Communication device
A communication device, data technology, applied in the direction of error prevention/detection using return channel, digital transmission system, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as increasing processing load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
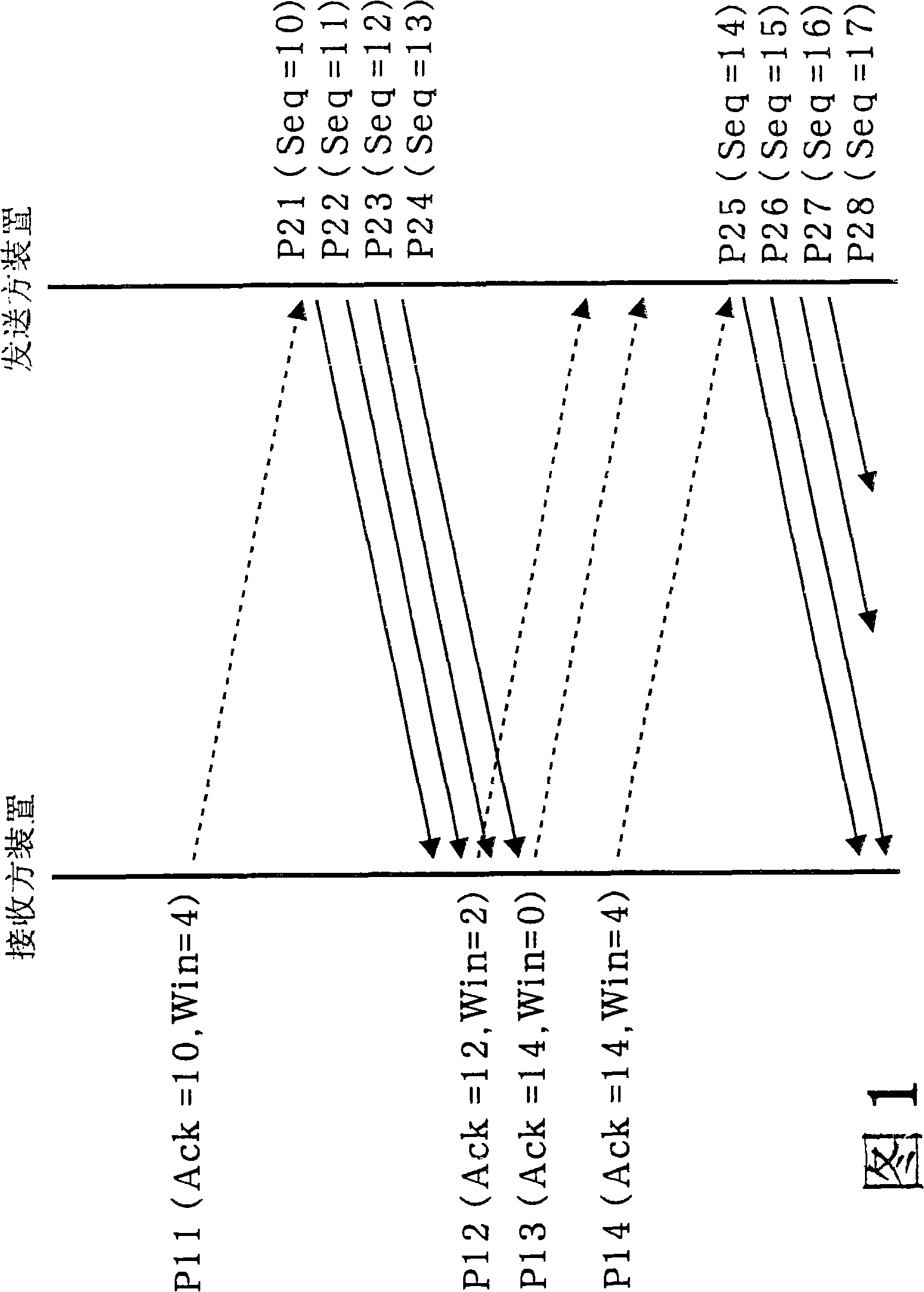
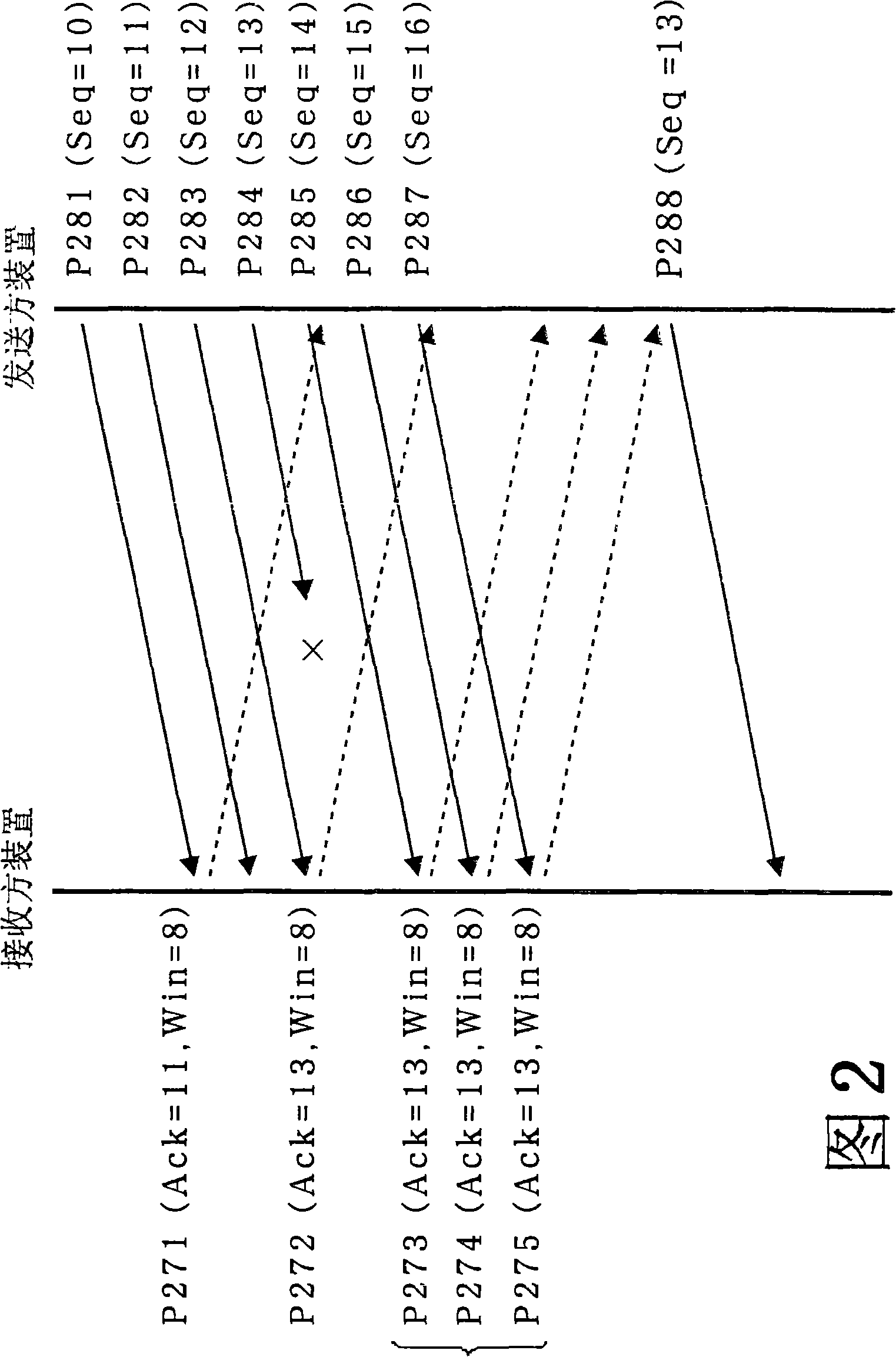
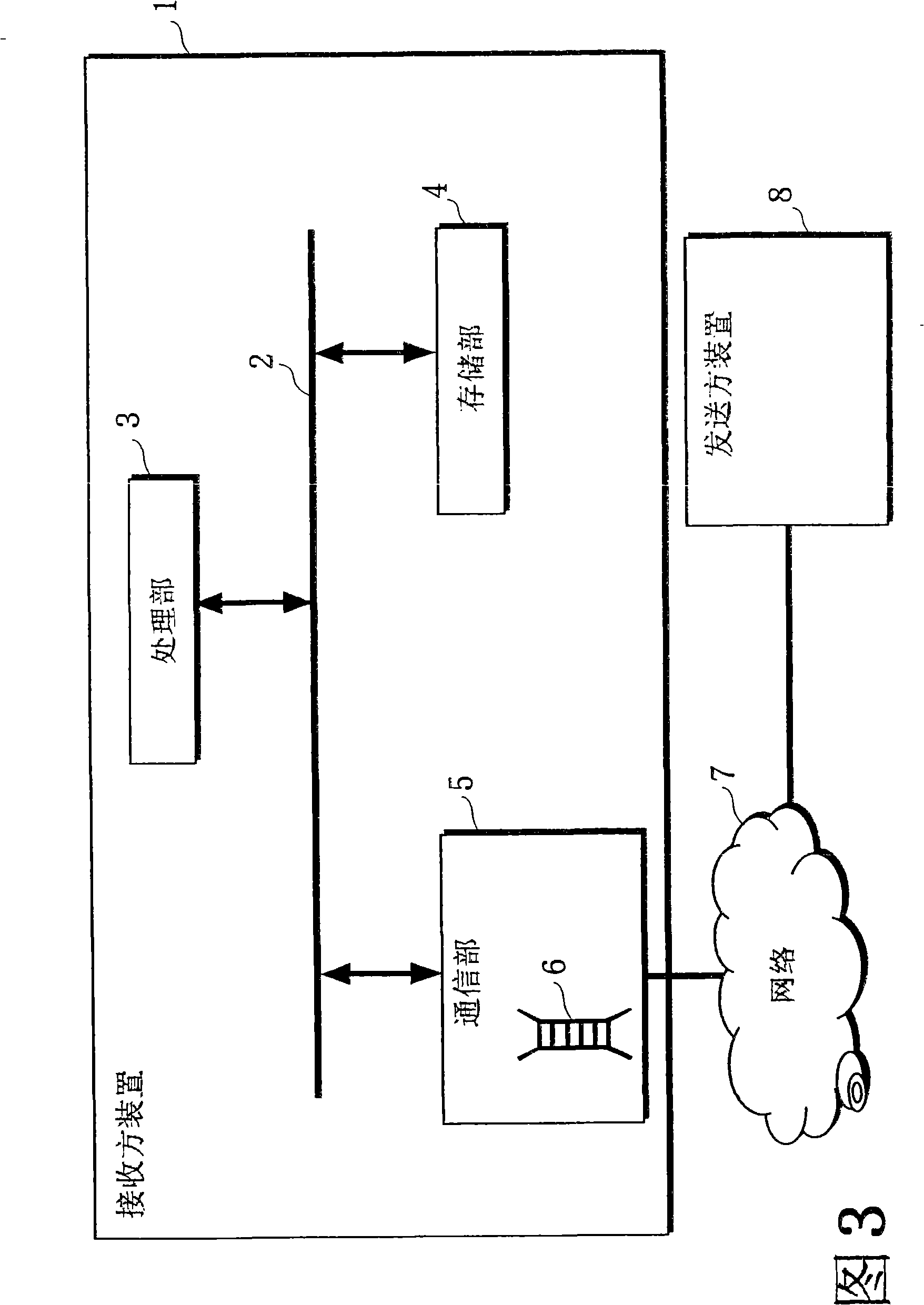
[0252] FIG. 8 is a schematic diagram of an example of the configuration of a communication device (receiver device) related to the present embodiment. The receiver device 31 is a device having a wired connection or wireless connection communication function with the network 37, and has an Ethernet (registered trademark) interface, for example. The network 37 includes a wired network or a wireless network, and examples include public networks such as the Internet.
[0253] The receiver device 31 includes a system bus 32 , a processing unit 33 , a storage unit 34 , and a communication unit 35 .
