Semantic event detection using cross-domain knowledge
An event and semantic technology applied in the field of classified digital content recording
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
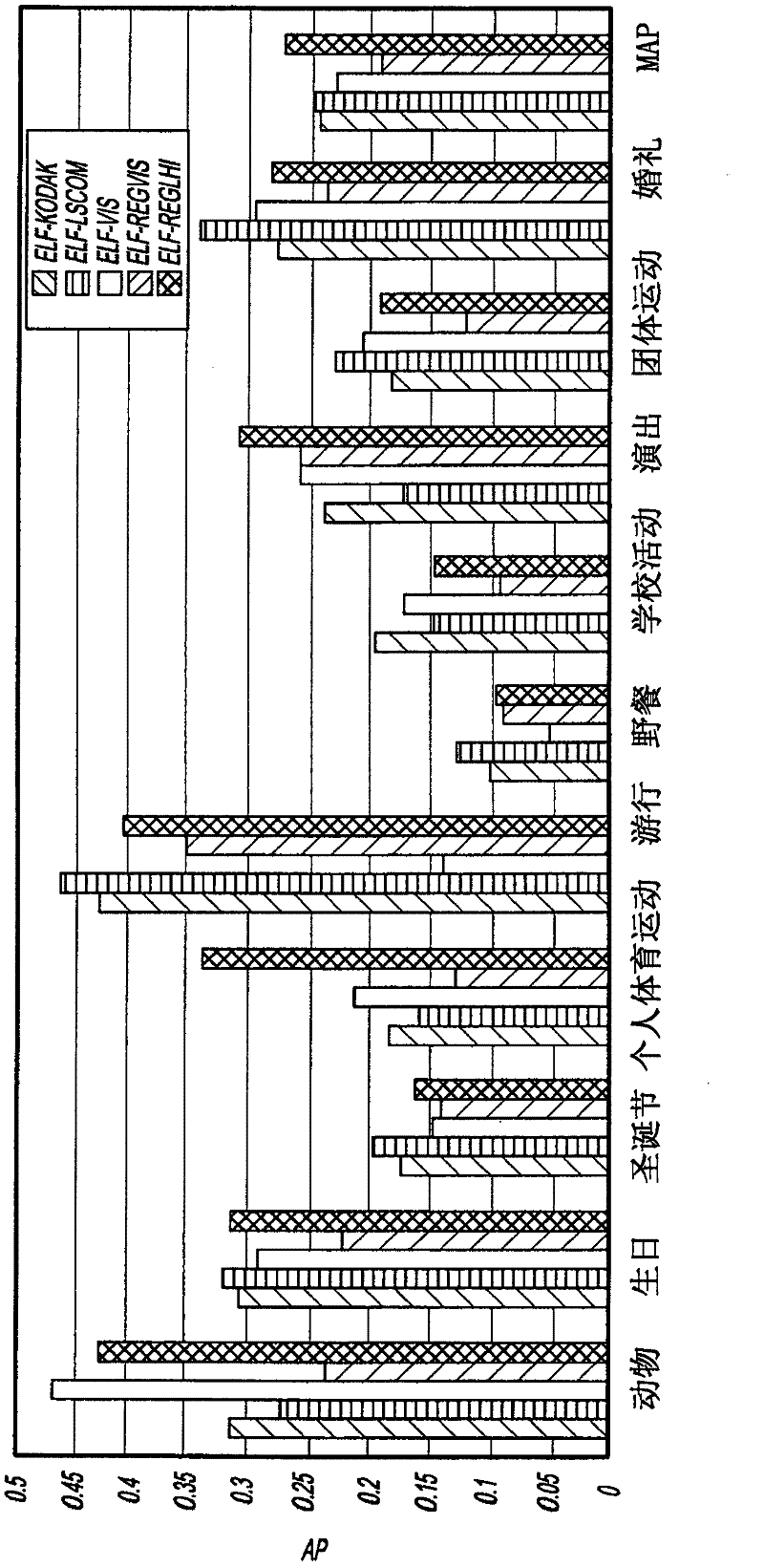
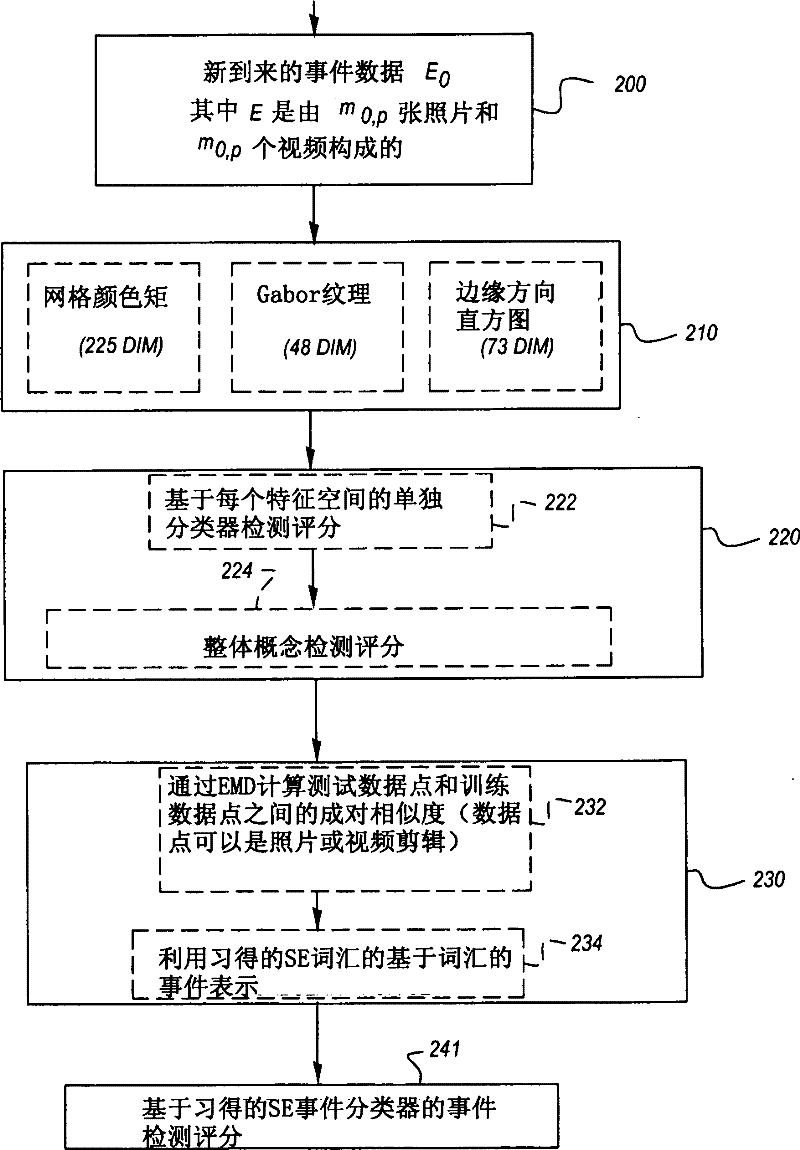
[0061]Complex semantic events often arise from the co-existence of basic visual concepts. For example, "wedding" is a semantic event associated with certain schema-formed visual concepts (such as "person", "flower", "park", etc.). Visual concepts are generally defined as pictorial content properties of images, and are often semantically represented by words that are broader than those used to identify