EKF-SLAM algorithm of self-adaptive dynamic observation domain
An EKF-SLAM and observation domain technology, applied in the field of navigation, can solve problems such as large dimensionality, reduced calculation efficiency, and affecting the real-time calculation performance of the algorithm, and achieve the effects of improving calculation efficiency, high estimation accuracy, and saving calculation time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
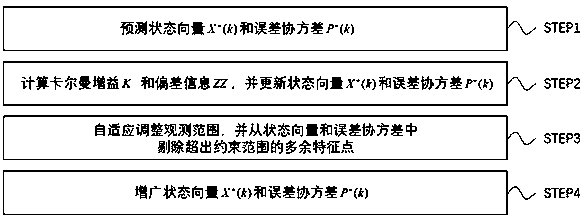
[0045] The present invention will be further explained below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. It should be understood that the following specific embodiments are only used to illustrate the present invention and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention.
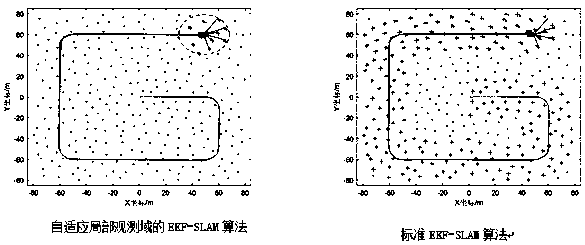
[0046] Taking a four-wheeled vehicle for SLAM tasks as an example, the following prerequisites are set: the vehicle pose vector X v =[x v ,y v ,θv ]′, feature point position vector X m =[x m1 ,y m1 ,...,x mn ,y mn ]'. Among them, (x v ,y v ) is the coordinates of the vehicle in the world coordinate system, θ v is the angle between the longitudinal axis of the vehicle and the positive direction of the x-axis of the world coordinate system (that is, the yaw angle), (x mi ,y mi ) is the coordinate of feature point i in the world coordinate system. During the running of the vehicle, the vehicle is controlled to move towards the next waypoint by the speed comma...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap