Radiator, and lighting device
A radiator and heat sink technology, which is applied to lighting devices, fixed lighting devices, cooling/heating devices of lighting devices, etc., can solve the problem of difficulty in inflow of air, and achieve the effect of alleviating air retention and improving heat dissipation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
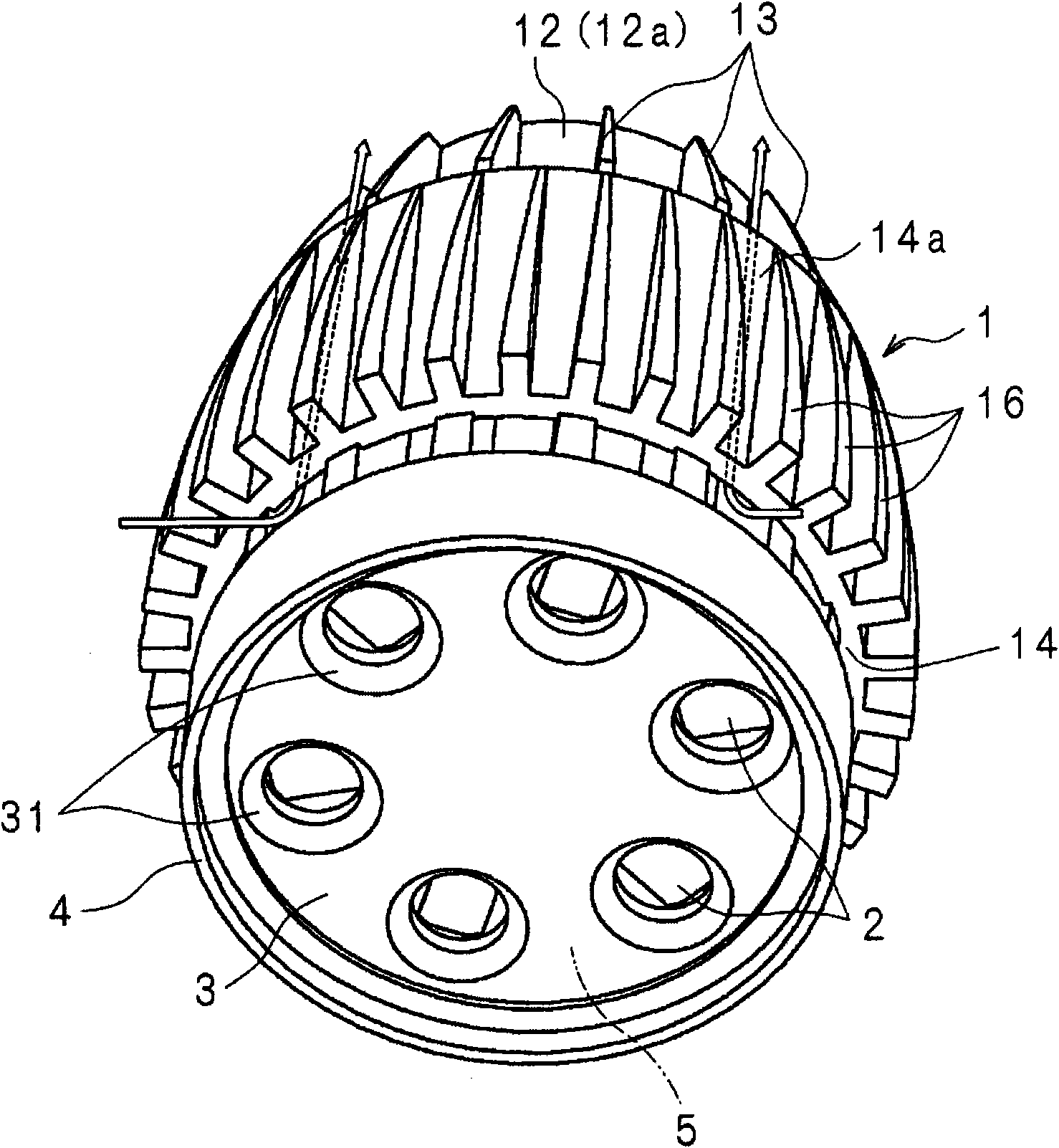
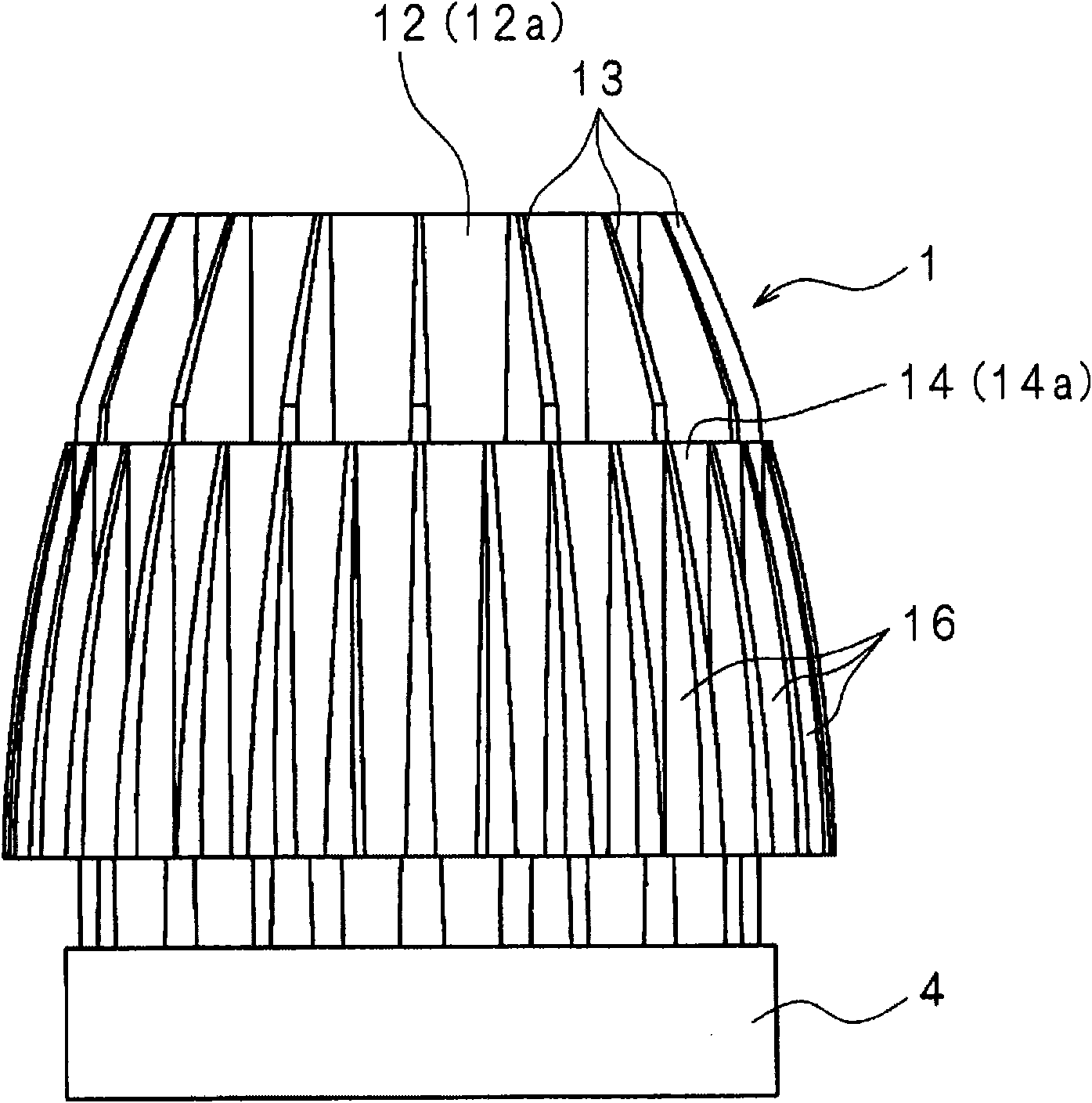
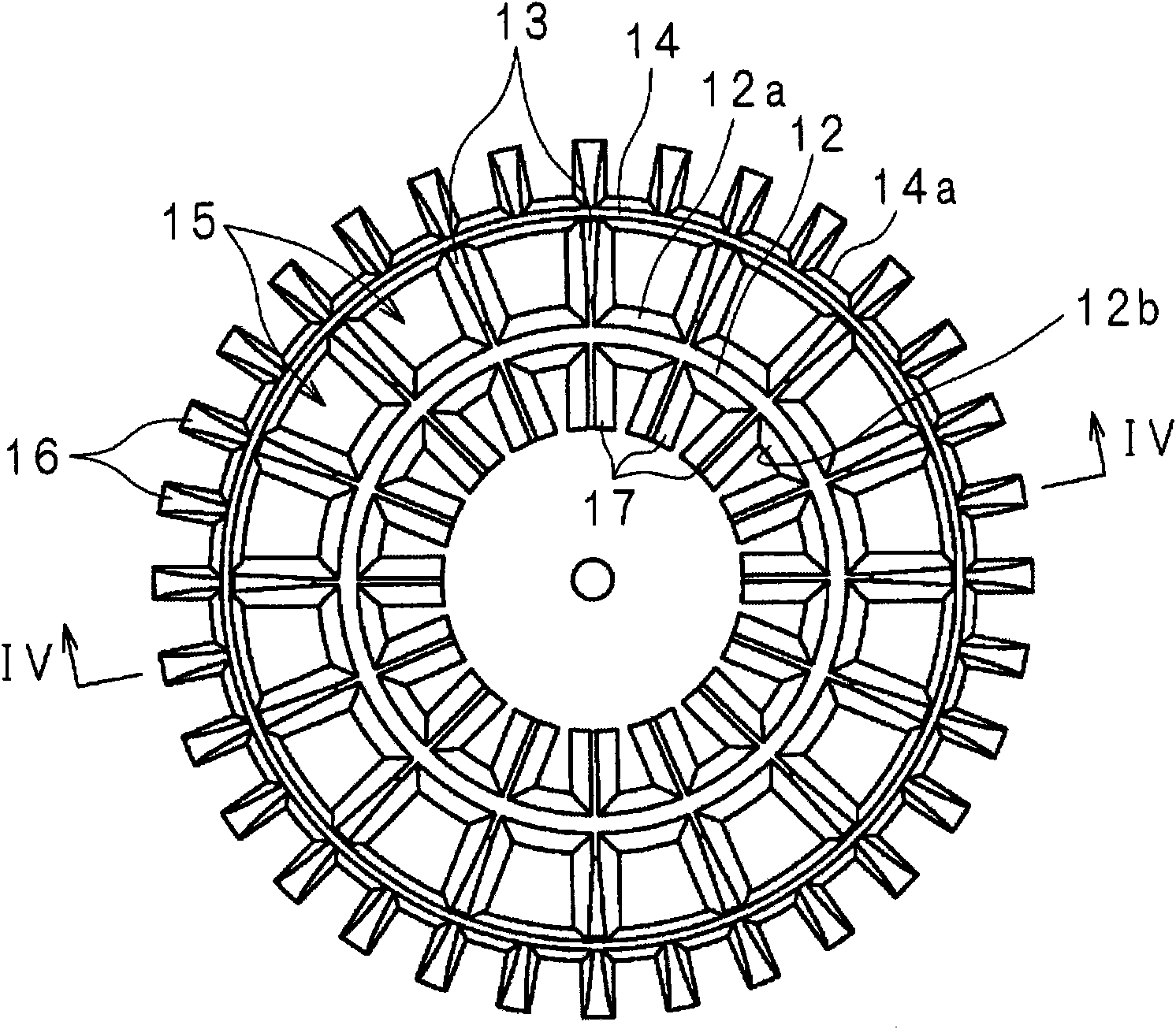
[0076] figure 1 is an external perspective view of the lighting device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, figure 2 is a schematic side view of the lighting device, image 3 is a schematic rear view of the lighting device, Figure 4 is along image 3 Schematic cross-sectional view of line IV-IV.
[0077] In the drawing, the heat sink 1 is made of metal such as aluminum. The outer shape of the radiator 1 is a so-called cannonball shape, that is, a cylinder whose diameter is reduced on one side in the axial direction.
