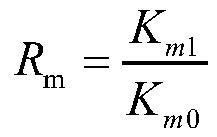A damage evaluation method for working fluid in fractured tight reservoirs that takes into account both foundation blocks and fracture systems
A technology for tight reservoirs and fracture systems, which is applied in the direction of material inspection products, soil material testing, etc., can solve the problem that the comprehensive damage process of foundation blocks and fractures cannot be simulated, and achieve short experiment time, simple operation process, and low economic cost Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
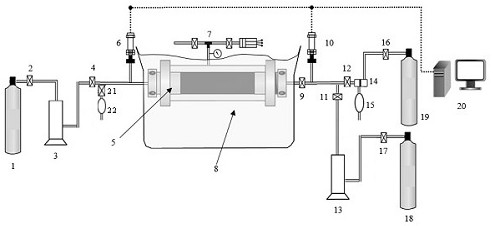
[0032] In order to verify the reliability of the present invention, a typical tight sandstone rock sample in a certain block of the Tarim Basin was used as an experimental rock sample, and the on-site drilling fluid with polysulfide system was used to evaluate the reservoir protection ability of the on-site drilling fluid, and to clarify the tight reservoir The damage ratio of the base block and fracture system under the action of the working fluid to be evaluated. The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0033] (1) Select a tight sandstone core plug in a block without macroscopic fractures, and dry it at 60°C for 48 hours;
[0034] (2) After applying a certain confining pressure to the core plunger, open valve 2, valve 4, valve 9, valve 12, valve 16, close valve 11, valve 21, and measure the permeability of the base block before the damage of the core plunger (K m0 );
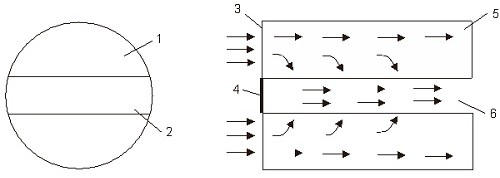
[0035] (3) cutting the core plunger along the direction of the central axis to create through-crack...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com