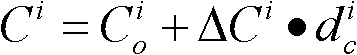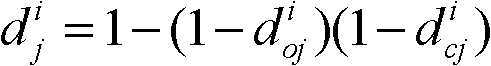Progressive method for identifying slack cable on the basis of angle monitoring during support generalized displacement
A technology for generalized displacement and angle monitoring of supports, used in tension measurement, measurement devices, testing of machine/structural components, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0150] For the health monitoring of the cable system of the cable structure during the generalized displacement of the support, the invention discloses a system and method capable of reasonably and effectively monitoring the health status of each cable of the cable system of the cable structure. The following descriptions of embodiments of the invention are merely exemplary in nature, and are in no way intended to limit the application or uses of the invention.
[0151] In the case of generalized displacement of the cable structure support, the present invention employs an algorithm for monitoring the health status of the cable system in the cable structure (including the degree of slack and damage of the cables). During specific implementation, the following steps are one of various steps that may be taken.
[0152] Step 1: Determine the type, location and quantity of the quantity to be monitored, and number them. The specific process is:
[0153] First determine the number...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com