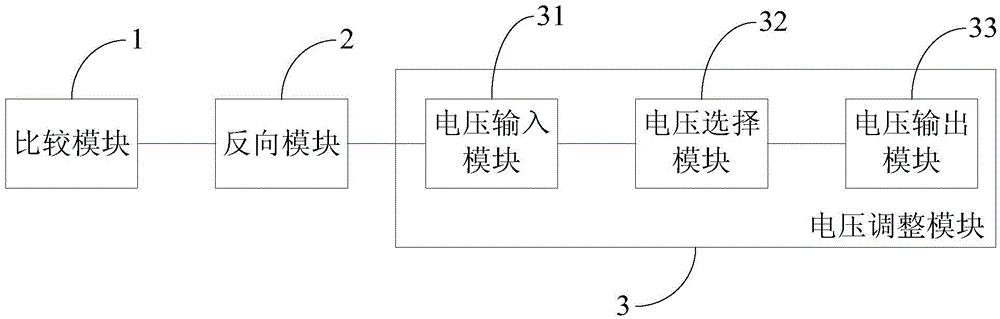
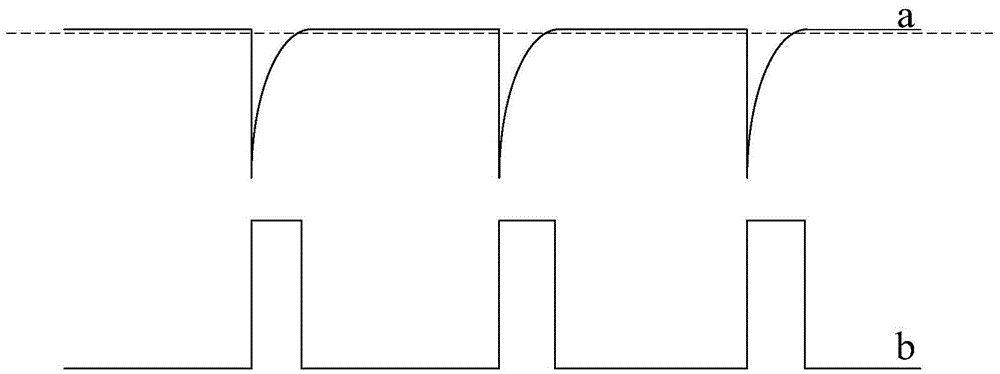
Common voltage compensation circuit, compensation method thereof, array substrate and display device
A common voltage and compensation circuit technology, applied to static indicators, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as abnormal gray scale display, crosstalk, and screen jitter
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
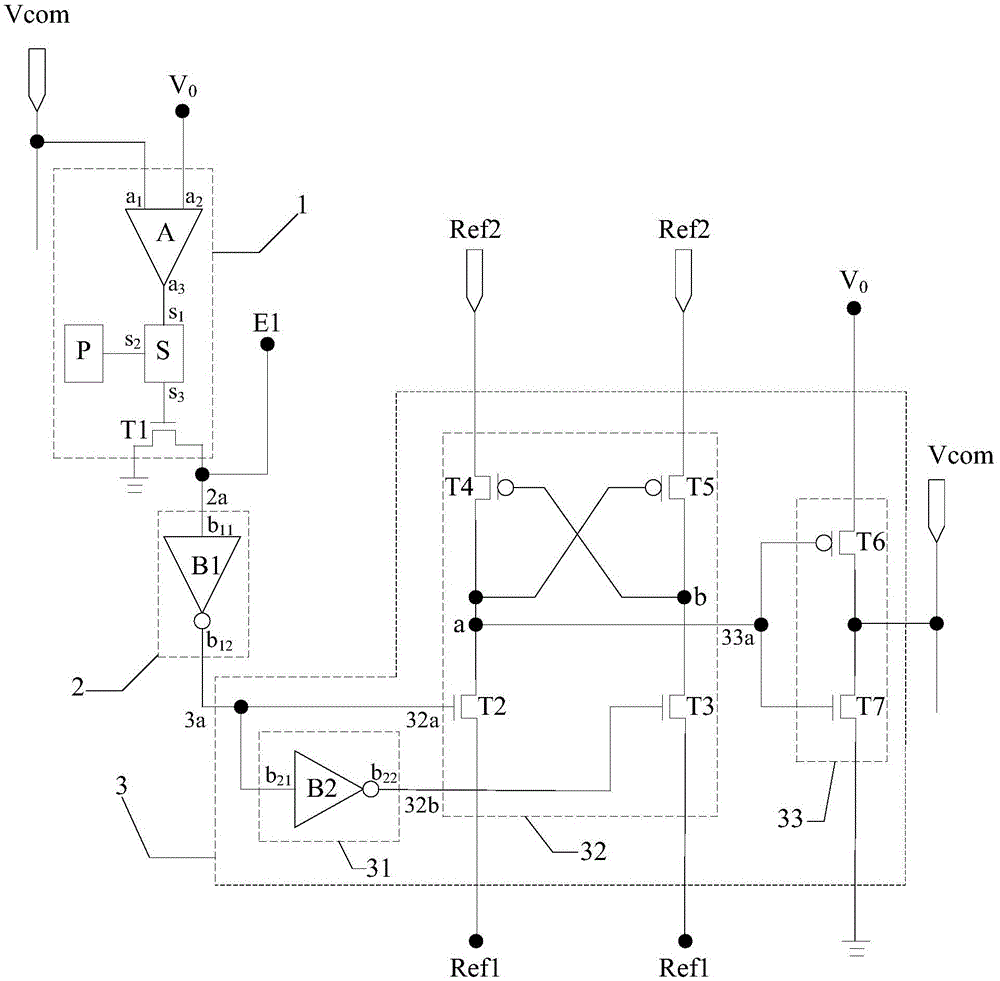
[0077] Example 1: If image 3 As shown, the control power supply P controls the sampler S to turn on, and the sampler S samples the comparison result of the common voltage and the reference voltage obtained by the comparator A:
[0078] When the difference between the common voltage and the reference voltage is greater than or equal to the preset threshold, the comparator A inputs a high-level signal to the gate of the first switching transistor T1 through the sampler S, so that the first switching transistor T1 is in a conducting state, so that the input terminal b of the first inverter B1 11 and the port E1 for inputting the first level signal is grounded; the gate of the first inverter B1 to the gate of the second switching transistor T2 and the input terminal b of the second inverter B2 21 output the second level signal, the second inverter B2 converts the second level signal into a zero-voltage signal and sends it to the gate of the third switching transistor T3, the sec...
example 2
[0080] Example 2: If Figure 4 As shown, the control power supply P controls the sampler S to turn on, and the sampler S samples the comparison result of the common voltage and the reference voltage obtained by the comparator A:
[0081] When the difference between the common voltage and the reference voltage is greater than or equal to the preset threshold, the comparator A inputs a high-level signal to the gate of the first switching transistor T1 through the sampler S, so that the first switching transistor T1 is in a conducting state, so that the input terminal b of the first inverter B1 11 and the port E1 for inputting the first level signal is grounded; the gate of the first inverter B1 to the gate of the second switching transistor T2 and the input terminal b of the second inverter B2 21 output the second level signal, the second inverter B2 converts the second level signal into a zero-voltage signal and sends it to the gate of the third switching transistor T3, the se...
example 3
[0083] Example 3: If Figure 5 As shown, the control power supply P controls the sampler S to turn on, and the sampler S samples the comparison result of the common voltage and the reference voltage obtained by the comparator A:
[0084] When the difference between the common voltage and the reference voltage is greater than or equal to the preset threshold, the comparator A inputs a high-level signal to the gate of the first switching transistor T1 through the sampler S, so that the first switching transistor T1 is in a conducting state, so that the input terminal b of the first inverter B1 11 and the port E1 for inputting the first level signal is grounded; the gate of the first inverter B1 to the gate of the second switching transistor T2 and the input terminal b of the second inverter B2 21 output the second level signal, the second inverter B2 converts the second level signal into a zero-voltage signal and sends it to the gate of the third switching transistor T3, the se...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com