[0078] The heat sink 1 has a disc-shaped heat transfer plate 11 . On one surface 11 a of the heat transfer plate 11 , a cylindrical inner cylinder 12 concentric with the heat transfer plate 11 is erected. The wall thickness of the inner cylinder 12 changes continuously in the axial direction, being thicker on the side of the heat transfer plate 11 and thinner on the side of the open end.
[0079] On the outer surface 12a of the inner tube ...
Embodiment approach 2
[0099] Figure 5 It is an external perspective view of the lighting device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. On the end of the inner tube 12 of the heat sink 1a where the LED modules 2, 2... are arranged, and between the first heat sinks 13, 13..., rectangular air vents 12c, 12c are arranged at equal intervals in the circumferential direction. … Due to other structures with figure 1 The shown embodiment 1 is the same, so the corresponding components adopt the same figure 1 The same reference numerals are used, and a detailed description of the structure is omitted.
[0100] By constituting the heat sink 1a in the above manner, the heat generated by the LED modules 2, 2, ... is transferred to the inner tube 12 as the LED modules 2, 2, ... are turned on, and the air inside the inner tube 12 is heated, as shown by the arrows in the figure. , the heated air flows out from the open end of the inner cylinder 12 to the outside, while the outside air flows in fro...
Embodiment approach 3
[0102] Figure 6 It is a schematic partial sectional view of the lighting device of Embodiment 3. On the circumferential edge of one surface 11a of the heat transfer plate 11 of the radiator 1b, a turbulence promoting member 11d protruding along the entire circumference of the heat transfer plate 11 and opposing the inner cylinder 11 is formed. set up. It is preferable to determine the height H of the turbulent flow promoting member 11d so that the relationship between the height H and the interval L between the turbulent flow promoting member 11d and the inner cylinder 12 satisfies a predetermined condition (L≈10H). Due to other structures with Figure 4 The shown embodiment 1 is the same, so the corresponding components adopt the same Figure 4 The same reference numerals are used, and a detailed description of the structure is omitted.
[0103] By constituting the heat sink 1b in the above manner, as shown by the arrows in the figure, swirls are generated due to the tur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com