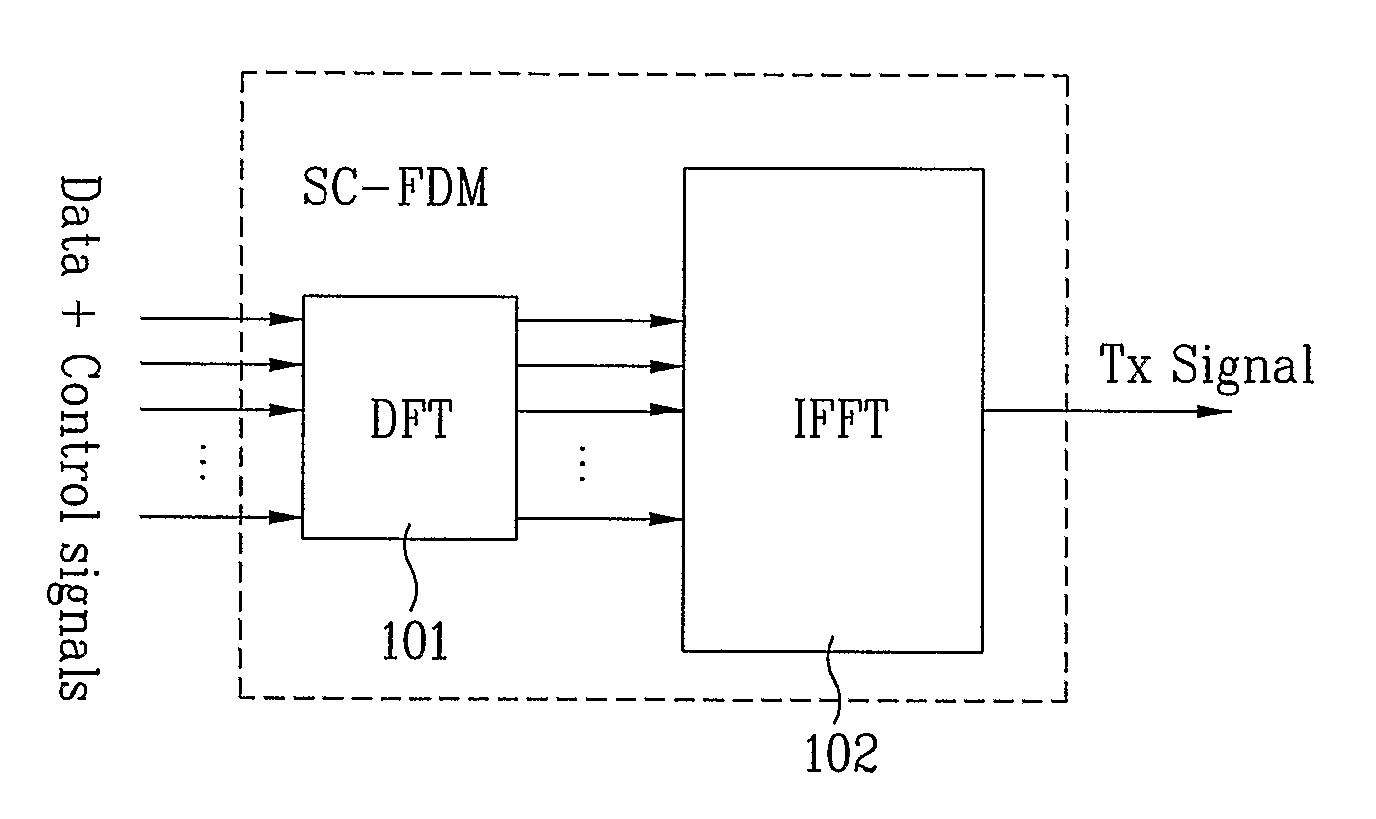
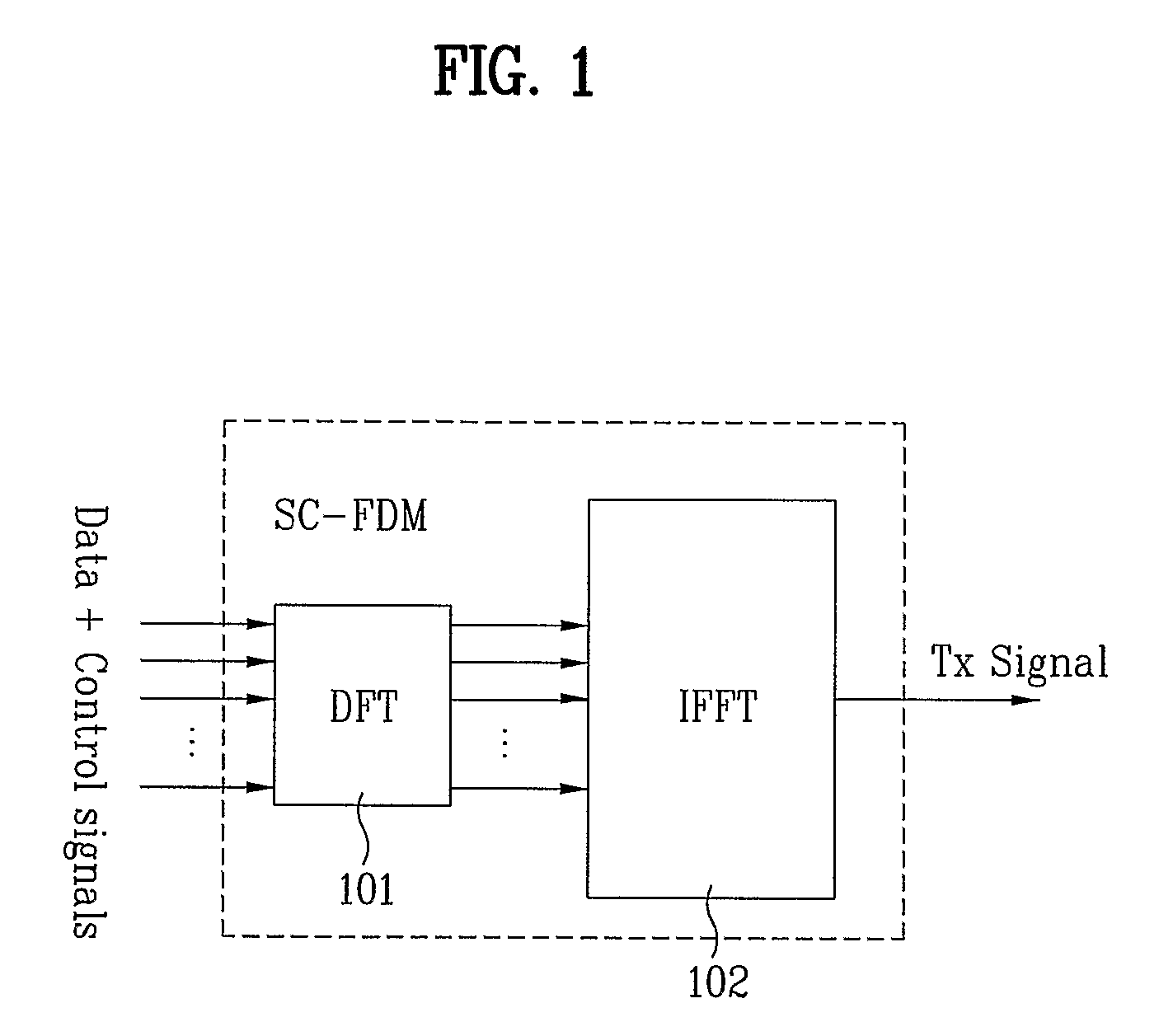
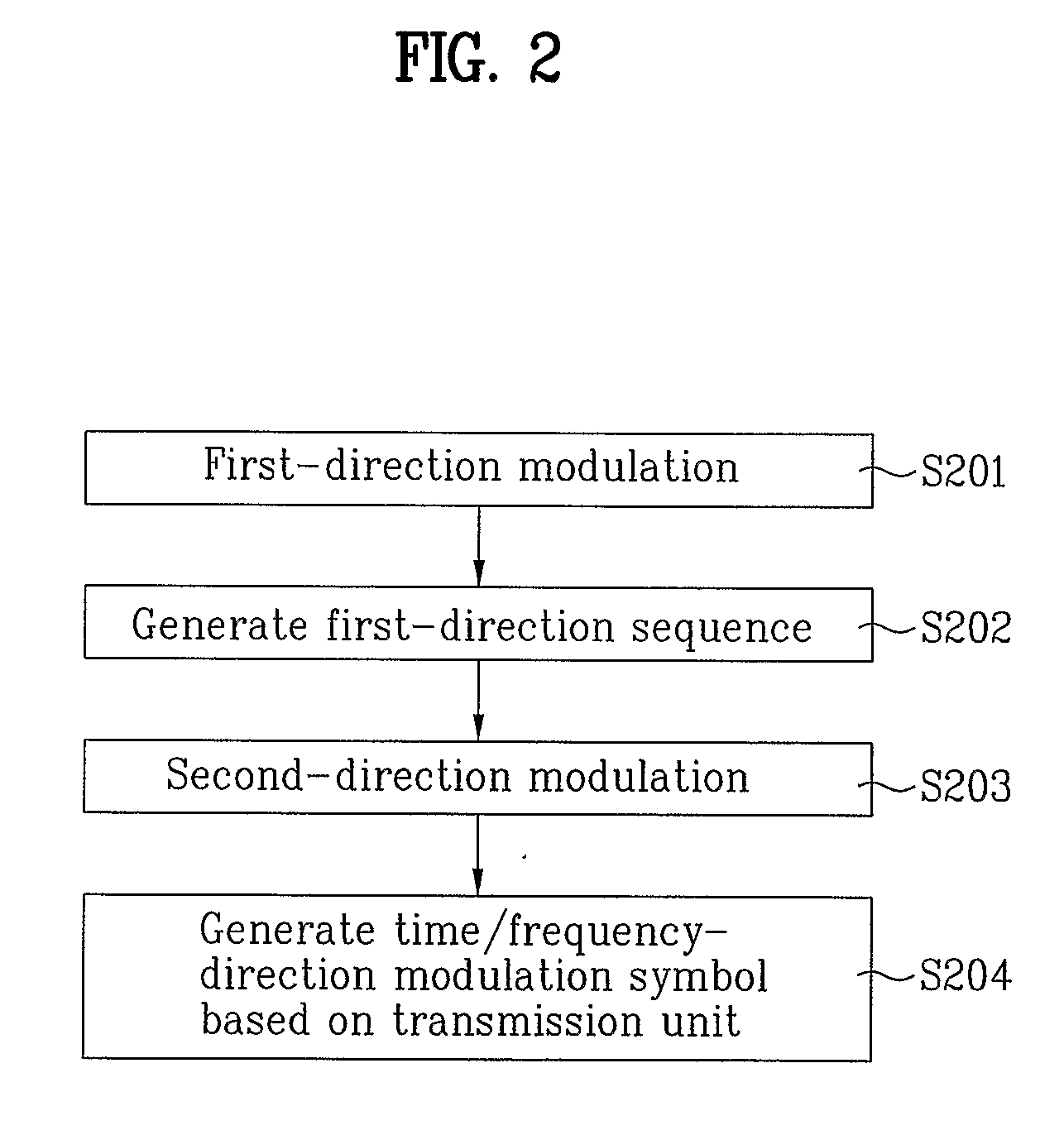
Sequence generation and transmission method based on time and frequency domain transmission unit
ActiveUS20100034165A1More informationMore transmissionError preventionModulated-carrier systemsTime domainControl signal
A method for generating / transmitting a transmission-unit symbol sequence is disclosed. In the case of transmission information, the information is modulated in time and frequency domains on the basis of a predetermined transmission unit (e.g., a transmission time interval TTI or slot), simultaneous transmission of the information is made, and then a transmission unit symbol is generated / transmitted. A transmission sequence is masked in each symbol contained in one transmission unit. Symbol-unit circular shift (cyclic shift) is applied to the masked result, so that transmission efficiency increases. A control signal transmission method for supporting a variety of formats and a signal transmission method based on a prime-length sequence are also provided.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
