Method and device for fault handing of optical channel bandwidth
An optical channel and bandwidth technology, applied in the field of optical communication, can solve the problems of inconsistent ODUflex path bandwidth status, inconsistent allocation, abnormal interruption, etc., and achieve the effect of expanding adaptation processing capacity, eliminating status inconsistency, and strong adaptability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
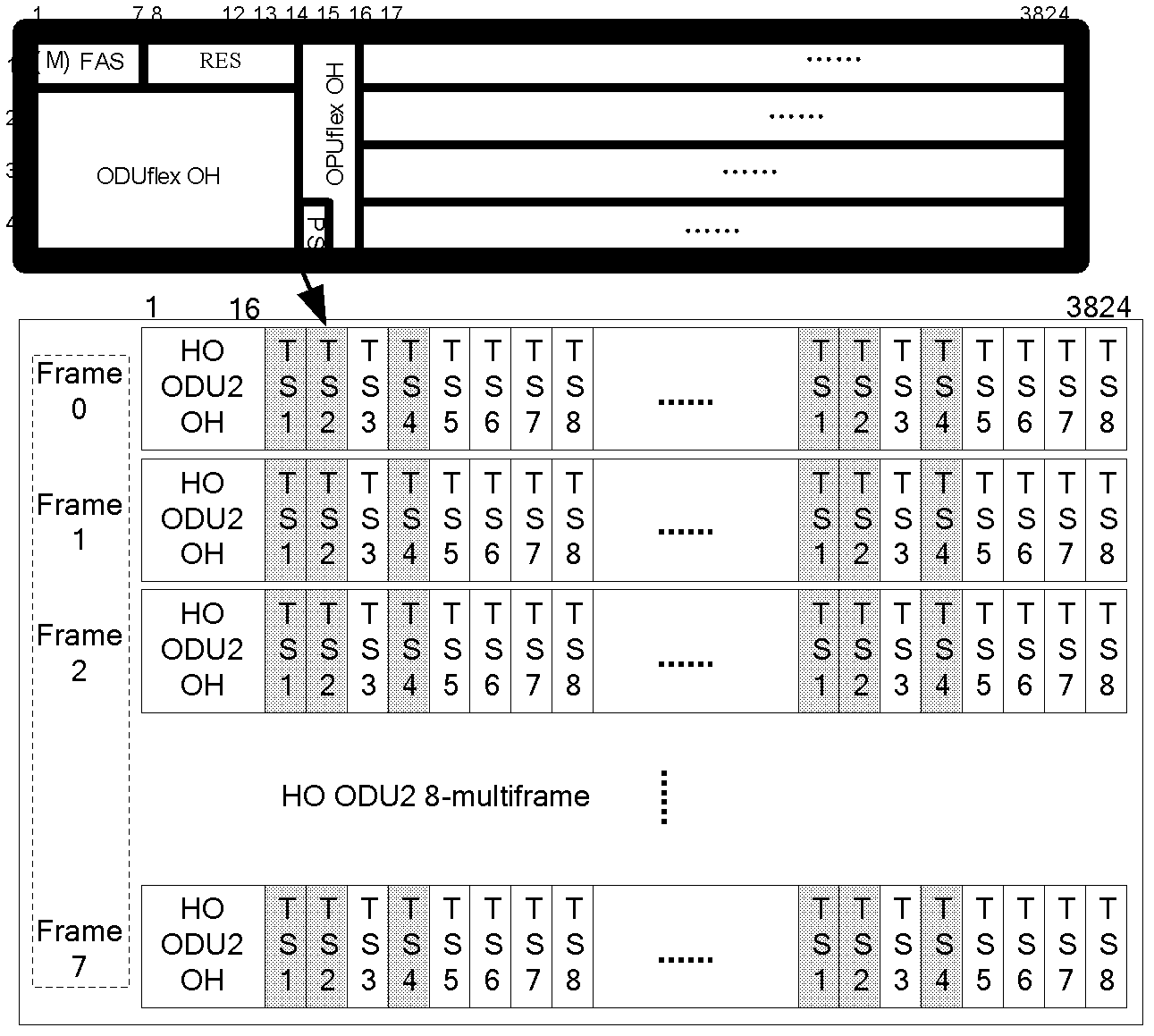
[0049] In the embodiment of the present invention, when a link failure occurs in ODUflex, the HAO protocol processing is generally forced to be interrupted, and some links in the ODUflex path have completed the high-order time slot adjustment, and some links have not completed the high-order time slot adjustment coexistence phenomenon . Troubleshooting based on the faulty LC includes two aspects. On the one hand, the faulty LC has completed the HO TS adjustment, and the ODUflex bandwidth adjustment can continue to process until the adjustment ends normally; on the other hand, the faulty LC has not completed HO TS adjustment enables ODUflex bandwidth adjustment to roll back abnormally or return to the same state as before adjustment during fault handling.
[0050] In practical applications, when a link failure occurs, the network management plane or the control plane can generate a fault command. The fault command can generate different commands based on judging whether the fau...
