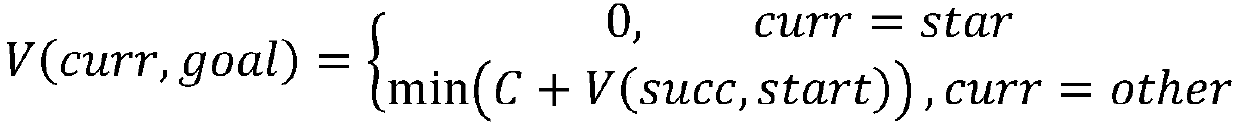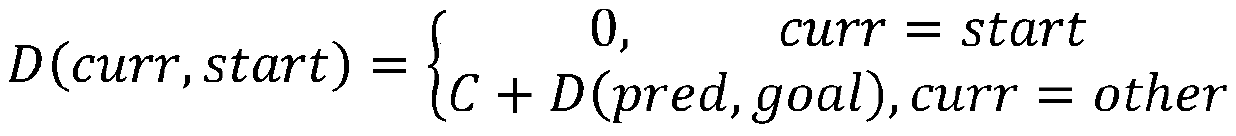Autonomous ship route planning method based on D*Lite optimization algorithm
A technology of autonomous driving and route planning, applied in navigation, calculation, surveying and navigation, etc., can solve problems such as high risk, long search time, and long time, and achieve the effect of increasing navigation safety and reducing time and space complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
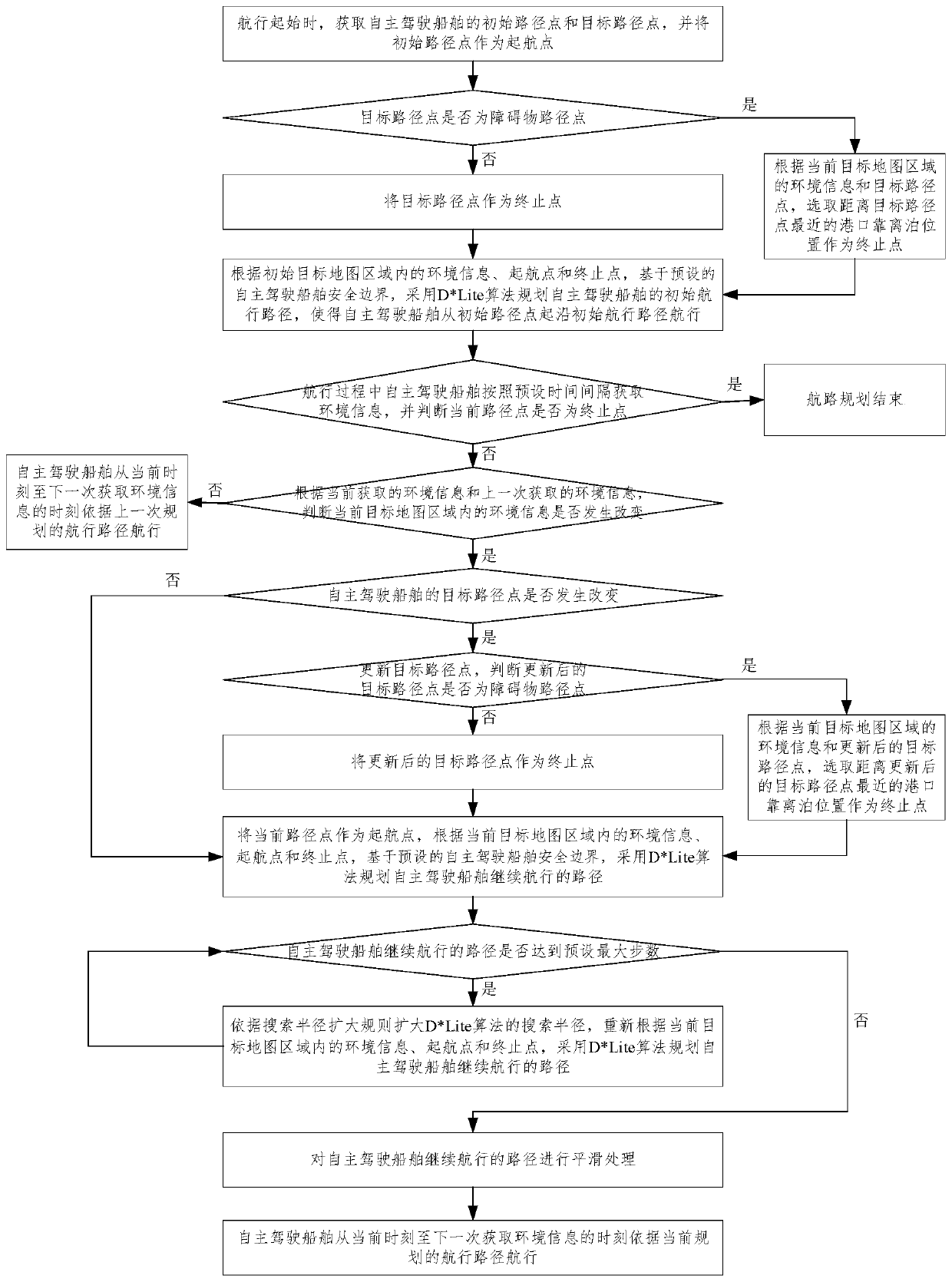
[0038] In order to better explain the present invention and facilitate understanding, the present invention will be described in detail below through specific embodiments in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0039] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a kind of self-driving ship route planning method based on D*Lite optimization algorithm, comprising the following steps:
[0040] Step S1. At the beginning of the voyage, the initial waypoint and the target waypoint of the autonomous ship are obtained, and the initial waypoint is used as the starting point, and the ending point is determined according to the target waypoint.
[0041] Preferably, determining the termination point according to the target waypoint includes: judging whether the target waypoint is an obstacle waypoint, if not, using the target waypoint as the termination point; if so, according to the environmental information of the current target map area and the target waypoint, Sel...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com