MAC layer reconfiguration in a mobile communication system
ActiveUS7321589B2Error preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementAccess networkRadio access network
The invention relates to method and apparatus for reconfiguring a MAC entity of a MAC layer of the apparatus receiving protocol data units from a mobile terminal via on uplink upon reconfiguration of the uplink channel. Further, the invention relates to methods and mobile terminals for triggering the transmission of a status report from an RLC entity configured for an uplink channel of a network element in a radio access network, as well as a method and terminal for configuring the MAC layer of the mobile terminal. In order to enable an efficient and fast generation of RLC status reports after an uplink channel reconfiguration the invention suggests new mechanisms to trigger the transmission of status reports upon uplink reconfiguration as well a new operation and configuration of radio access network elements and UEs upon uplink channel reconfiguration, in particular a transmission time interval (TTI) reconfiguration.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Method and apparatus for soft buffer partitioning in time-division duplexing system
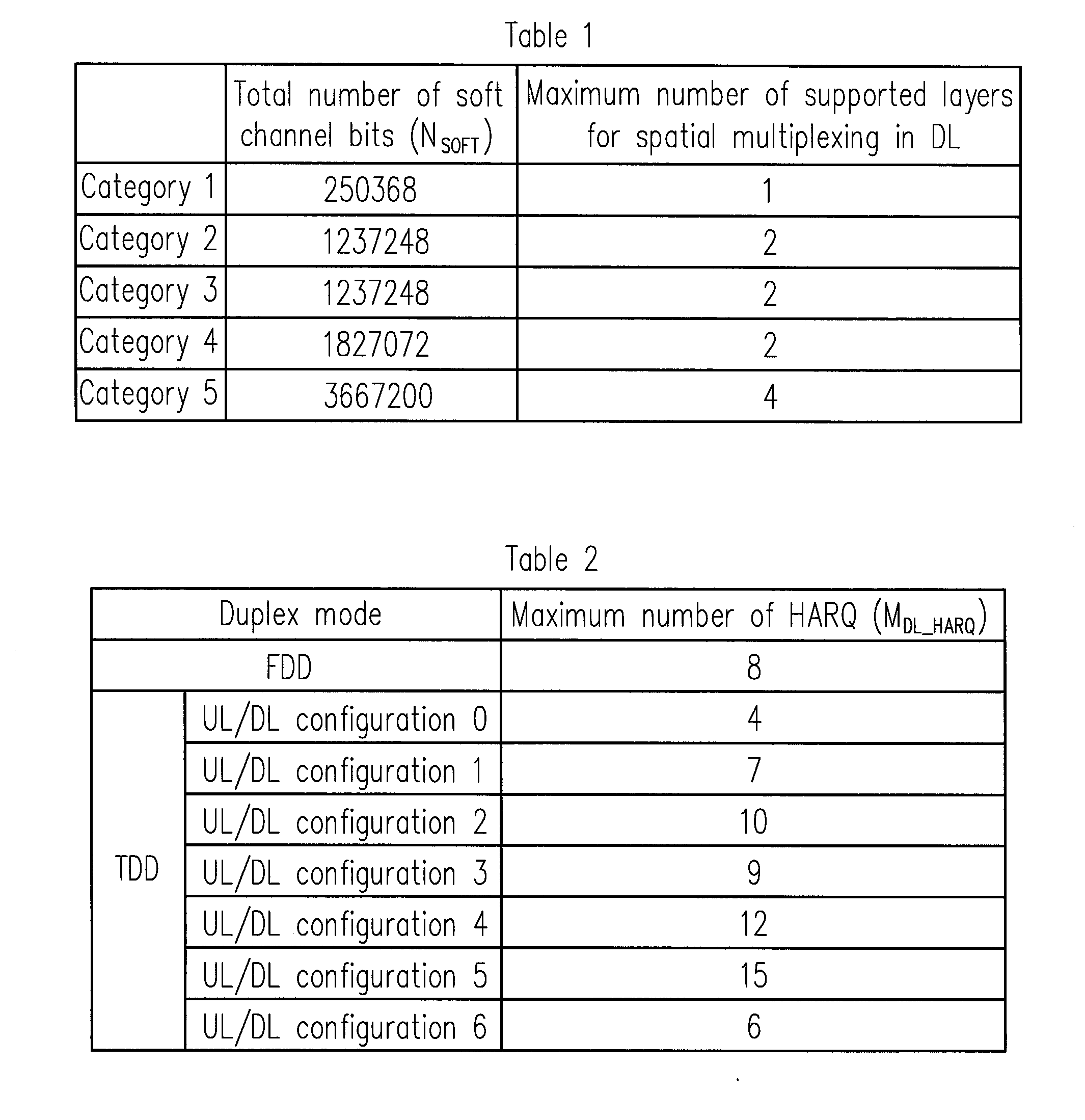
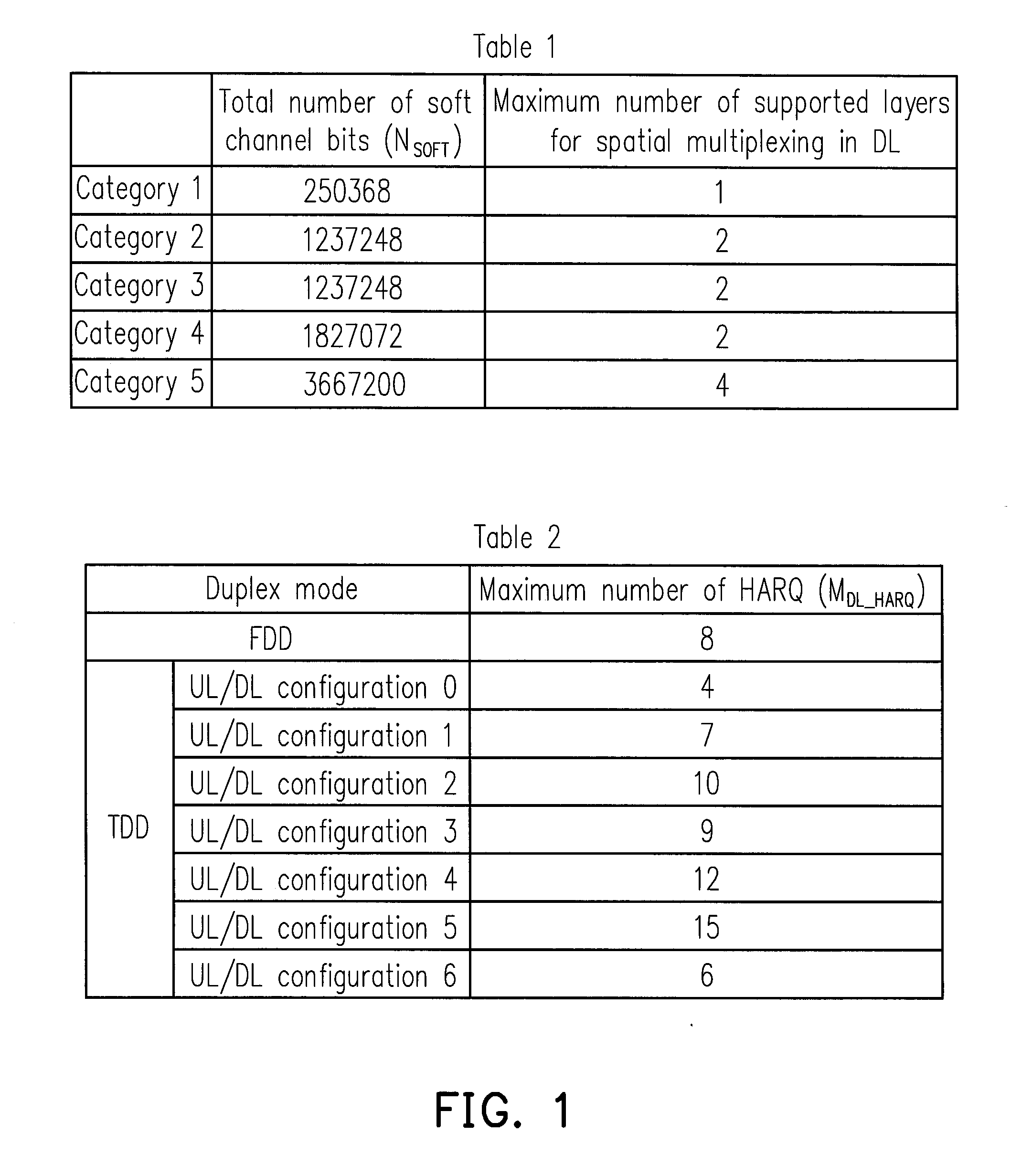
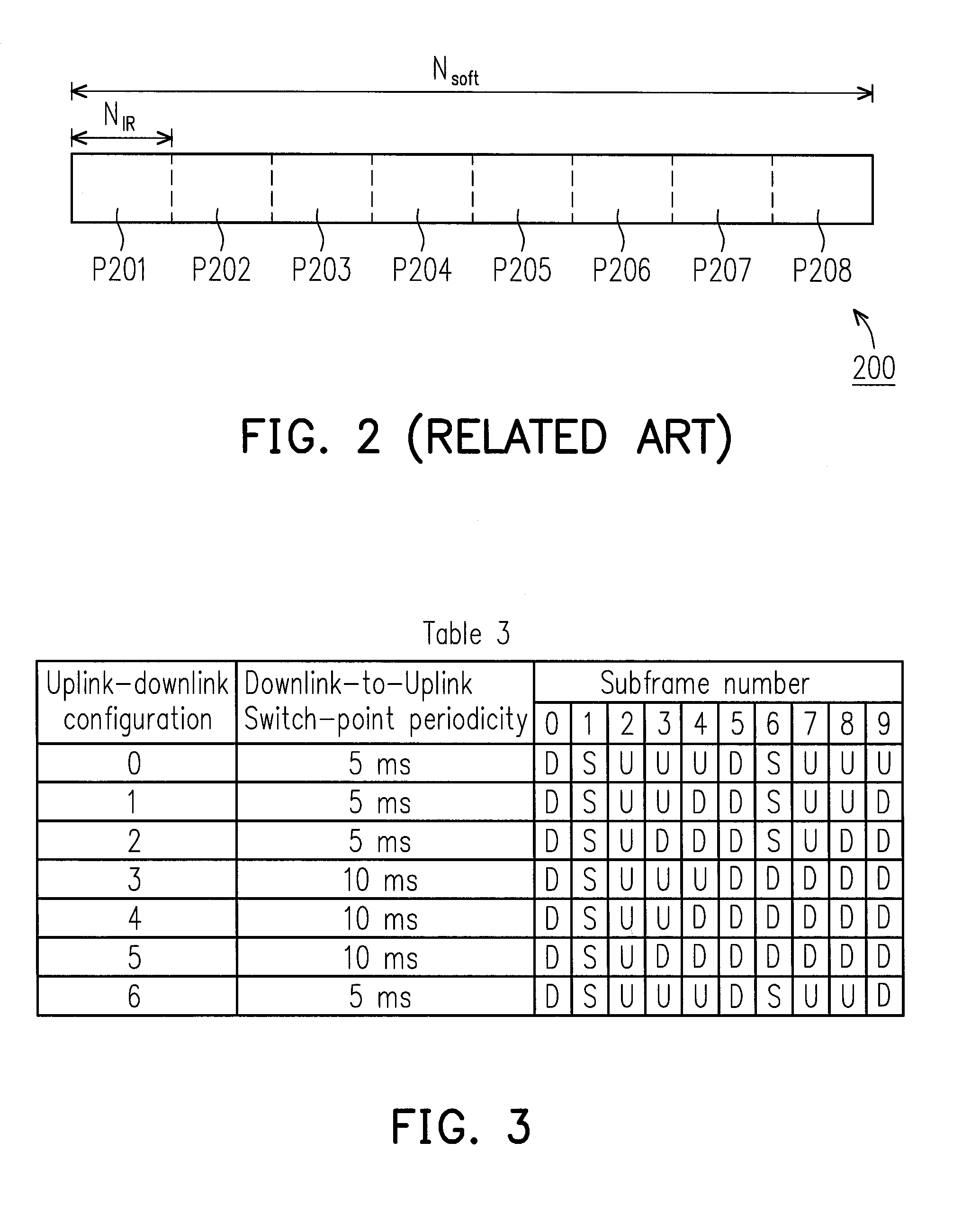
ActiveUS20130051289A1Error preventionTime-division multiplexComputer scienceTransmission Time Interval
A method for partitioning a soft buffer in a time-division duplex system and an apparatus using the same are disclosed. The method includes the following steps. A total number of soft channel bits, a maximum number of transport blocks transmittable to a user equipment (UE) in a transmission time interval (TTI), a maximum number of downlink (DL) hybrid automatic retransmit request (HARQ) processes, and a configured maximum number of HARQ processes are determined. A partition size of the soft buffer is selected according at least to the total number of soft channel bits, the maximum number of transport blocks transmittable to the UE in the TTI, the maximum number of DL HARQ processes, and the preconfigured maximum number of HARQ processes.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Extension of physical downlink control channels in a communication system
