Method, system and computer program for distributing a plurality of jobs to a plurality of computers
A computer program, computer technology, applied in the field of assigning multiple jobs to multiple computers, systems and computer programs, can solve the problem of affecting system job throughput, failing to recognize the degree of impact of a given job deployment on subsequent jobs And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] A. Overview
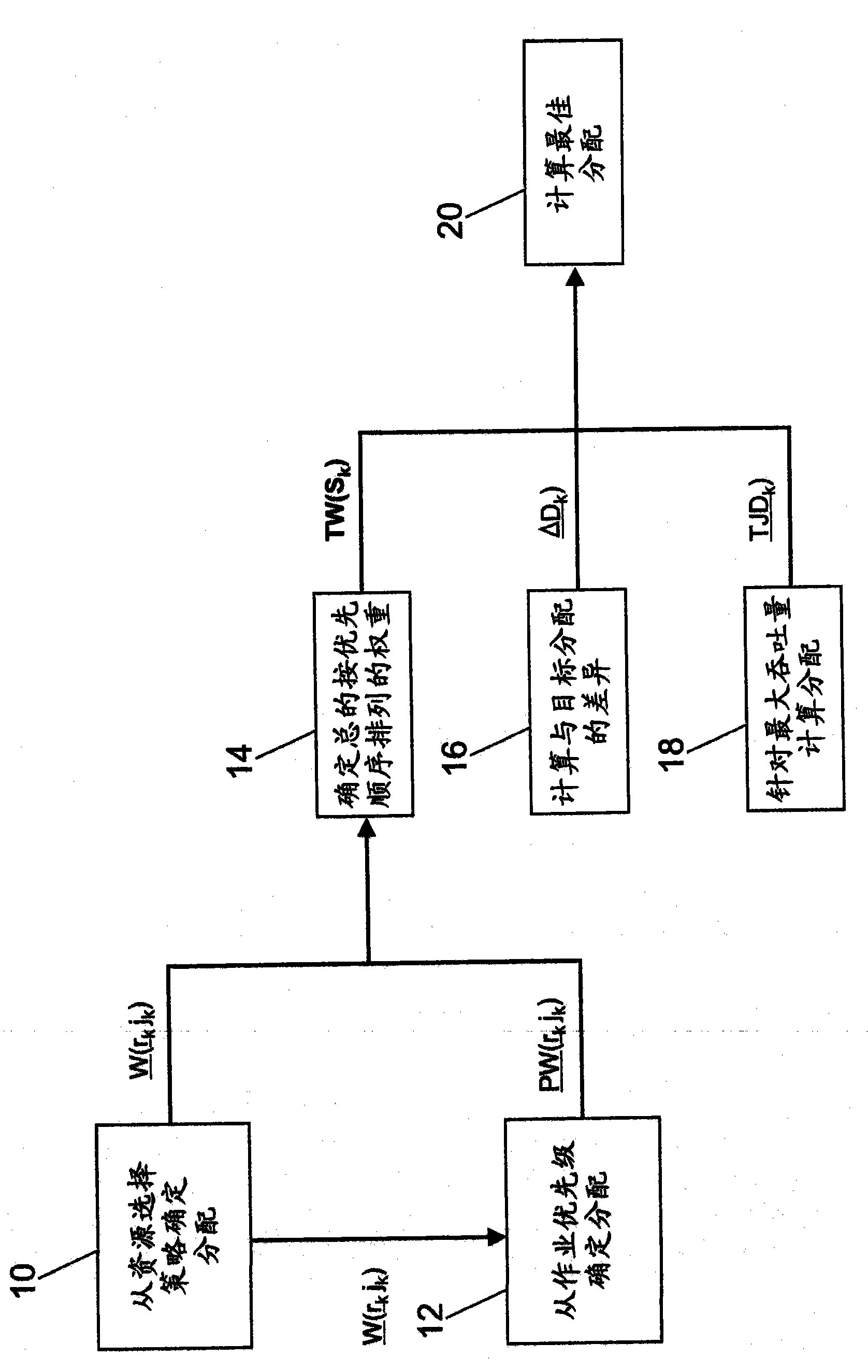
[0029] A preferred embodiment provides a mechanism for determining an optimal workload allocation from a plurality of candidate workload allocations, each of which has been determined to optimize a particular aspect of a workload scheduling problem. More specifically, refer to figure 1 , the preferred embodiment determines (10) workload allocation ((W( r k , j k ))). From this workload distribution ((W( r k , j k ))), the preferred embodiment optionally determines (12) workload distribution (PW( r k , j k )).
[0030] From one or both of the above parameters, the preferred embodiment determines (14) the workload distribution according to the overall prioritized weight parameter. The preferred embodiment also determines (16) a workload assignment that attempts to match previously determined candidate workload assignments to the target assignment. Similarly, the preferred embodiment calculates (18) other workload distributions that attempt to m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com