Multi-touch sensing through frustrated total internal reflection
a technology of total internal reflection and multi-touch sensing, applied in the direction of counting objects on conveyors, instruments, specific gravity measurements, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the application of multi-touch sensing to use that requires relatively low resolution, system stability problems, and friction at the interaction surface. , the effect of reducing glar
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
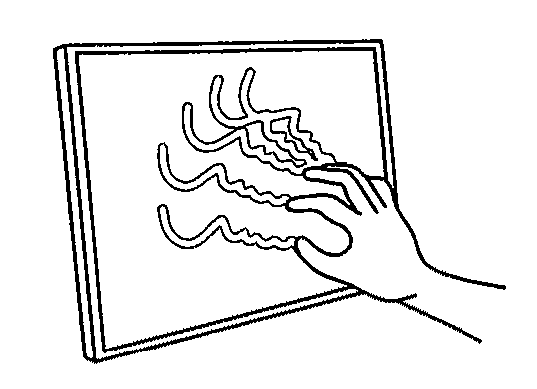
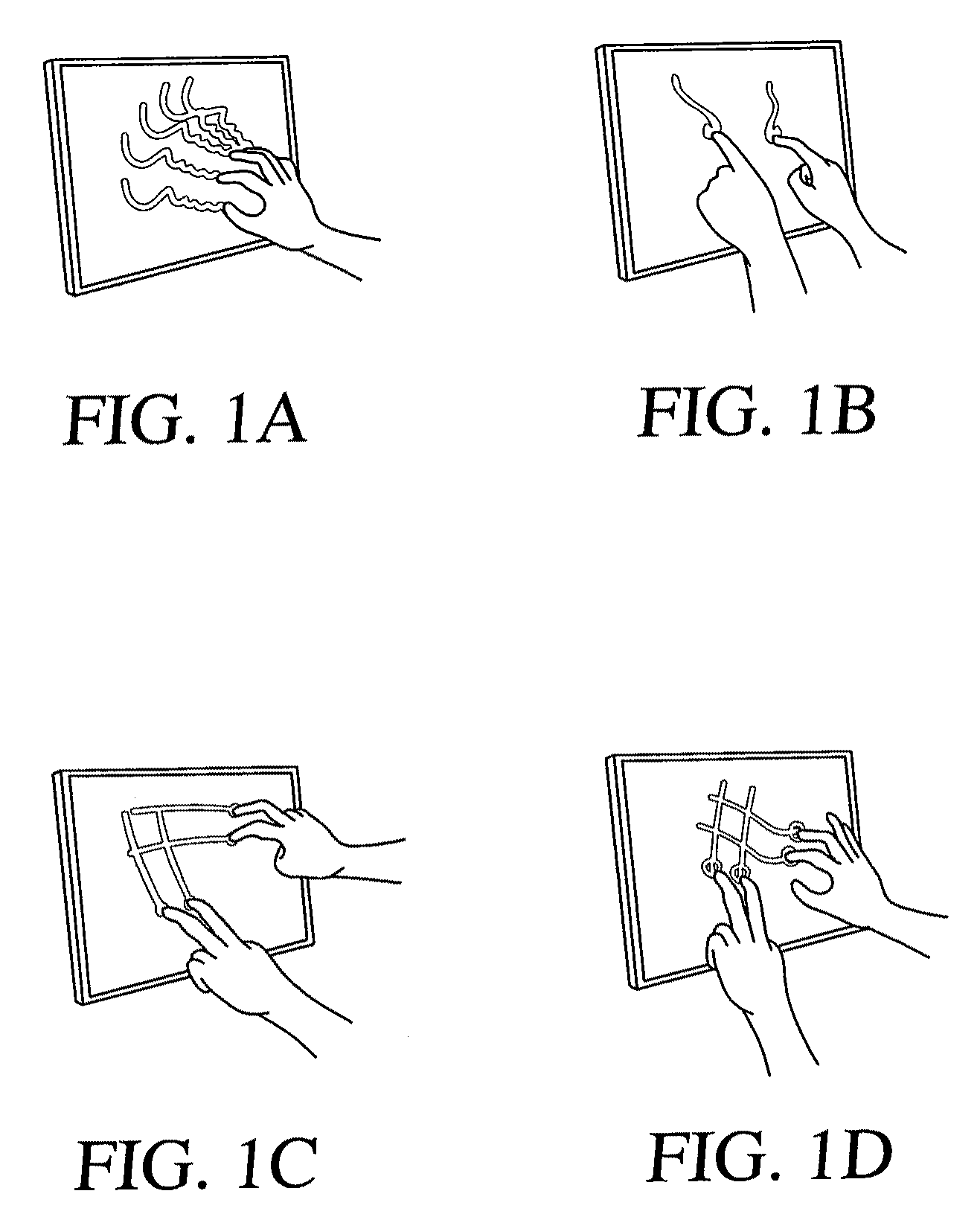
[0127] Multi-touch sensing enables a user to interact with a system with more than one finger at a time, as in chording and bi-manual operations. Multi-touch sensing may accommodate multiple users simultaneously, which is especially useful for larger shared-display systems such as interactive walls and tabletops. FIGS. 1A through 1D of the drawings show several simple examples of multi-touch sensing of the present invention.