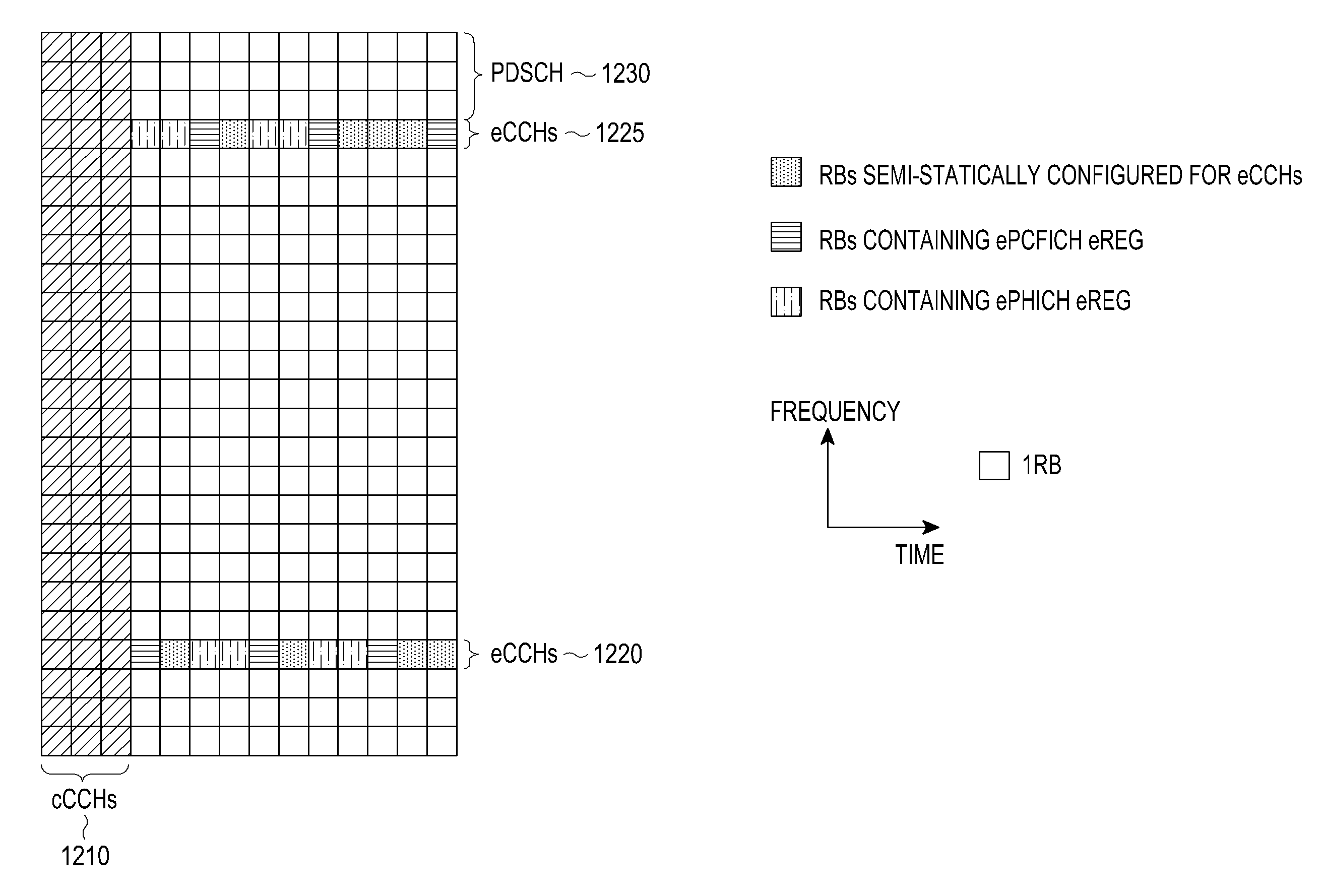
ActiveUS20130039299A1Transmission path divisionReceiver specific arrangementsCommunications systemResource element
Methods and apparatuses are described for a User Equipment (UE) to receive enhanced Control CHannels (eCCHs), including enhanced Physical Downlink Control CHannels (ePDCCHs), transmitted in a set of Resource Blocks (RBs) over a Transmission Time Interval (TTI). A method includes transmitting a first control signal to a first UE over a first number of Resource Elements (Res) in a subset of the RBs and over a first number of the transmission symbols in the TTI; transmitting a second control signal to a second UE over a second number of the REs in the subset of the RBs and over a second number of the transmission symbols in the TTI; and transmitting a reference signal of the first type over a third number of the REs in the subset of the RBs and over a third number of the transmission symbols in the TTI.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
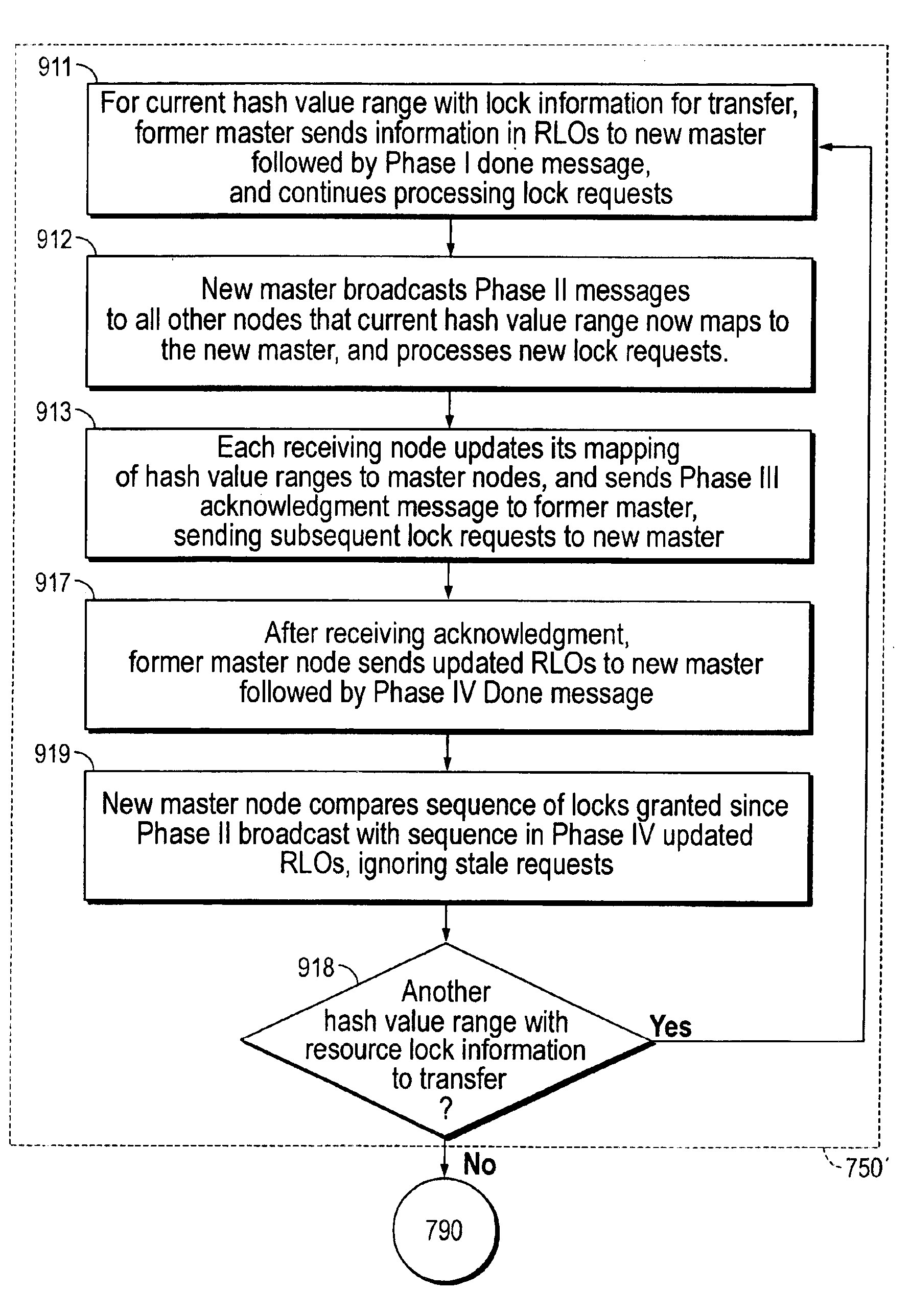
Techniques for DLM optimization with transferring lock information
