Fine steel cord with a low structural elongation
A thin steel wire, elongation technology, applied in rope making auxiliary devices, mechanical equipment, coatings, etc., can solve problems such as twisting, belt pullout, and damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
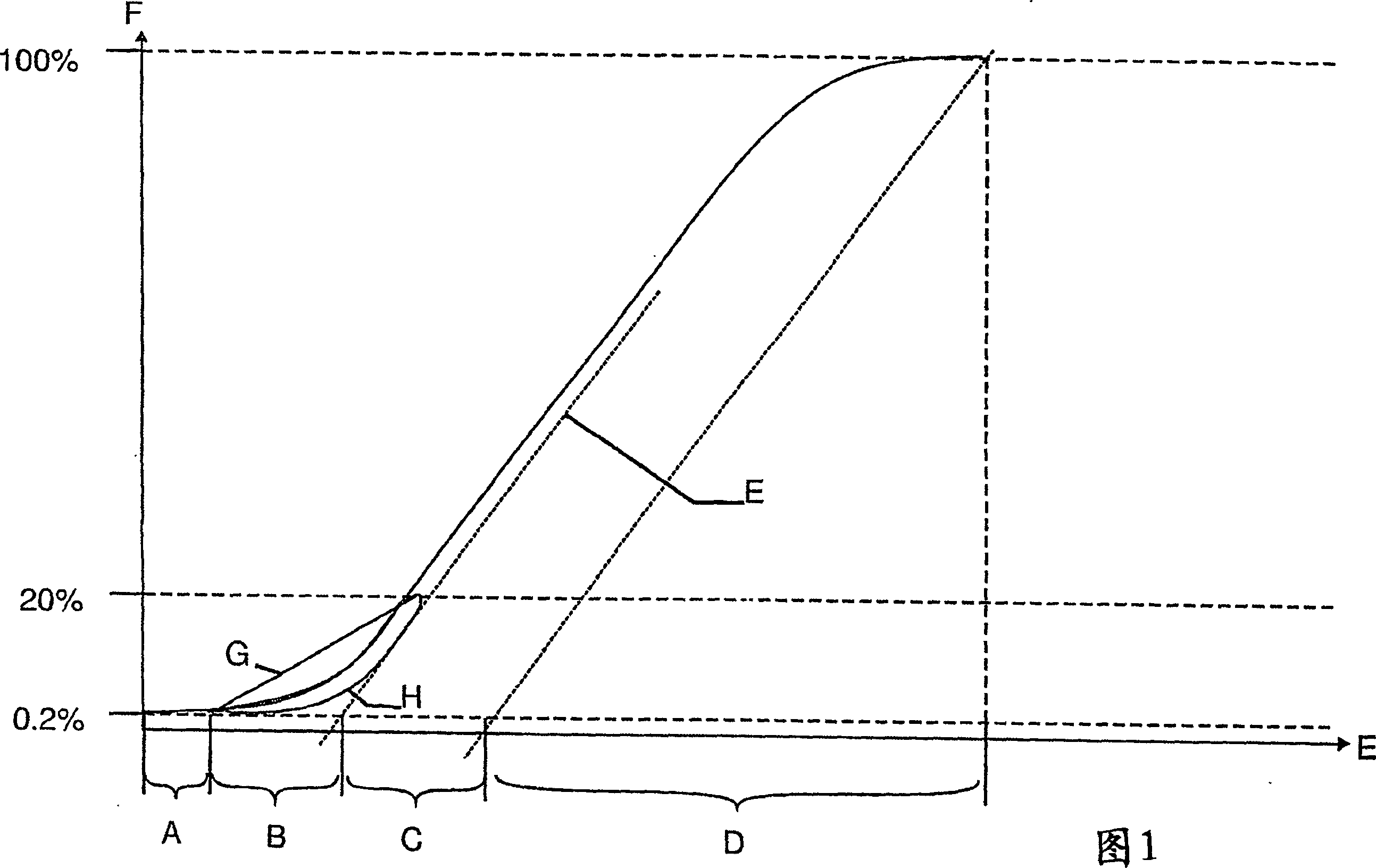
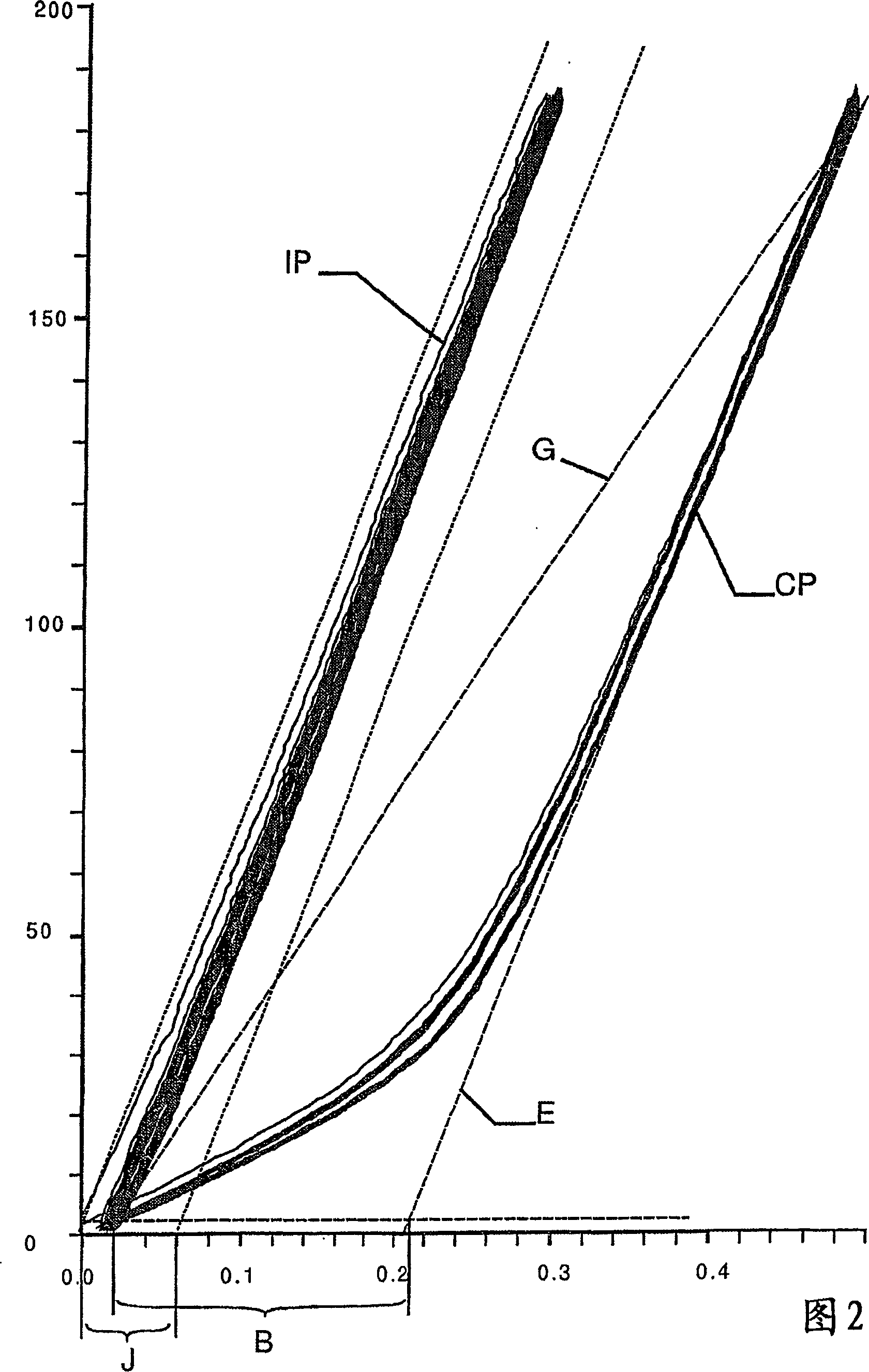
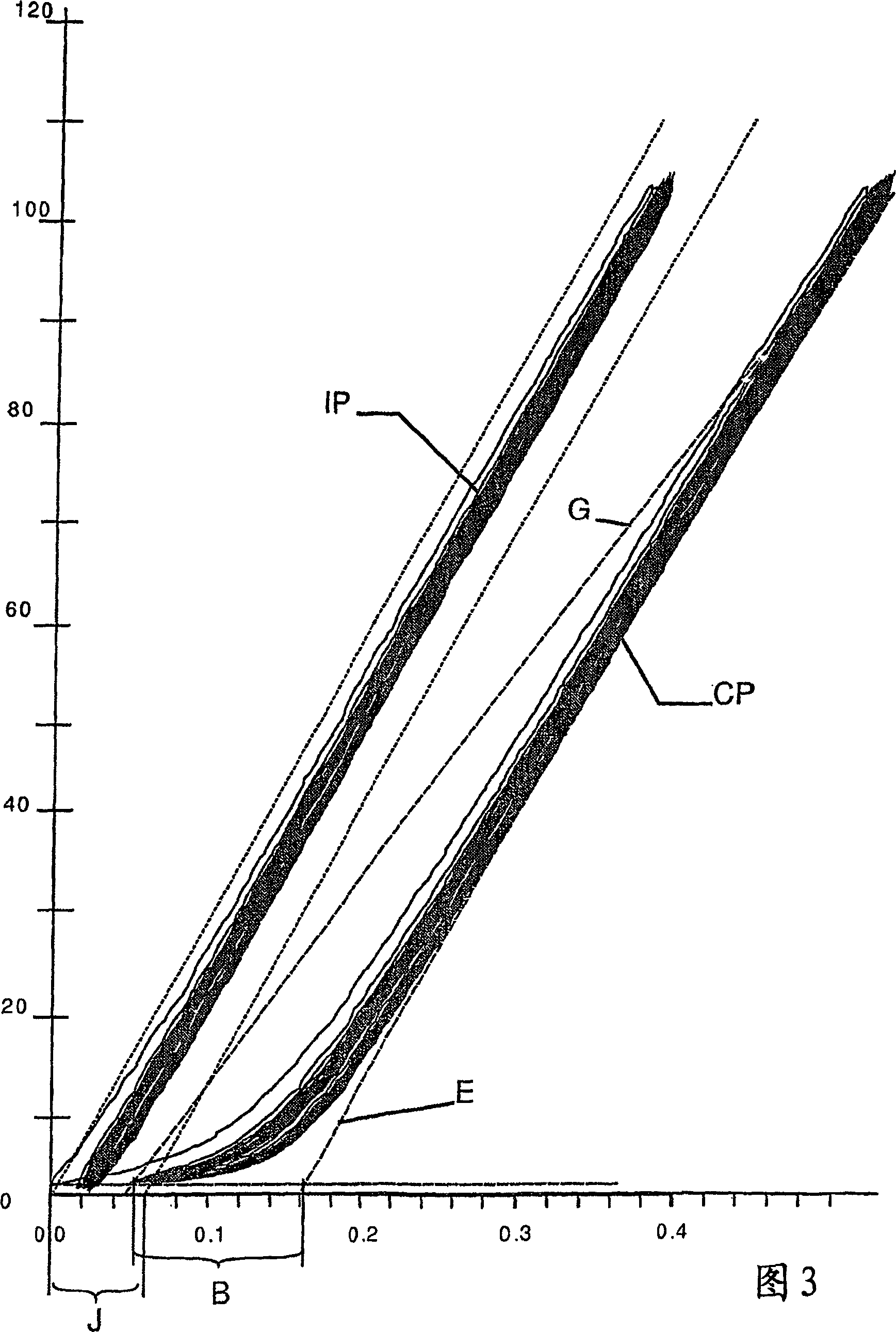
[0060] In a first preferred embodiment, the inventors produced a cord of the 7×3 type, which is characterized by the following formula:
[0061] [(3×0.15) 9s +6×(3×0.15) 9s ] 8Z
[0062] That is: the core strand is composed of 3 twisted wires, the twist length of these wires in the S direction is 9mm, the core strand is combined with 6 outer strands to form a cord, the outer The strands also consisted of 3 wires twisted together with a twist length of 9 mm in the S direction. The strands are twisted into cords in the Z direction with a twist length of 8 mm. The wire is that of plain carbon steel with a carbon content of approximately 0.725 wt% C and has a hot dipped zinc coating. Cords are produced from threads according to the methods of the prior art and according to the method of the invention. The metal cross-sectional area of the cord is 0.371mm 2 (according to DIN 3051, i.e. sum of wire cross-sections).
[0063] first by means of Figure 4a to introduce existin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com