[0254] The communication unit 35 is hardware connected to the system bus 32 . The communication unit 35 has a function of transmitting packets stored in the storage unit 34 to the network 37 and a function of receiving packets from the network 37 . Furthermore, the communication unit 35 has a storage area (hereinafter referred to as FIFO) 36 for temporarily holding packets recei...
example 1
[0272] Example 1: The update amount and the predetermined interval can be calculated according to the following formula according to the capacity of the FIFO 36 and the transmission capacity of the system bus 32 .
[0273] Update amount=capacity of FIFO36... (Formula 3)
[0274] Predetermined interval=capacity of FIFO 36 / transfer capability of system bus 32...(Formula 4)
[0275] Specifically, when the capacity of the FIFO 36 of the receiver device 31 is 4 KB and the transfer capability of the system bus 32 is 40 Mbps, the update amount is 4 KB according to the capacity of the FIFO 36, and the predetermined interval is the time required for the system bus 32 to transfer 4 KB. 0.8 milliseconds. Furthermore, since the predetermined interval is set to 0.8 milliseconds or more, the amount of data transfer can be controlled to be less than the transfer capacity of the system bus 32 , which can also be regarded as 1 millisecond. And, when calculating the specified interval...
example 2
[0276] Example 2: The update amount and the specified interval can be calculated according to the following formula according to the capacity of FIFO36 and the bit rate requested by the application program.
[0277] Update amount=capacity of FIFO36... (formula 5)
[0278] Prescribed interval=RTT / CEILING((((bit rate required by application program×RTT) / 8) / update amount, 1)...(Formula 6)
[0279] CEILING(A, B) outputs the result of rounding up A by B.
[0280] Specifically, the size of the FIFO 36 of the receiver device 31 is 4 KB, and when the bit rate requested by the application program is 10 Mbps and the RTT is 10 milliseconds, the update amount is 4 KB according to the size of the FIFO 36 . And, in this case, since the bit rate requested by the application program is 10 Mbps, the application program needs to receive 12.5 KB of data in 1 RTT (10 milliseconds). Therefore, if an increment of 4KB is considered as the update amount, 3.125 times are required in 1RTT, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com