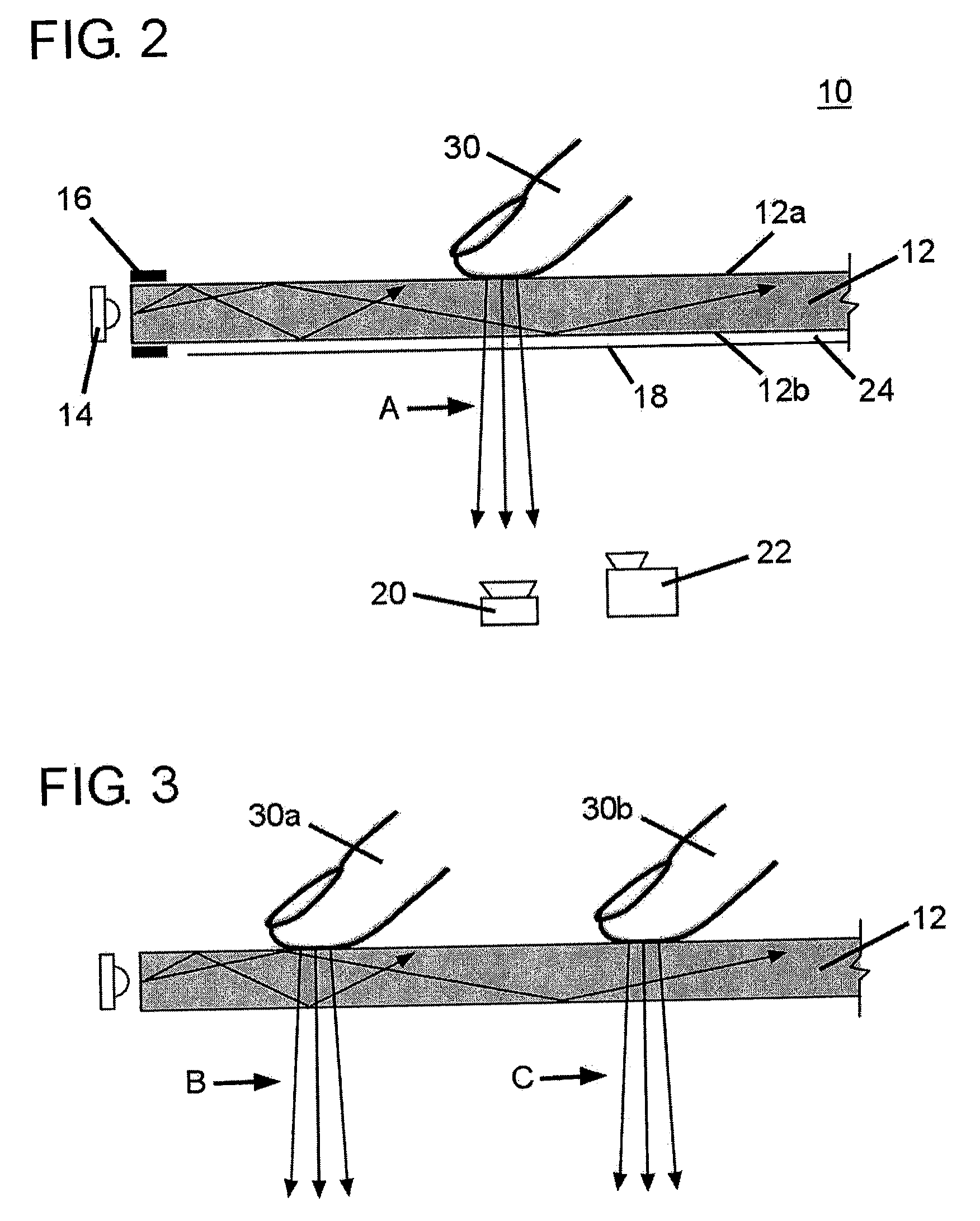
[0128] Multi-touch sensing in accordance with the present invention is based on frustrated total internal reflection (FTIR). When light encounters an interface to a medium with a lower index of refraction, such as glass to air, the light becomes refracted to an extent which depends on its angle of incidence. Beyond a certain critical angle, the light undergoes total internal reflection (TIR). But, if another material is placed at the interface, total internal reflection is frustrated, causing light to escape the waveguide. Since the concept of FTIR is well known...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com