specific events. Thus, visual concepts form a subset of image content properties that can contribute to specific events.
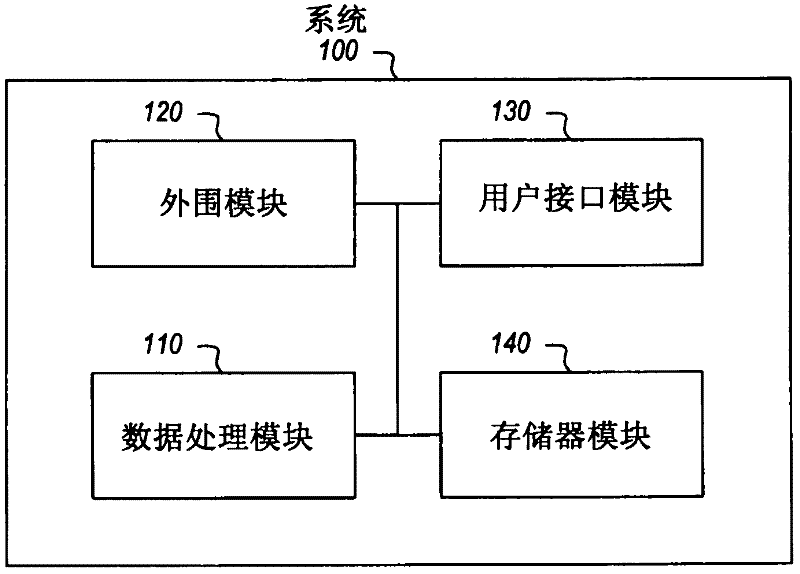
[0062] In the present invention, basic visual concepts are first detected from images, and a semantic event detector is built in the concept space instead of the original low-level feature space. The benefits of this approach include at least two aspects. First, visual concepts are higher-level and more intuitive descriptors than original low-level features. As described in "Visual event detection using multi-dimensional concept dynamics" published by IEEE...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com