InactiveUS6920454B1Shorten the timeImprove performanceData processing applicationsResource allocationHash functionDistributed lock manager
Techniques for optimizing a distributed lock manager (DLM) include transferring lock information to a new master without freezing one or more shared resources. A hash value range is associated with the resources by a hash function. A first master node is established as master for the resources in response to a hash value range being mapped to the first master node. Responsibility for mastering the resources is transferred from the first master node to a second master node during a transfer time interval. Lock requests received at a receiving node, either the first master node or the second master node, are processed by the receiving node during the transfer time interval.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Preamble length for discontinuous control channel transmission
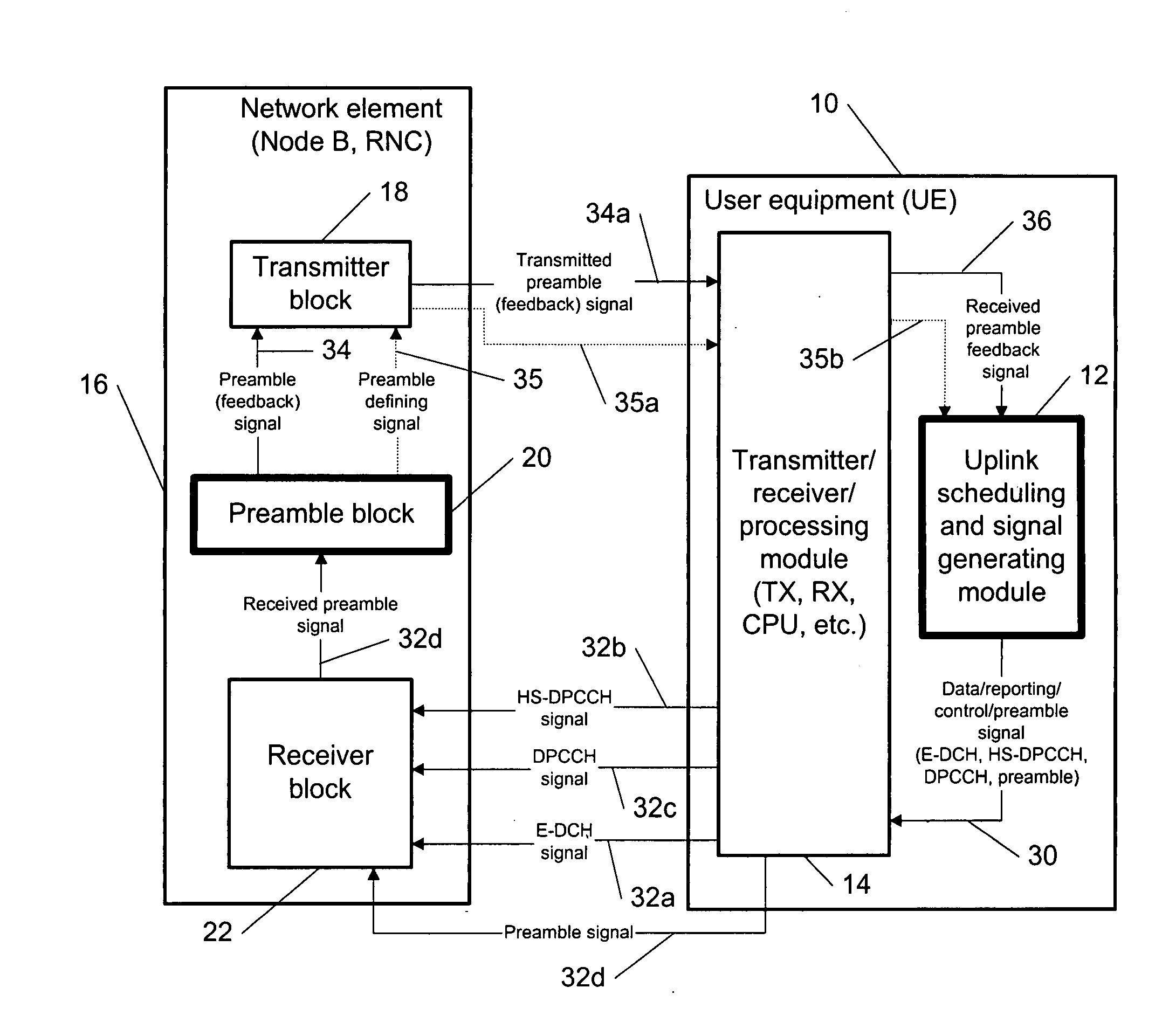
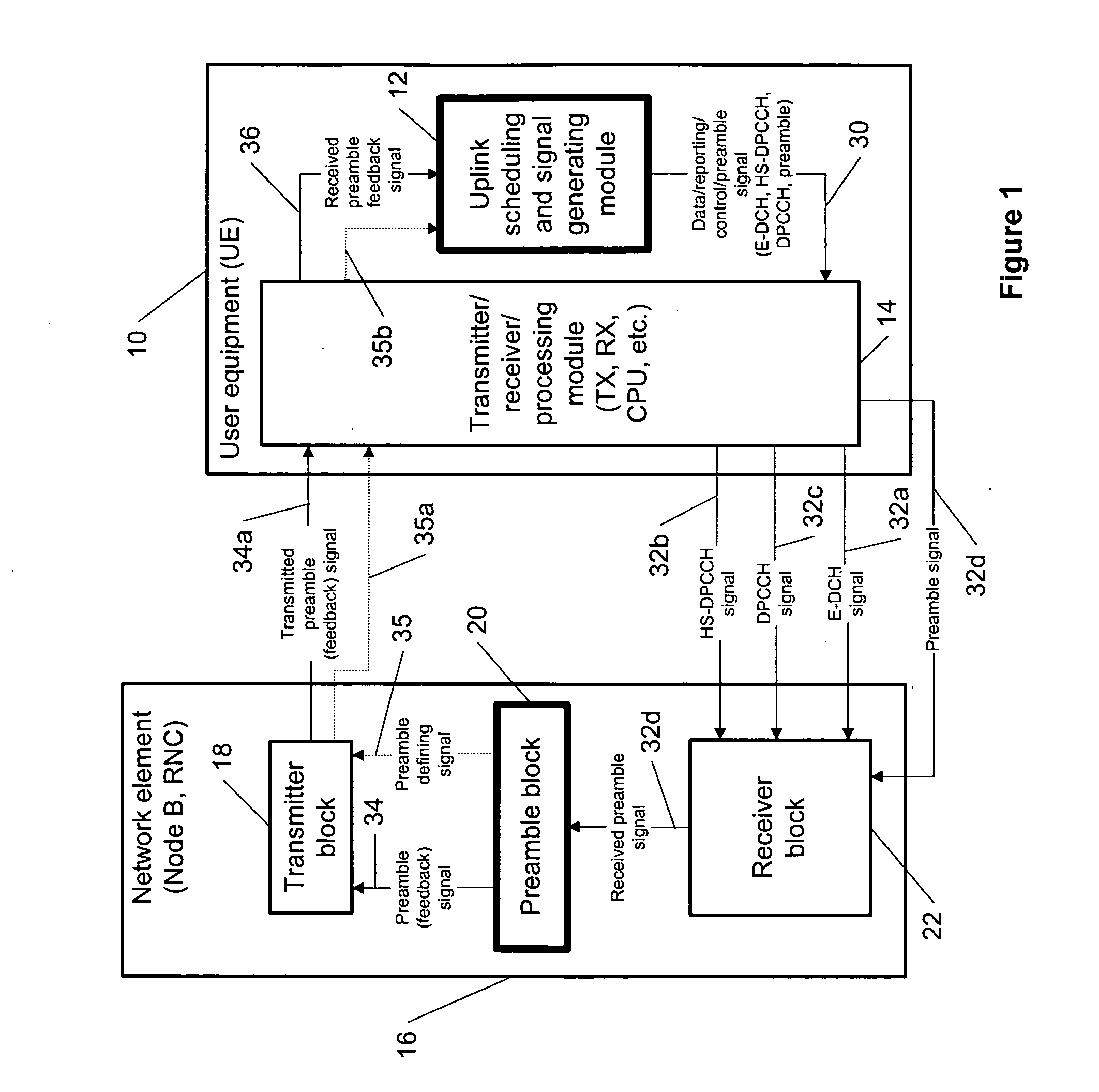