Embodiment 2
[0056] see Figure 6 , an embodiment of the present invention provides a method for troubleshooting an optical channel bandwidth fault, and the method specifically includes:
[0057] Step 201: Determine whether the faulty link in the ODUflex path has completed high-order time slot adjustment;
[0058] Specifically, when the lossless bandwidth adjustment is performed on the ODUflex path, each link in the ODUflex path performs high-order time slot adjustment respectively. When a link is faulty, the faulty link in the ODUflex path may or may not have completed the high-order time slot adjustment. In this embodiment of the present invention, according to whether the faulty link has completed the high-order time slot adjustment, a Different adjustment strategies.
[0059] In practical applications, when a link in the ODUflex path fails, the network management plane or the control plane generates a fault handling instruction. The fault handling instruction can generate different i...
Embodiment 3
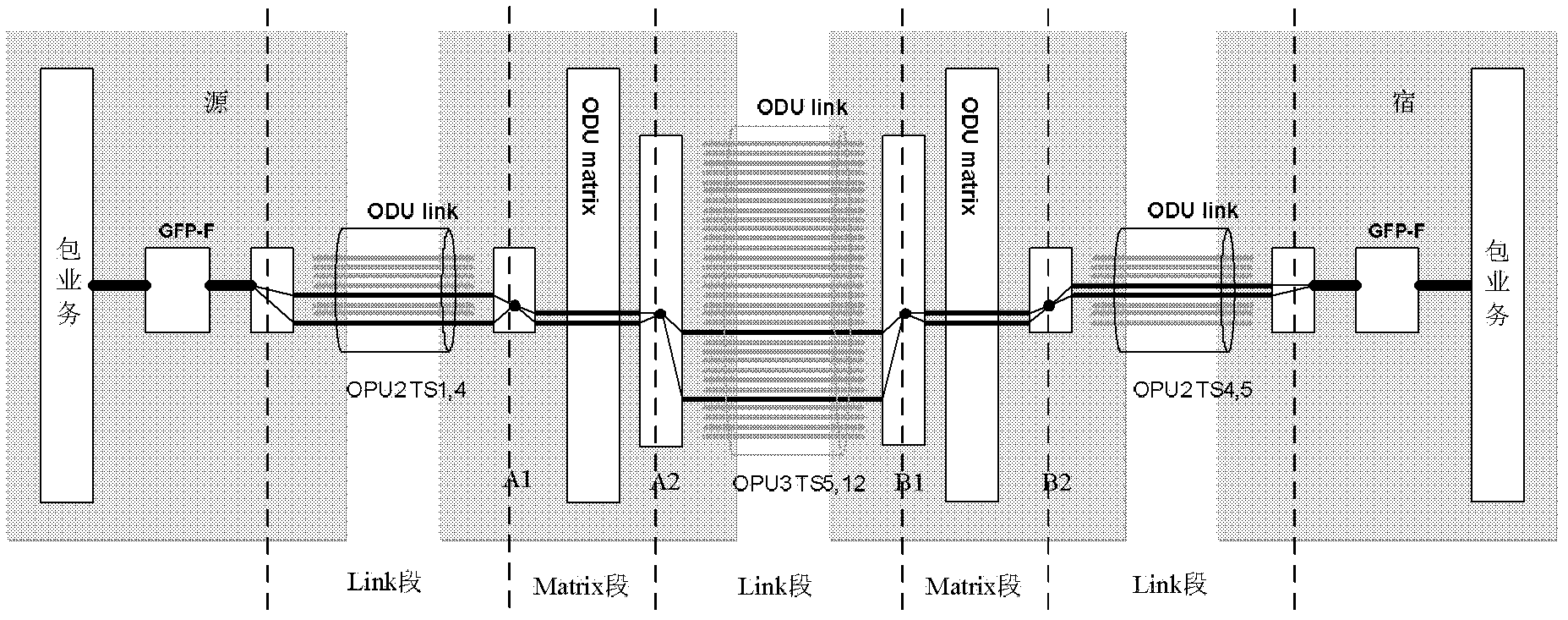
[0117] In practical applications, various faults may occur in the bandwidth of the optical channel, which are generally divided into two-way faults and one-way faults. The solution of the present invention will be described below using the two-way faults in the optical channel bandwidth.
[0118] In this embodiment, it is assumed that LC has a bidirectional fault (BC segment fault), see Figure 13 Troubleshooting of ODUflex bandwidth adjustment as shown.
[0119] If the faulty LC (BC section) completes the HO TS adjustment, such as Figure 14 As shown, adopt method 2 to process as follows:
[0120] 1. The network elements connected to the faulty LC in the ODUflex path, that is, the B-side and the C-side, perform the adjustment protocol loopback respectively, and insert the BWR adjustment protocol information extracted from the uplink back into the downlink; at this time, the original ODUflex The path (ABCD) is divided into left and right two sections to adjust the protocol t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com