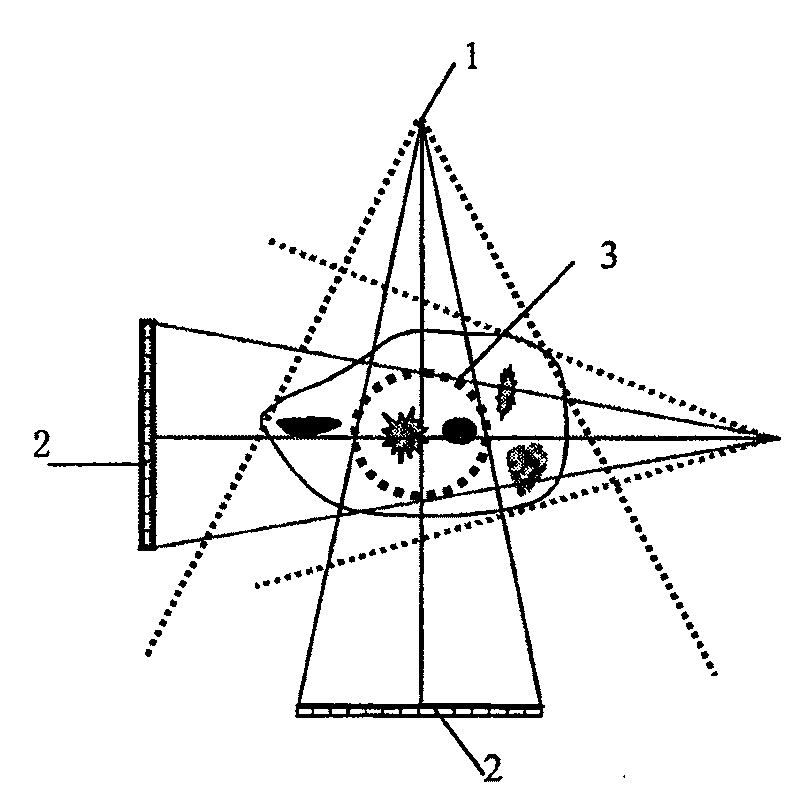
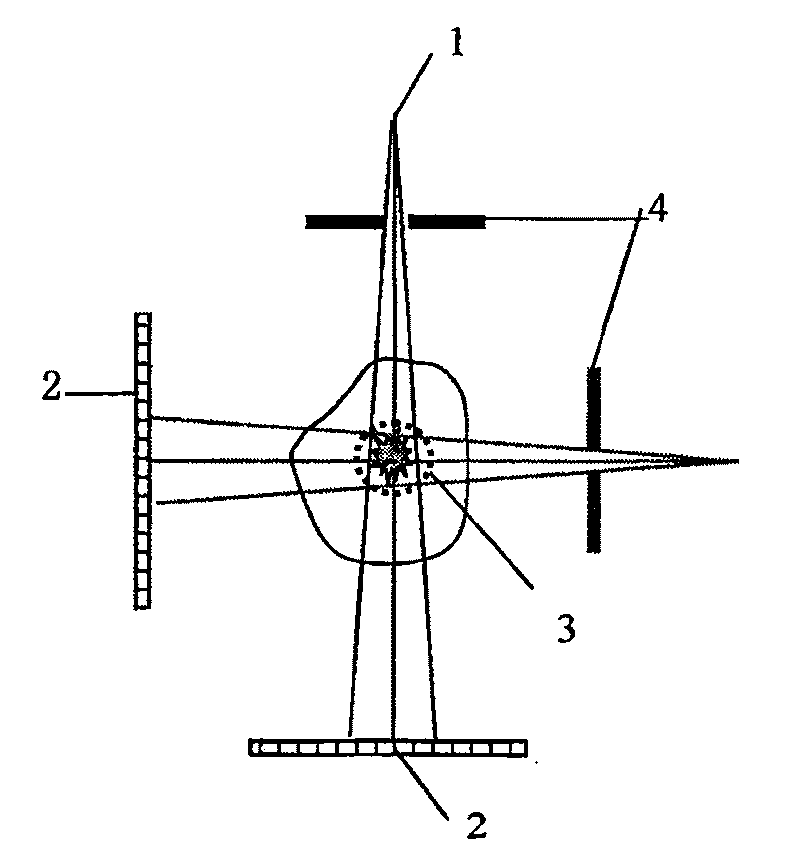
Blocked scan rebuilding and space assembly method of large object image-forming with cone-beam CT
A block scanning, large object technology, applied in the field of medical equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
[0070] Specific embodiment 1: the block local reconstruction of Shepp-Logan mold, as Figure 10 Shown:
[0071] Step 1. Divide the Shepp-Logan mold into 5 blocks, such as Figure 5 shown;
[0072] Step 2. Place each segmented area of the Shepp-Logan mold in the scanning field of view of the cone beam CT, that is, in the rotation of the turntable
[0073] In the heart area, each block area is sequentially placed in the scanning field of view of cone beam CT by using the method of spatial translation;
[0074] Step 3: Cone beam scanning is performed on each partition of the Shepp-Logan mold to obtain cone beam projection images. A full scan acquires about 300 projection images. Half scans acquire about 160 images.
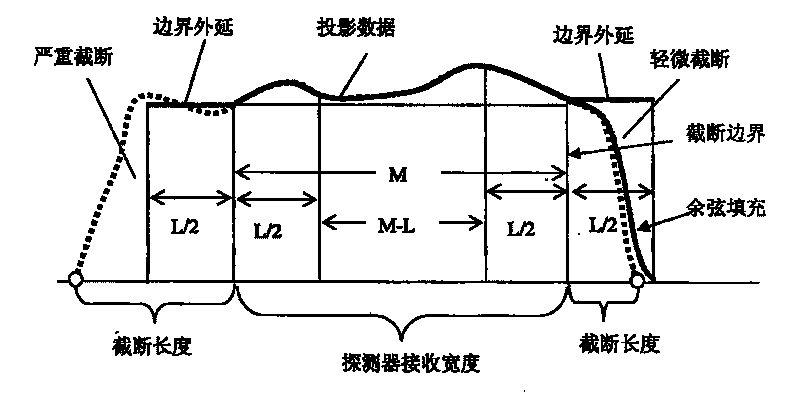
[0075] Step 4, filling the truncated area of the projected image, such as figure 2 shown;
[0076] Step 5, adopt FDK method or convolution back projection method to carry out three-dimensional volume reconstruction, adopt the method of convolution back pro...
specific Embodiment 2
[0079] Specific embodiment 2: filling the data of the projected truncated image of the breast mold;
[0080] Figure 8 (a) Cone beam projection image of the breast cast without transverse truncation; Figure 8 (b) Transversely truncated projected images caused by adjusting the ray collimator; Figure 8 (c) Transversely truncated projected image after boundary extension filling.
[0081] Figure 9 is the partially reconstructed image of the breast mold; the first row shows the case of transverse truncated projection without padding (see Figure 8 Partial reconstruction of (b)), you can see the Gibbs effect caused by boundary truncation, which is manifested as a very bright edge in the reconstructed image; the second line shows that after the horizontal truncated projection is filled (see Figure 8 Local reconstruction of (c)), where the Gibbs effect is reduced and the reconstruction performance is improved in the region near the boundary.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com