The specification and drawings present a new method, system, apparatus and software product for defining a preamble length of a preamble (e.g., a power control preamble) for a discontinuous control channel transmission using, e.g., a dedicated physical control channel (DPCCH) for transmitting the preamble. The preamble length can be optimized using a predetermined criterion depending on a transmission gap length (which can be variable) in the discontinuous control signal (e.g., transmitted on the DPCCH) or in a discontinuous data signal, e.g., transmitted on an enhanced dedicated channel (E-DCH), and / or on a length of a transmission timing interval (TTI) of the discontinuous data. Furthermore, a power in the preamble can be changed in time using a further predetermined criterion.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Apparatus and method to allocate communication resources for an aperiodic data packet in a communication system
ActiveUS20100150114A1Time-division multiplexChannel coding adaptationCommunications systemUplink scheduling
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
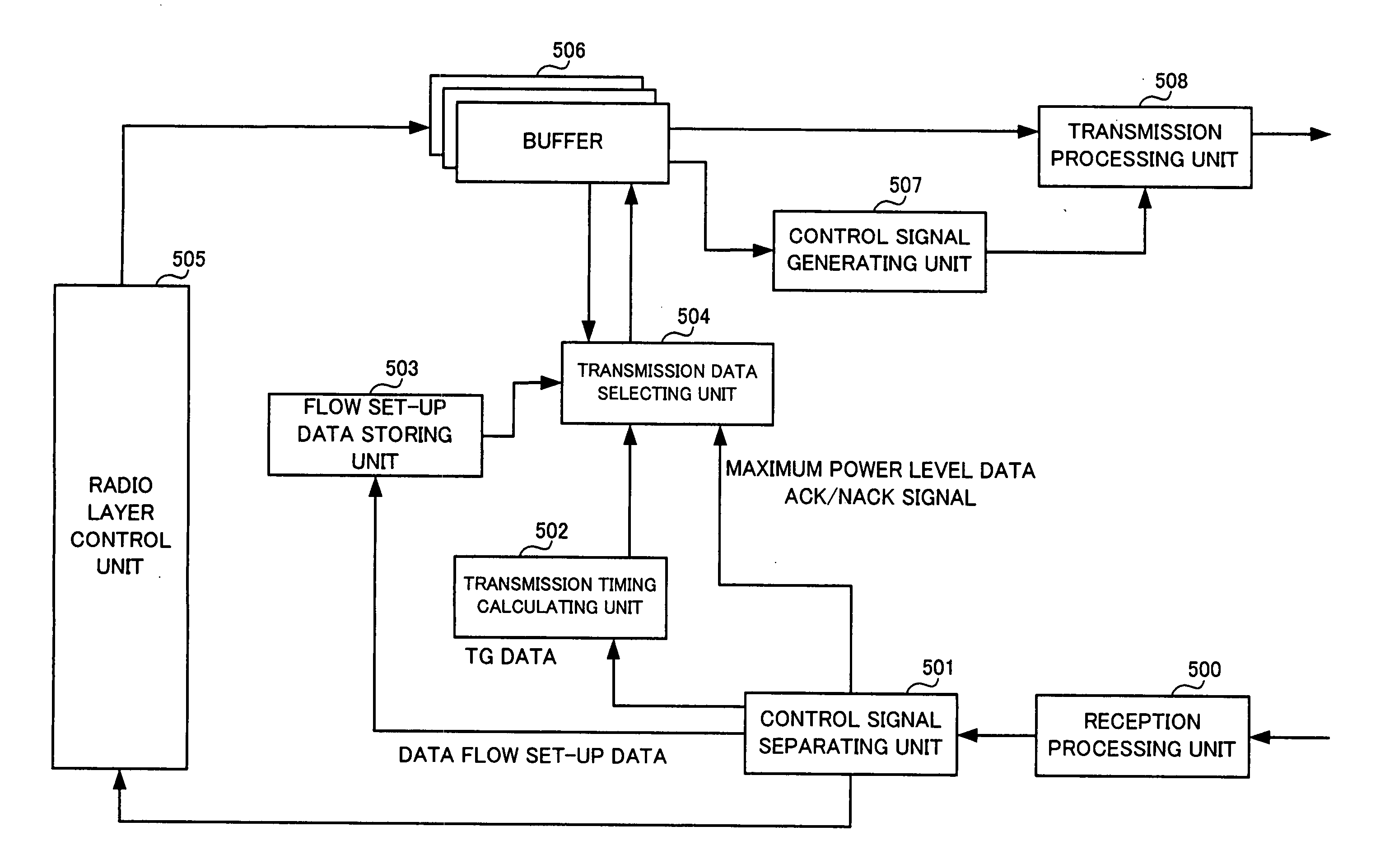
Communication control method, wireless communication system, mobile station, base station and base station control unit
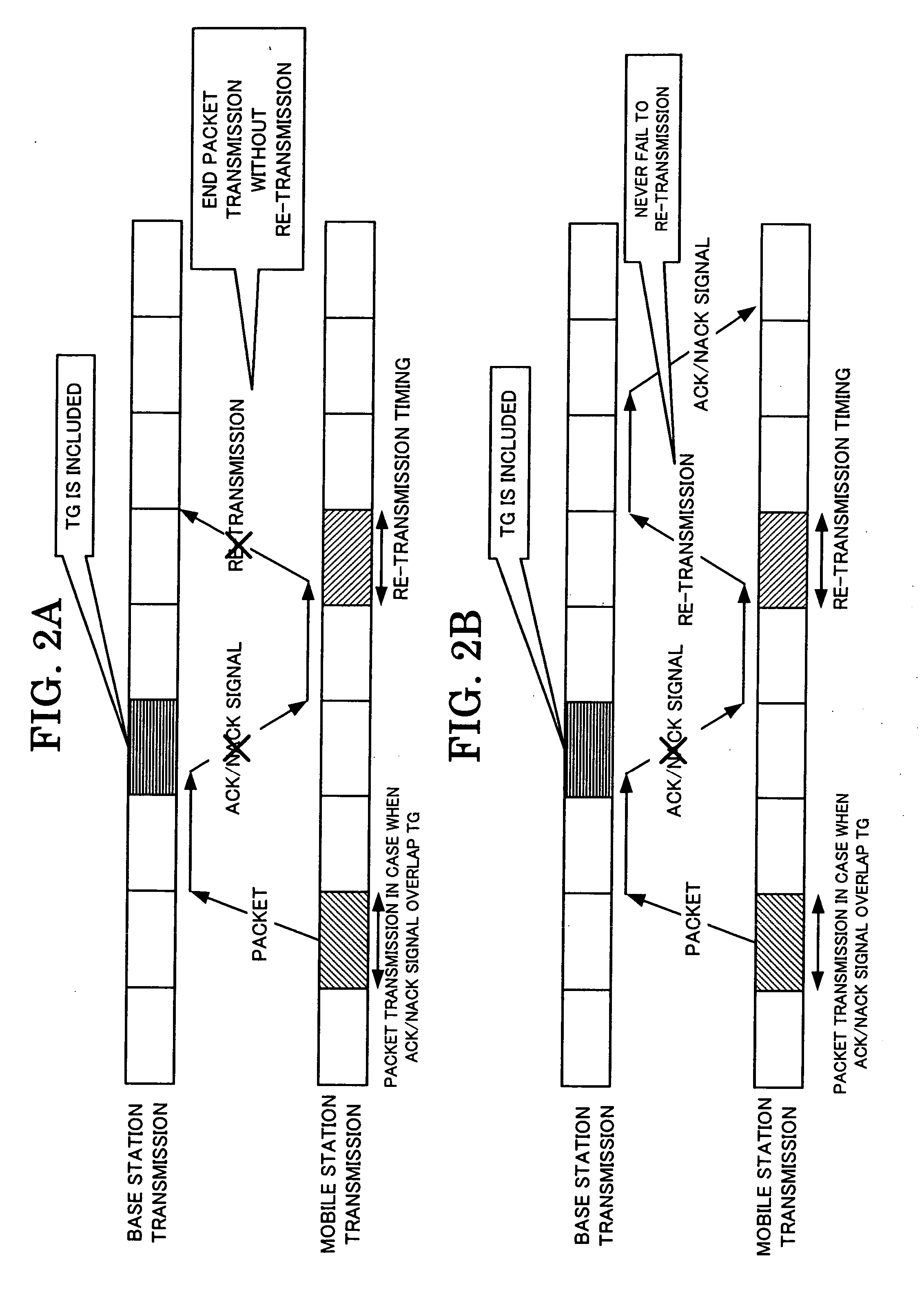
InactiveUS20060146762A1Quality improvementReduce delaysPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemMobile station
A wireless communication, in which mobile and base stations setup uplink and downlink channels, and the mobile station transmits data flows. The base station interrupts transmission via the downlink setup with the mobile station in the predetermined transmission interruption time interval. The mobile station determines, in response to the data flow, packet transmission in a first transmission time interval for the predetermined time interval determined from the transmission interruption time interval or re-transmission of the packets transmitted in the first transmission time interval. The mobile station transmits packets in response to the determination. The base station transmits an arrival confirmation signal for the transmitted packets. The mobile station performs re-transmission in response to the arrival confirmation signal or to the determination.
Owner:NEC CORP
Radio communication system, mobile station, and radio base station
InactiveUS20090016265A1Shorten transmission intervalReduce transmission delayError preventionSecret communicationPacket communicationCommunications system
A radio communication system of an HARQ method that makes an HARQ transmission interval of subpackets appropriate and reduces data transmission delay resulting from subpacket retransmission. In the radio communication system in which a packet is transmitted and receives with the HARQ method between a base station and multiple radio mobile stations, each of the base station and the multiple radio mobile stations has: a packet transmission circuit for transmitting subpackets in predetermined intervals; a packet reception circuit for repeating decoding processing by combining a newly received subpacket and a previously received former subpacket until an original packet is successfully decoded; and a HARQ control equipped with a function of, for packet communication whose data length is short, transmitting a subpacket or response from the packet transmission circuit in an HARQ transmission interval that is shortened from the HARQ transmission interval of the normal mode.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com